1. 事务的初始化注册(从 @EnableTransactionManagement 开始)
(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {跟进这个 TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector 类
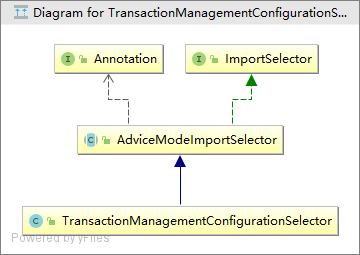
发现这个类是通过 Selector 引入的, 学过spring容器初始化源码分析会知道
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
}
selectImports这个方法最终会被调用
然后会发现抽象类实现了这个方法
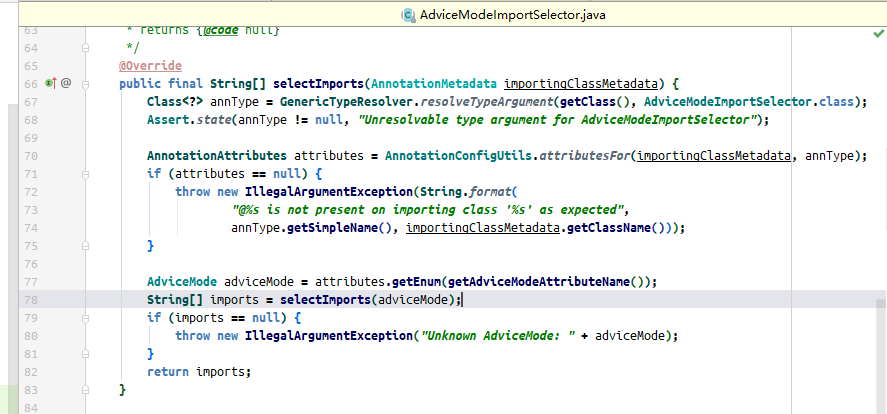
并且在78行调用了一个新的selectImports方法
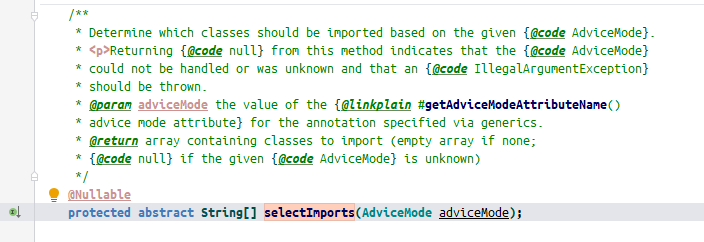
发现这个方法未实现, 说明在他的之类里面被实现了
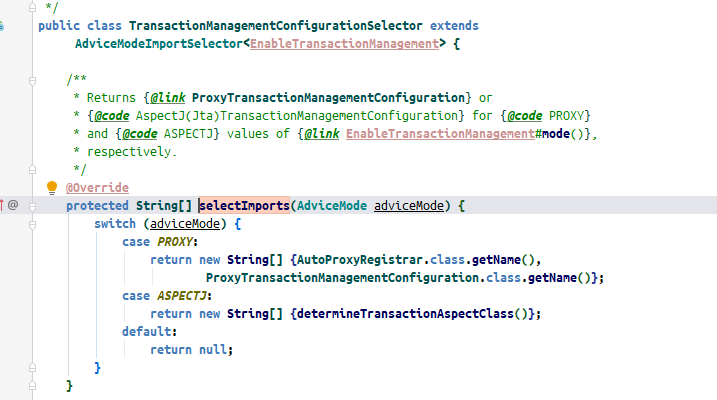
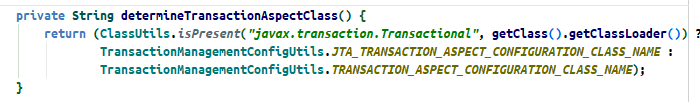
上图就是实现的过程, 还有如果是aspectj的话调用determineTransactionAspectClass方法
总体初始化过程就是这样, 现在开始源码级别的分析
首先分析
org.springframework.context.annotation.AdviceModeImportSelector#selectImports(org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata)
public final String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
// 拿出了EnableTransactionManagement 注解的Class类
Class<?> annType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(getClass(), AdviceModeImportSelector.class);
Assert.state(annType != null, "Unresolvable type argument for AdviceModeImportSelector");
// 拿到了注解中的所有属性字段(这里所有都是默认的, 我们没有添加任何值)
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (attributes == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"@%s is not present on importing class '%s' as expected",
annType.getSimpleName(), importingClassMetadata.getClassName()));
}
// 去拿 mode 中的值, 这里拿出的是代理模式(这里默认存在两个模式, 一个代理模式, 另一个是aspectJ模式)
AdviceMode adviceMode = attributes.getEnum(getAdviceModeAttributeName());
// 返回子类中实现的selectImports方法执行的结果(这里是代理模式所以默认是org.springframework.context.annotation.AutoProxyRegistrar和org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 这两个类)
String[] imports = selectImports(adviceMode);
if (imports == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown AdviceMode: " + adviceMode);
}
// 注册这两个类
return imports;
}
如果上面是AspectJ模式的话, 那么就会在两个类中选取一个
前提是根据 javax.transaction.Transactional 注解是否存在如果存在注册
org.springframework.transaction.aspectj.AspectJJtaTransactionManagementConfiguration
否则注册
org.springframework.transaction.config.TransactionManagementConfigUtils#TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME
这里暂时不分析AspectJ模式
那么现在留下了两个注入容器的类到底做了啥???
org.springframework.context.annotation.AutoProxyRegistrarorg.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration(1) 分析 AutoProxyRegistrar做了什么?
发现这个类也是为了注册某些bean而使用的
org.springframework.context.annotation.AutoProxyRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean candidateFound = false;
Set<String> annTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
for (String annType : annTypes) {
AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (candidate == null) {
continue;
}
Object mode = candidate.get("mode");
Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass");
if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() &&
Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) {
candidateFound = true;
if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) {
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
return;
}
}
}
}
if (!candidateFound && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
String name = getClass().getSimpleName();
logger.info(String.format("%s was imported but no annotations were found " +
"having both 'mode' and 'proxyTargetClass' attributes of type " +
"AdviceMode and boolean respectively. This means that auto proxy " +
"creator registration and configuration may not have occurred as " +
"intended, and components may not be proxied as expected. Check to " +
"ensure that %s has been @Import'ed on the same class where these " +
"annotations are declared; otherwise remove the import of %s " +
"altogether.", name, name, name));
}
}
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);上面的这个代码里面注册了一个类
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator使用
key: org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator
value: org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
借助Map注册到容器中
到这里就知道它的作用了, 就是注册了这个类 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
(2) 分析ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration做了什么?
注入的第二个类
org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration看下它都做了什么?
public abstract class AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration implements ImportAware {
protected AnnotationAttributes enableTx;
/**
* Default transaction manager, as configured through a {@link TransactionManagementConfigurer}.
*/
protected TransactionManager txManager;
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
// 获取EnableTransactionManagement注解的属性存入enableTx
this.enableTx = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(importMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableTransactionManagement.class.getName(), false));
if (this.enableTx == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"@EnableTransactionManagement is not present on importing class " + importMetadata.getClassName());
}
}
(required = false)
void setConfigurers(Collection<TransactionManagementConfigurer> configurers) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
return;
}
if (configurers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Only one TransactionManagementConfigurer may exist");
}
TransactionManagementConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();
this.txManager = configurer.annotationDrivenTransactionManager();
}
(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTIONAL_EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)
(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public static TransactionalEventListenerFactory transactionalEventListenerFactory() {
return new TransactionalEventListenerFactory();
}
}
(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource,
TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
从上面来看, 就是注册了几个Bean
1) org.springframework.transaction.event.TransactionalEventListenerFactory
2) org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(通知)
3) org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor(切点)
4) org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(Advisor对象)
(3) 分析事务的使用过程
(由于不知道如何抓取事务处理过程在哪里, 所以我们在service的方法上插入断点, 准备通过调用栈查看调用过程)
类似于这样
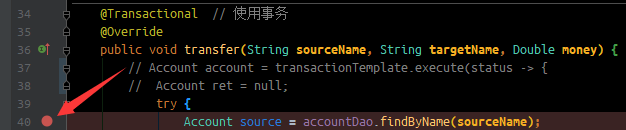
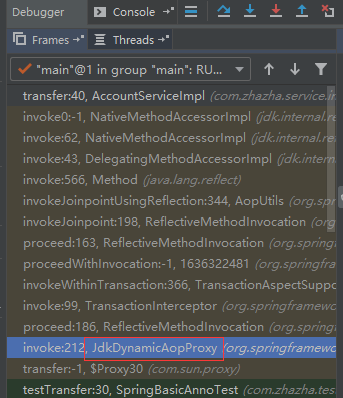
发现最先调用的是 JdkDynamicAopProxy 这个类
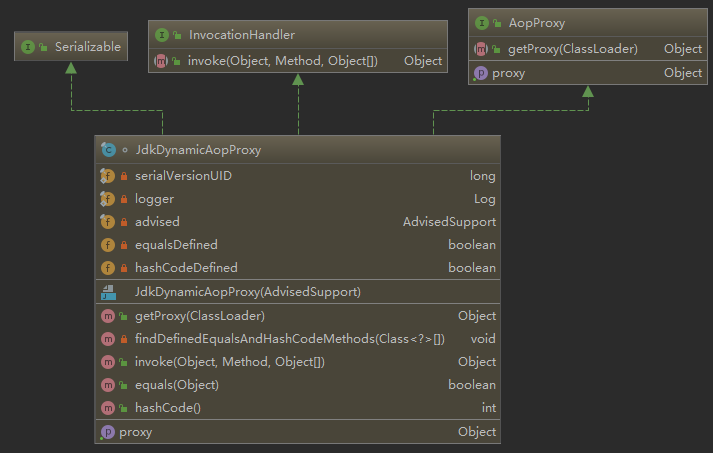
想看了下类图
发现了使用了动态代理的两个接口类
AopProxy
InvocationHandler
估计这个类和动态代理有关系
先看这个类中的一个方法
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializableprivate void findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces) {
// 参数获取了很多的代理类存在的接口
for (Class<?> proxiedInterface : proxiedInterfaces) {
// 遍历接口
Method[] methods = proxiedInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
// 获取接口上的所有方法
for (Method method : methods) {
// 遍历方法
// 判断是否存在Equals方法
if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
this.equalsDefined = true;
}
// 是否存在HashCode方法
if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
this.hashCodeDefined = true;
}
// 判断如果两个都存在这返回
if (this.equalsDefined && this.hashCodeDefined) {
return;
}
}
}
}
调用代理方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
// 获取我们的serviceImpl实现类
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
// 判断是否存在equals
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return equals(args[0]);
}
// 判断是否存在 hashCode
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// 拿出serviceImpl类
target = targetSource.getTarget();
// 拿到serviceImpl的Class对象
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
//
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// 关键的代码执行
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
进入上面的关键代码后
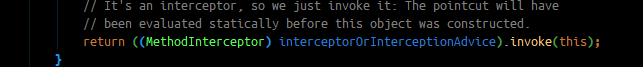
关注这个代码
再次进入下面这个方法
org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
后就会看见关键的事务代码
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 这里我们不满足条件
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) {
throw new TransactionUsageException(
"Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method +
". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead.");
}
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType());
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(
method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 满足条件
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// 获取事务信息
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// 调用事务修饰的方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清除事务信息ThreadLocal
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 事务的提交
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
2. 分析JdbcTemplate
分析这个, 就相当于分析如何初始化Jdbctemplate的初始化和使用还有销毁过程
(1) JdbcTemplate初始化
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
设置了数据源
afterPropertiesSet函数里面做了个简单的判断(isLazyInit 条件默认为true. 所以不需要判断这个)
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (getDataSource() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'dataSource' is required");
}
if (!isLazyInit()) {
getExceptionTranslator();
}
}
(2) JdbcTemplate使用
1) query
分析
public void testFindOne() throws Exception {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), 1);
System.out.println(accounts.get(0));
}
queryForObject
public <T> T queryForObject(String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper, Object... args) throws DataAccessException {
List<T> results = query(sql, args, new RowMapperResultSetExtractor<>(rowMapper, 1));
return DataAccessUtils.nullableSingleResult(results);
}
和
query
public <T> List<T> query(String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper, Object... args) throws DataAccessException {
return result(query(sql, args, new RowMapperResultSetExtractor<>(rowMapper)));
}
的区别
多了个 1
public <T> T query(String sql, Object[] args, ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException {
return query(sql, newArgPreparedStatementSetter(args), rse);
}
// newArgPreparedStatementSetter(args)内部new了个ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter
protected PreparedStatementSetter newArgPreparedStatementSetter( Object[] args) {
return new ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter(args);
}
public <T> T query(String sql, PreparedStatementSetter pss, ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException {
return query(new SimplePreparedStatementCreator(sql), pss, rse);
}
public <T> T query(String sql, PreparedStatementSetter pss, ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException {
return query(new SimplePreparedStatementCreator(sql), pss, rse);
}
public <T> T query(
PreparedStatementCreator psc, final PreparedStatementSetter pss, final ResultSetExtractor<T> rse)
throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(rse, "ResultSetExtractor must not be null");
logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL query");
// psc ===> sql, pss ====> args, rse ===> Type
return execute(psc, new PreparedStatementCallback<T>() {
public T doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
if (pss != null) {
// 值把它设置进去, 这里面就是简单的数值设置
pss.setValues(ps);
}
// 执行sql语句获取结果集
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 把参数绑定到结果中
return rse.extractData(rs);
}
finally {
// 结果集关闭
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs);
if (pss instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) pss).cleanupParameters();
}
}
}
});
}
public <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action)
throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(psc, "PreparedStatementCreator must not be null");
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String sql = getSql(psc);
logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL statement" + (sql != null ? " [" + sql + "]" : ""));
}
// 分析这里, 获取线程绑定Connection的链接
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 获取PreparedStatement, 底层jdbc方式获取
ps = psc.createPreparedStatement(con);
// 设置最大行数、抓取数量和超时时间
applyStatementSettings(ps);
// 调用到doInPreparedStatement 执行lambda函数
T result = action.doInPreparedStatement(ps);
handleWarnings(ps);
return result;
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
// Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock
// in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet.
if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
}
String sql = getSql(psc);
psc = null;
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
ps = null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con = null;
throw translateException("PreparedStatementCallback", sql, ex);
}
finally {
if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
}
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
}
}
获取线程绑定链接
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
conHolder.requested();
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(fetchConnection(dataSource));
}
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
// Else we either got no holder or an empty thread-bound holder here.
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
// 分析这个方法
Connection con = fetchConnection(dataSource);
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
try {
// Use same Connection for further JDBC actions within the transaction.
// Thread-bound object will get removed by synchronization at transaction completion.
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
holderToUse.requested();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// Unexpected exception from external delegation call -> close Connection and rethrow.
releaseConnection(con, dataSource);
throw ex;
}
}
return con;
}
Connection con = fetchConnection(dataSource);
protected Connection getConnectionFromDriver( String username, String password) throws SQLException {
// 主要存储数据库账号和密码
Properties mergedProps = new Properties();
Properties connProps = getConnectionProperties();
if (connProps != null) {
mergedProps.putAll(connProps);
}
if (username != null) {
mergedProps.setProperty("user", username);
}
if (password != null) {
mergedProps.setProperty("password", password);
}
// 将账号和密码传到数据库引擎中去获取数据库链接, 分析这个方法
Connection con = getConnectionFromDriver(mergedProps);
if (this.catalog != null) {
con.setCatalog(this.catalog);
}
if (this.schema != null) {
con.setSchema(this.schema);
}
return con;
}
Connection con = getConnectionFromDriver(mergedProps);
protected Connection getConnectionFromDriverManager(String url, Properties props) throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, props);
}
上面的代码就看到了熟悉的代码
DriverManager.getConnection 新手入门写的Jdbc代码就有这句话
至此这个方法分析完毕 fetchConnection
开始分析
T result = action.doInPreparedStatement(ps);
执行lambda语句
pss.setValues(ps) 简单的设置值到sql里面进行查找
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
if (this.args != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.args.length; i++) {
Object arg = this.args[i];
doSetValue(ps, i + 1, arg);
}
}
}
下面就这个可看可不看, 其实就是对类型进行比较, 然后设置value进去
private static void setValue(PreparedStatement ps, int paramIndex, int sqlType,
String typeName, Integer scale, Object inValue) throws SQLException {
if (inValue instanceof SqlTypeValue) {
((SqlTypeValue) inValue).setTypeValue(ps, paramIndex, sqlType, typeName);
}
else if (inValue instanceof SqlValue) {
((SqlValue) inValue).setValue(ps, paramIndex);
}
else if (sqlType == Types.VARCHAR || sqlType == Types.LONGVARCHAR ) {
ps.setString(paramIndex, inValue.toString());
}
else if (sqlType == Types.NVARCHAR || sqlType == Types.LONGNVARCHAR) {
ps.setNString(paramIndex, inValue.toString());
}
else if ((sqlType == Types.CLOB || sqlType == Types.NCLOB) && isStringValue(inValue.getClass())) {
String strVal = inValue.toString();
if (strVal.length() > 4000) {
// Necessary for older Oracle drivers, in particular when running against an Oracle 10 database.
// Should also work fine against other drivers/databases since it uses standard JDBC 4.0 API.
if (sqlType == Types.NCLOB) {
ps.setNClob(paramIndex, new StringReader(strVal), strVal.length());
}
else {
ps.setClob(paramIndex, new StringReader(strVal), strVal.length());
}
return;
}
else {
// Fallback: setString or setNString binding
if (sqlType == Types.NCLOB) {
ps.setNString(paramIndex, strVal);
}
else {
ps.setString(paramIndex, strVal);
}
}
}
else if (sqlType == Types.DECIMAL || sqlType == Types.NUMERIC) {
if (inValue instanceof BigDecimal) {
ps.setBigDecimal(paramIndex, (BigDecimal) inValue);
}
else if (scale != null) {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, sqlType, scale);
}
else {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, sqlType);
}
}
else if (sqlType == Types.BOOLEAN) {
if (inValue instanceof Boolean) {
ps.setBoolean(paramIndex, (Boolean) inValue);
}
else {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, Types.BOOLEAN);
}
}
else if (sqlType == Types.DATE) {
if (inValue instanceof java.util.Date) {
if (inValue instanceof java.sql.Date) {
ps.setDate(paramIndex, (java.sql.Date) inValue);
}
else {
ps.setDate(paramIndex, new java.sql.Date(((java.util.Date) inValue).getTime()));
}
}
else if (inValue instanceof Calendar) {
Calendar cal = (Calendar) inValue;
ps.setDate(paramIndex, new java.sql.Date(cal.getTime().getTime()), cal);
}
else {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, Types.DATE);
}
}
else if (sqlType == Types.TIME) {
if (inValue instanceof java.util.Date) {
if (inValue instanceof java.sql.Time) {
ps.setTime(paramIndex, (java.sql.Time) inValue);
}
else {
ps.setTime(paramIndex, new java.sql.Time(((java.util.Date) inValue).getTime()));
}
}
else if (inValue instanceof Calendar) {
Calendar cal = (Calendar) inValue;
ps.setTime(paramIndex, new java.sql.Time(cal.getTime().getTime()), cal);
}
else {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, Types.TIME);
}
}
else if (sqlType == Types.TIMESTAMP) {
if (inValue instanceof java.util.Date) {
if (inValue instanceof java.sql.Timestamp) {
ps.setTimestamp(paramIndex, (java.sql.Timestamp) inValue);
}
else {
ps.setTimestamp(paramIndex, new java.sql.Timestamp(((java.util.Date) inValue).getTime()));
}
}
else if (inValue instanceof Calendar) {
Calendar cal = (Calendar) inValue;
ps.setTimestamp(paramIndex, new java.sql.Timestamp(cal.getTime().getTime()), cal);
}
else {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, Types.TIMESTAMP);
}
}
// 这次执行的就是这样
else if (sqlType == SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN || (sqlType == Types.OTHER &&
"Oracle".equals(ps.getConnection().getMetaData().getDatabaseProductName()))) {
if (isStringValue(inValue.getClass())) {
ps.setString(paramIndex, inValue.toString());
}
else if (isDateValue(inValue.getClass())) {
ps.setTimestamp(paramIndex, new java.sql.Timestamp(((java.util.Date) inValue).getTime()));
}
else if (inValue instanceof Calendar) {
Calendar cal = (Calendar) inValue;
ps.setTimestamp(paramIndex, new java.sql.Timestamp(cal.getTime().getTime()), cal);
}
else {
// Fall back to generic setObject call without SQL type specified.
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue);
}
}
else {
// Fall back to generic setObject call with SQL type specified.
ps.setObject(paramIndex, inValue, sqlType);
}
}
对象绑定到结果集
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNumber) throws SQLException {
Assert.state(this.mappedClass != null, "Mapped class was not specified");
// 获取bean
T mappedObject = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.mappedClass);
// 放置到Bean包装中
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(mappedObject);
// 初始化Bean包装类
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取总共有多少列的sql参数需要填写
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
Set<String> populatedProperties = (isCheckFullyPopulated() ? new HashSet<>() : null);
for (int index = 1; index <= columnCount; index++) {
// 根据元数据和索引数列的位置确定这个索引的名字为 id
String column = JdbcUtils.lookupColumnName(rsmd, index);
// 将这个名字去掉空格然后所有字母修改为小写
String field = lowerCaseName(StringUtils.delete(column, " "));
// 根据名字获取PropertyDescriptor对象
PropertyDescriptor pd = (this.mappedFields != null ? this.mappedFields.get(field) : null);
if (pd != null) {
try {
// 根据结果集, 索引和PropertyDescriptor获取值, 分析内部代码①
Object value = getColumnValue(rs, index, pd);
if (rowNumber == 0 && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping column '" + column + "' to property '" + pd.getName() +
"' of type '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(pd.getPropertyType()) + "'");
}
try {
// 设置值到结果中, 查看源码分析②
bw.setPropertyValue(pd.getName(), value);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (value == null && this.primitivesDefaultedForNullValue) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Intercepted TypeMismatchException for row " + rowNumber +
" and column '" + column + "' with null value when setting property '" +
pd.getName() + "' of type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(pd.getPropertyType()) +
"' on object: " + mappedObject, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
if (populatedProperties != null) {
populatedProperties.add(pd.getName());
}
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
throw new DataRetrievalFailureException(
"Unable to map column '" + column + "' to property '" + pd.getName() + "'", ex);
}
}
else {
// No PropertyDescriptor found
if (rowNumber == 0 && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No property found for column '" + column + "' mapped to field '" + field + "'");
}
}
}
if (populatedProperties != null && !populatedProperties.equals(this.mappedProperties)) {
throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException("Given ResultSet does not contain all fields " +
"necessary to populate object of class [" + this.mappedClass.getName() + "]: " +
this.mappedProperties);
}
return mappedObject;
}
①分析 Object value = getColumnValue(rs, index, pd) 源码
protected Object getColumnValue(ResultSet rs, int index, PropertyDescriptor pd) throws SQLException {
// 结果集, 索引, 该索引的类型
return JdbcUtils.getResultSetValue(rs, index, pd.getPropertyType());
}
根据类型去获取需要的value
public static Object getResultSetValue(ResultSet rs, int index, Class<?> requiredType) throws SQLException {
if (requiredType == null) {
return getResultSetValue(rs, index);
}
Object value;
// 根据索引获取value
if (String.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getString(index);
}
else if (boolean.class == requiredType || Boolean.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getBoolean(index);
}
else if (byte.class == requiredType || Byte.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getByte(index);
}
else if (short.class == requiredType || Short.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getShort(index);
}
else if (int.class == requiredType || Integer.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getInt(index);
}
else if (long.class == requiredType || Long.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getLong(index);
}
else if (float.class == requiredType || Float.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getFloat(index);
}
else if (double.class == requiredType || Double.class == requiredType ||
Number.class == requiredType) {
value = rs.getDouble(index);
}
else if (BigDecimal.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getBigDecimal(index);
}
else if (java.sql.Date.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getDate(index);
}
else if (java.sql.Time.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getTime(index);
}
else if (java.sql.Timestamp.class == requiredType || java.util.Date.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getTimestamp(index);
}
else if (byte[].class == requiredType) {
return rs.getBytes(index);
}
else if (Blob.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getBlob(index);
}
else if (Clob.class == requiredType) {
return rs.getClob(index);
}
else if (requiredType.isEnum()) {
// Enums can either be represented through a String or an enum index value:
// leave enum type conversion up to the caller (e.g. a ConversionService)
// but make sure that we return nothing other than a String or an Integer.
Object obj = rs.getObject(index);
if (obj instanceof String) {
return obj;
}
else if (obj instanceof Number) {
// Defensively convert any Number to an Integer (as needed by our
// ConversionService's IntegerToEnumConverterFactory) for use as index
return NumberUtils.convertNumberToTargetClass((Number) obj, Integer.class);
}
else {
// e.g. on Postgres: getObject returns a PGObject but we need a String
return rs.getString(index);
}
}
else {
// Some unknown type desired -> rely on getObject.
try {
return rs.getObject(index, requiredType);
}
catch (AbstractMethodError err) {
logger.debug("JDBC driver does not implement JDBC 4.1 'getObject(int, Class)' method", err);
}
catch (SQLFeatureNotSupportedException ex) {
logger.debug("JDBC driver does not support JDBC 4.1 'getObject(int, Class)' method", ex);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
logger.debug("JDBC driver has limited support for JDBC 4.1 'getObject(int, Class)' method", ex);
}
// Corresponding SQL types for JSR-310 / Joda-Time types, left up
// to the caller to convert them (e.g. through a ConversionService).
String typeName = requiredType.getSimpleName();
if ("LocalDate".equals(typeName)) {
return rs.getDate(index);
}
else if ("LocalTime".equals(typeName)) {
return rs.getTime(index);
}
else if ("LocalDateTime".equals(typeName)) {
return rs.getTimestamp(index);
}
// Fall back to getObject without type specification, again
// left up to the caller to convert the value if necessary.
return getResultSetValue(rs, index);
}
// Perform was-null check if necessary (for results that the JDBC driver returns as primitives).
return (rs.wasNull() ? null : value);
}
② bw.setPropertyValue(pd.getName(), value);
public void setValue(final Object value) throws Exception {
// 这里就是获取setId这个方法
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
// 是否使用反射权限穿透
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
// 获取对象和value, 然后设置到这个对象中
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
这个wrappedObject就是上面的Bean, 如果设置它, 就相当于设置上面那个Bean
public final Object getWrappedInstance() {
Assert.state(this.wrappedObject != null, "No wrapped object");
return this.wrappedObject;
}
至此将值设置到结果的query方法分析完毕
2) update
现在分析update方法, 看下是否存在不同
public void testSave() throws Exception {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account(name, money) VALUES (?, ?)", "ccc", 1234f);
}
进入发现前面的源码都差不多
发现都差不多, 就中间的
protected int update(final PreparedStatementCreator psc, final PreparedStatementSetter pss) {
// ...
int rows = ps.executeUpdate();
// ...
}
是不一样的
3.分析线程绑定Connection的方法
public class JdbcTemplate extends JdbcAccessor implements JdbcOperations {
public <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action)
throws DataAccessException {
// ...
// 分析这段话
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
// ...
}
}
初始化的时候已经使用构造方法存入了DataSource
protected DataSource obtainDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
Assert.state(dataSource != null, "No DataSource set");
return dataSource;
}
public abstract class DataSourceUtils {
public static Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws CannotGetJdbcConnectionException {
try {
// 分析它
return doGetConnection(dataSource);
} catch (...) {
// ...
}
}
}
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
// 根据线程名字获取该线程中前一次获取的链接 Connection
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 判断前一次不存在链接或者它不是线程绑定的链接
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
conHolder.requested();
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(fetchConnection(dataSource));
}
// 直接拿出前一次缓存的Connection
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
// Else we either got no holder or an empty thread-bound holder here.
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
// 链接持有者不存在链接, 则去抓取
// 内部代码就是简单的 Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 上面注解的代码就是拿出一个新的Connection
Connection con = fetchConnection(dataSource);
// 判断Connection是否绑定了线程, (如果需要绑定线程的话, 需要在new Connection链接的时候调用
// TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization();
// 并且将这个Connection加入到Spring容器中 {@Bean}, 看 ① 的代码)
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
try {
// 对事务中的其他JDBC操作使用相同的连接, 线程绑定对象将在事务完成时通过同步删除
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
// 构造器的方式构造一个新的链接持有者, 并且将链接存入持有者体内
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
// 将链接设置到链接持有者中
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
// 链接持有者是链接索引自增
holderToUse.requested();
// 注册链接持有者
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
// 设置标志, 表示同步初始化器初始化完毕
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
// 绑定到资源对象
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// 来自外部委托调用的意外异常——>关闭连接并重新抛出
// 如果发生异常, 这关闭链接
releaseConnection(con, dataSource);
throw ex;
}
}
return con;
}
①
public Connection connection(DataSource dataSource) {
// 让这个线程通过 JdbcTemplate 获取的 Connection 是同一个
TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization();
return DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
}
有一个线程, 则只要这个线程工作没做完, 那么Connection就会一直是同一个, 这样就保证了所有的业务是在同一个事务中