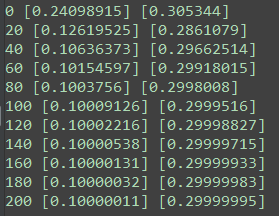
1 # _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ 2 """ 3 author:Bevishe 4 date:2019-05-04 5 """ 6 7 import numpy as np 8 import pandas as pd 9 import tensorflow as tf 10 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 11 ''' 12 使用tensorflow来自己实现一个简单的线性回归 13 ''' 14 #返回0-1之间100个符合均匀分布的随机数 15 x_data = np.random.rand(100).astype(np.float32) 16 y_data = x_data*0.1 +0.3 17 18 #create the tensorflow structure 19 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0)) 20 biase = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1])) 21 22 y = Weights*x_data +biase 23 24 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data)) 25 26 optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5) 27 train = optimizer.minimize(loss) 28 29 init = tf.initialize_all_variables() 30 31 #end 32 33 sess = tf.Session() 34 sess.run(init) 35 36 for step in range(201): 37 sess.run(train) 38 y_ = x_data*sess.run(Weights) + sess.run(biase) 39 plt.plot(x_data,y_data,color = 'r') 40 plt.plot(x_data,y_,color = 'b') 41 plt.show() 42 if step%20 == 0: 43 print(step,sess.run(Weights),sess.run(biase))