1.设置android:layout_weight时要注意:
首先声明只有在Linearlayout中,该属性才有效。
android:layout_width的属性值,如果设置为match_parent时就会出现比例和所要设置的android:layout_weight不一样
(下面有例子 vertical和horizontal是一样的);android:layout_weight的真实含义是:一旦View设置了该属性(假设有效的情况下),
那么该 View的宽度等于原有宽度(android:layout_width)加上剩余空间的占比,所以layout_width一般都设置成0dp!
[部分代码:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:text="用户名:"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@style/Text"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/userName"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:hint="请输入用户名"/>
</LinearLayout>
效果正常:

<----------------------------------------------------------------------->
【反面与讲解:】
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="button2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button3"/>
</LinearLayout>
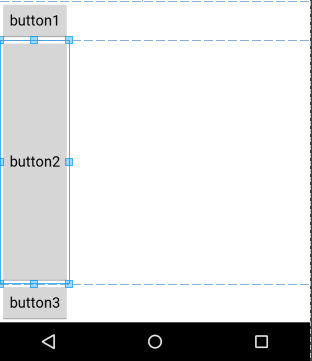
效果图如下:
讲解如下:
1、我们只有在button2使用了layout_weight属性,并赋值为1;但是button1和button2并没有使用这个属性,根据API可以知道,他们的layout_weight属性等于0。
2、LinearLayout如果显式包含layout_weight属性时,会measure两次;第一次将正常计算三个button的宽高,第二次将结合layout_weight的值分配剩余的空间。
通俗点来总结:Android系统先按照你设置的3个Button高度Layout_height=wrap_content,给你分配好他们3个的高度,然后会把剩下来的屏幕空间全部赋给Button2,因为只有他的权重值是1,这也是为什么Button2占了那么大的一块空间。
在layout_width设置为match_parent的时候,layout_weight所代表的是你的控件要优先尽可能的大,但这个大是有限度的,即match_parent。
在layout_width设置为wrap_content的时候,layout_weight所代表的是你的控件要优先尽可能的小,但这个大是有限度的,即wrap_content。
这是对于这种仅仅记住怎么用而不是为什么这么用的做法,作为一个有追求有理想的程序员是不会苟同的,因为说不定哪天,咱们又忘了口诀,所以我们要从原理上理解为啥是这个样子的。
依照上面的理解,这个现象的出现在于layout_width="match_parent"这个原因导致的;开始下面的分析:
1、系统先给3个TextView分配他们所要的宽度match_parent,也就指定了每一个TextView都是填满他的父控件,这里就是整个屏幕的宽度。
2、由于如果包含layout_width这个属性,LinearLayout将会进行第二次measure,此时将会根据权重分配剩余的空间,在这里剩余空间=1个parent_width-3个parent_width=-2个parent_width (parent_width指的是屏幕宽度 )。
3、第一个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width(match_parent的宽度) + 1/5(他所占剩余空间的权重比列) * 剩余空间大小(-2 parent_width)=3/5parent_width
同理第二个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 2/5*(-2parent_width)=1/5parent_width;
第三个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 2/5*(-2parent_width)=1/5parent_width;
部分代码: