前言
文章标题一开始提及到了一个令人感到有些抽象又显得有些很"大"的词,限流.其实这个词语在很多行业都可以用到,比如最近春运,各大主要城市,火车站,地铁站都要做到限流吧,避免人流量过大造成事故或间接事故,这叫人流量限流,同理也可以用在车流量上.如果基于这个背景,把这里的人群和车辆抽象为数据,对数据进行限流,就是本篇文章的主题了.可能就有人疑惑了,数据为什么要做限流,怎么做限流,有什么好处呢,带着这个疑问,仔细的阅读下文的分析吧.
数据的限流
数据的限流更让人理解的称呼应该是"数据流的限流".数据流指的就是传输中的源源不断的数据.这些数据传输会耗尽大量的网络带宽,bandwith.一台机器的网络带宽必定是有限的,如果带宽被这台机器上的某些任务用满的话,就会造成正常任务网络传输数据受到影响.如果带宽长时间的被打满之后,还会造成机器IO报警.所以限流的目的正在与此.可能造成网络带宽迅速被占满的不一定都是恶意的程序或服务,程序中一个疏忽的处理或小错误都可能会造成大规模数据的传输.所以与其去劝导用户规范写程序,还不如从系统层面进行强加管理限制,把主动权掌握在自己手中.
Hadoop的数据限流
数据限流是一涉及面很大的词,数据类型,使用场景就有很多,所以本文只分析我们所想要分析的数据限流,就是hadoop内部的限流机制.在写本文之前,我稍微搜素了一下网上关于此方面的文章,发现确实相关文章少之又少.但是作为一个大型的分布式存储系统,数据的读写操作一定是非常频繁的,所以数据的传输量一定很大.在数据量传输很大的情况下,如何保证避免出现个别服务把带宽占满的情况就显得格外重要。有一点是至少明确的,在Hadoop中跑的job的读写数据操作都需要是正常的。为了方便下文的描述,我们可以称此类型的数据传输为"普通任务数据流",既然这里已经先定义一个了,那就必然还存在另外的数据流传输,而且类型比想象中的多了许多:
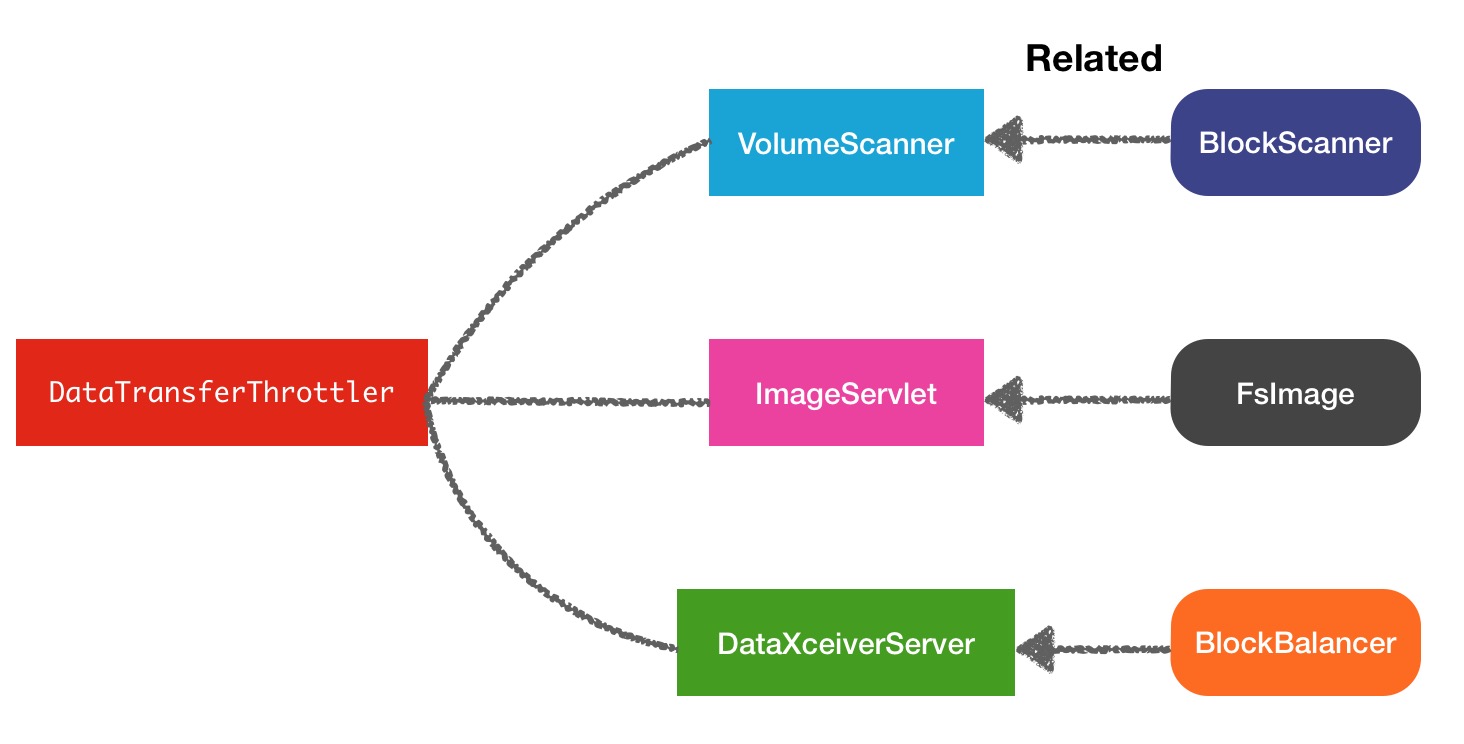
1.Balancer数据平衡数据流
2.Fsimage镜像文件的上传下载数据流传输
3.VolumeScanner磁盘扫描的数据读操作的数据数据传输
看完这3个结果,第一个Balance的数据流还是能想得到的,后面2个如果你没有从源码中进行分析,很容易会忽略掉.因为以上列举的3种属于非正常业务的数据流传输,是在系统自身内部进行的,所以hadoop对这3种操作做了限流操作.限流相关的类名叫做DataTransferThrottler,限流关系图结构如下:
DataTransferThrottler限流原理
data-transfer数据传输的限流原理在DataTransferThrottler中有着非常巧妙的设计.先看一下这个类的源码注释:
/**
* a class to throttle the data transfers.
* This class is thread safe. It can be shared by multiple threads.
* The parameter bandwidthPerSec specifies the total bandwidth shared by
* threads.
*/
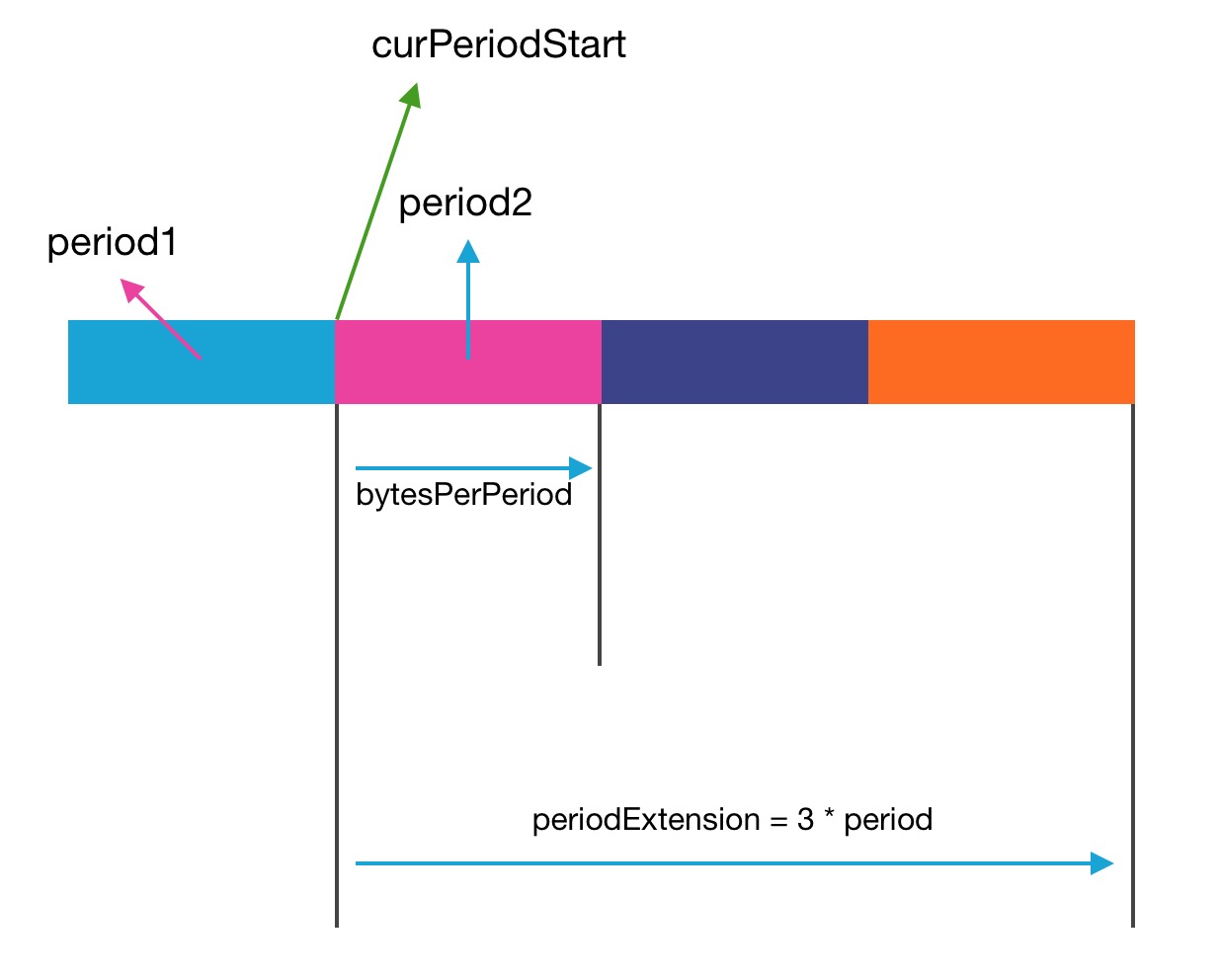
public class DataTransferThrottler { private final long period; // period over which bw is imposed
private final long periodExtension; // Max period over which bw accumulates.
private long bytesPerPeriod; // total number of bytes can be sent in each period
private long curPeriodStart; // current period starting time
private long curReserve; // remaining bytes can be sent in the period
private long bytesAlreadyUsed;所以每个period周期内的可允许传输字节数就是很关键的变量,他是根据传入的带宽上限值进行转换.
/**
* Constructor
* @param period in milliseconds. Bandwidth is enforced over this
* period.
* @param bandwidthPerSec bandwidth allowed in bytes per second.
*/
public DataTransferThrottler(long period, long bandwidthPerSec) {
this.curPeriodStart = monotonicNow();
this.period = period;
//将带宽按照周期做比例转化
this.curReserve = this.bytesPerPeriod = bandwidthPerSec*period/1000;
this.periodExtension = period*3;
}public synchronized void throttle(long numOfBytes, Canceler canceler) {
if ( numOfBytes <= 0 ) {
return;
}
//当前的可传输的字节数减去当前发送/接收字节数
curReserve -= numOfBytes;
//当前字节使用量
bytesAlreadyUsed += numOfBytes;
//如果curReserve<=0,说明当前周期内可使用字节数已经用完
while (curReserve <= 0) {
//如果设置了canceler对象,则不会进行限流操作
if (canceler != null && canceler.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
long now = monotonicNow();
long curPeriodEnd = curPeriodStart + period;
// 如果当前时间还在本周期时间内的话,则必须等待此周期的结束,
// 重新获取新的可传输字节量
if ( now < curPeriodEnd ) {
// Wait for next period so that curReserve can be increased.
try {
wait( curPeriodEnd - now );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Abort throttle and reset interrupted status to make sure other
// interrupt handling higher in the call stack executes.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
} else if ( now < (curPeriodStart + periodExtension)) {
// 如果当前时间已经超过此周期的时间且不大于最大周期间隔,则增加可接受字节数,
// 并更新周期起始时间为前一周期的末尾时间
curPeriodStart = curPeriodEnd;
curReserve += bytesPerPeriod;
} else {
// 如果当前时间超过curPeriodStart + periodExtension,则表示
// 已经长时间没有使用Throttler,重新重置时间
// discard the prev period. Throttler might not have
// been used for a long time.
curPeriodStart = now;
curReserve = bytesPerPeriod - bytesAlreadyUsed;
}
}
//传输结束,当前字节使用量进行移除
bytesAlreadyUsed -= numOfBytes;
}数据流限流在Hadoop中的使用
了解完了DataTransferThrottler中的限流原理之后,我们有必要了解hadoop在哪些地方对数据做了限流动作,其实答案在上文中也已经提过.
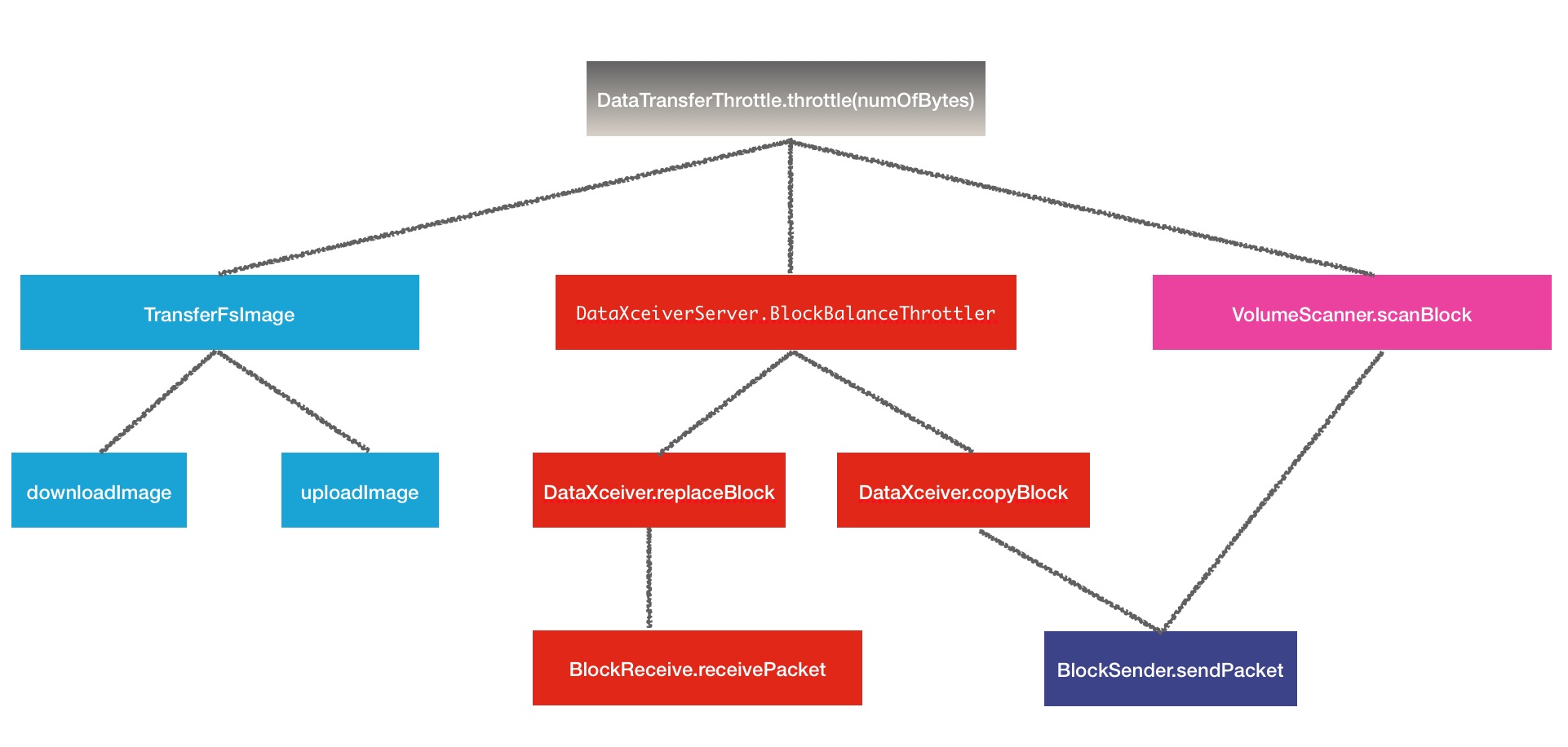
一.Balancer
数据balaner平衡的操作,其中这个throttler对象是在DataXceiverServer被调用的
//set up parameter for cluster balancing
this.balanceThrottler = new BlockBalanceThrottler(
conf.getLong(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_BANDWIDTHPERSEC_KEY,
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_BANDWIDTHPERSEC_DEFAULT),
conf.getInt(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_MAX_NUM_CONCURRENT_MOVES_KEY,
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_MAX_NUM_CONCURRENT_MOVES_DEFAULT));public static final String DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_BANDWIDTHPERSEC_KEY = "dfs.datanode.balance.bandwidthPerSec";
public static final long DFS_DATANODE_BALANCE_BANDWIDTHPERSEC_DEFAULT = 1024*1024; @Override
public void copyBlock(final ExtendedBlock block,
final Token<BlockTokenIdentifier> blockToken) throws IOException {
...
long beginRead = Time.monotonicNow();
// send block content to the target
long read = blockSender.sendBlock(reply, baseStream,
dataXceiverServer.balanceThrottler);
long duration = Time.monotonicNow() - beginRead;
datanode.metrics.incrBytesRead((int) read);
datanode.metrics.incrBlocksRead();
datanode.metrics.incrTotalReadTime(duration);
...@Override
public void replaceBlock(final ExtendedBlock block,
final StorageType storageType,
final Token<BlockTokenIdentifier> blockToken,
final String delHint,
final DatanodeInfo proxySource) throws IOException {
...
// receive a block
blockReceiver.receiveBlock(null, null, replyOut, null,
dataXceiverServer.balanceThrottler, null, true);
// notify name node
datanode.notifyNamenodeReceivedBlock(
block, delHint, blockReceiver.getStorageUuid());
LOG.info("Moved " + block + " from " + peer.getRemoteAddressString()
+ ", delHint=" + delHint);
}
... private int sendPacket(ByteBuffer pkt, int maxChunks, OutputStream out,
boolean transferTo, DataTransferThrottler throttler) throws IOException {
int dataLen = (int) Math.min(endOffset - offset,
(chunkSize * (long) maxChunks));
int numChunks = numberOfChunks(dataLen); // Number of chunks be sent in the packet
int checksumDataLen = numChunks * checksumSize;
int packetLen = dataLen + checksumDataLen + 4;
boolean lastDataPacket = offset + dataLen == endOffset && dataLen > 0;
...
if (throttler != null) { // rebalancing so throttle
throttler.throttle(packetLen);
}
return dataLen;
} /**
* Receives and processes a packet. It can contain many chunks.
* returns the number of data bytes that the packet has.
*/
private int receivePacket() throws IOException {
// read the next packet
packetReceiver.receiveNextPacket(in);
...
if (throttler != null) { // throttle I/O
throttler.throttle(len);
}
return lastPacketInBlock?-1:len;
}二.TransferFsImage
transferFsImage指的是fsImage中的镜像文件的上传下载的过程.可能是hadoop的设计者考虑到经常性的fsImage文件的传输对集群短时间内的带宽也会有所影响,因此也进行了带宽限制的操作.上传下载fsImage例子比较类似,举其中下载镜像文件为例子:
@Override
protected void doPut(final HttpServletRequest request,
final HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
final FSImage nnImage = NameNodeHttpServer.getFsImageFromContext(context);
final Configuration conf = (Configuration) getServletContext()
.getAttribute(JspHelper.CURRENT_CONF);
final PutImageParams parsedParams = new PutImageParams(request, response,
conf);
final NameNodeMetrics metrics = NameNode.getNameNodeMetrics();
validateRequest(context, conf, request, response, nnImage,
parsedParams.getStorageInfoString());
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().doAs(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run() throws Exception {
...
InputStream stream = request.getInputStream();
try {
long start = monotonicNow();
MD5Hash downloadImageDigest = TransferFsImage
.handleUploadImageRequest(request, txid,
nnImage.getStorage(), stream,
parsedParams.getFileSize(), getThrottler(conf));
.../**
* Construct a throttler from conf
* @param conf configuration
* @return a data transfer throttler
*/
public final static DataTransferThrottler getThrottler(Configuration conf) {
long transferBandwidth =
conf.getLong(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_IMAGE_TRANSFER_RATE_KEY,
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_IMAGE_TRANSFER_RATE_DEFAULT);
DataTransferThrottler throttler = null;
if (transferBandwidth > 0) {
throttler = new DataTransferThrottler(transferBandwidth);
}
return throttler;
}public static final String DFS_IMAGE_TRANSFER_RATE_KEY =
"dfs.image.transfer.bandwidthPerSec";
public static final long DFS_IMAGE_TRANSFER_RATE_DEFAULT = 0; //no throttlingprivate static MD5Hash receiveFile(String url, List<File> localPaths,
Storage dstStorage, boolean getChecksum, long advertisedSize,
MD5Hash advertisedDigest, String fsImageName, InputStream stream,
DataTransferThrottler throttler) throws IOException {
...
int num = 1;
byte[] buf = new byte[HdfsConstants.IO_FILE_BUFFER_SIZE];
while (num > 0) {
num = stream.read(buf);
if (num > 0) {
received += num;
for (FileOutputStream fos : outputStreams) {
fos.write(buf, 0, num);
}
if (throttler != null) {
throttler.throttle(num);
}
}
}三.VolumeScanner
volume-scanner的意思是磁盘扫描.而磁盘扫描的目的则是为了发现坏的块.坏的块一般发生在读操作异常的情况下,所以这个阶段写的block块会被列为suspectBlock可疑块.hadoop设计者为了确保本节点的IO不受影响,特意对磁盘扫描的带宽做了预先限制,防止这一个附属操作程序影响正常业务.方法在VolumeScanner.scanBlock方法中调用:
/**
* Scan a block.
*
* @param cblock The block to scan.
* @param bytesPerSec The bytes per second to scan at.
*
* @return The length of the block that was scanned, or
* -1 if the block could not be scanned.
*/
private long scanBlock(ExtendedBlock cblock, long bytesPerSec) {
...
BlockSender blockSender = null;
try {
blockSender = new BlockSender(block, 0, -1,
false, true, true, datanode, null,
CachingStrategy.newDropBehind());
throttler.setBandwidth(bytesPerSec);
long bytesRead = blockSender.sendBlock(nullStream, null, throttler);
resultHandler.handle(block, null);
return bytesRead;
//...@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Conf(Configuration conf) {
this.targetBytesPerSec = Math.max(0L, conf.getLong(
DFS_BLOCK_SCANNER_VOLUME_BYTES_PER_SECOND,
DFS_BLOCK_SCANNER_VOLUME_BYTES_PER_SECOND_DEFAULT));
...public static final String DFS_BLOCK_SCANNER_VOLUME_BYTES_PER_SECOND = "dfs.block.scanner.volume.bytes.per.second";
public static final long DFS_BLOCK_SCANNER_VOLUME_BYTES_PER_SECOND_DEFAULT = 1048576L;限流部分的操作就是上述3个部分,结构图如下:
思维发散
学习了整个限流部分的代码之后,还是可以看到很多设计的巧妙之处.但是同样存在美中不足之处,个人总结出了2点.
1.第一个是DataTransferThrottler的period存在"hard-code",period的周期长短的设置对于带宽的影响也不容忽视,原因在上文已经提到过.目前hard-code的设置的是500ms.
/** Constructor
* @param bandwidthPerSec bandwidth allowed in bytes per second.
*/
public DataTransferThrottler(long bandwidthPerSec) {
this(500, bandwidthPerSec); // by default throttling period is 500ms
}2.上述带宽限制的场景都一个共同点,都还只是在非Job层面做的,并没有在正常的read,write block操作做限制,这样的话,Job的数据传输将会使用光已有带宽,个人感觉可以把这方面的限制也加上,做出可配,默认不开启正常的读写带宽限制,原理与balancer的coplyBlcok和replaceBlock操作类似.这样的话,readBlock和writeBlock会变得更灵活,目前readBlock传入的throttler为null.
read = blockSender.sendBlock(out, baseStream, null); // send data类似对比
Throttler限流方案是hadoop中限制资源使用的一种手段.其实在Hadoop中,还有类似其他的类似限制资源滥用的方法,比如Quota配额机制.HDFS中的配额机制指的是对每个目录下,我可以设置该目录下的space count存储空间使用,和namespace count,命名空间使用计数,可以理解为子文件数,通过Quota就可以限制目录下创建过多的文件或写入过量饿数据.否则,就会抛出异常.相关代码的定义如下:
/**
* Counters for namespace, storage space and storage type space quota and usage.
*/
public class QuotaCounts {
// Name space and storage space counts (HDFS-7775 refactors the original disk
// space count to storage space counts)
private EnumCounters<Quota> nsSsCounts;
// Storage type space counts
private EnumCounters<StorageType> tsCounts;相关链接
Issue 链接: https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HDFS-9756
Github patch链接:https://github.com/linyiqun/open-source-patch/tree/master/hdfs/HDFS-9756