前言
如果说你是一名hadoop集群的日常维护者,那么你肯定经历过很多的节点上下线工作.例如,随着业务规模的高速扩张,集群的资源渐渐的不够使用的时候,一般正常的做法是通过增加机器来达到线性扩展的效果.当然,当这些机器在使用的过程中,出现了机器老化而引发的各自问题的时候,比如磁盘坏了,又比如某些机器网络偶尔连接不上了等,这个时候,就要把这些机器从集群中挪掉,切忌不能图一时的小利益,将这些机器留在集群中,往往像这样的异常机器会影响到集群整体的运行效率,因为不同机器上跑的任务会相互关联,你的没跑完,我的任务就必须等.今天本篇文章所要围绕的主题就是与机器的下线操作有关.
节点下线操作具体是什么意思
这里要解释一个略显的比较专业的名词:节点下线.对应的单词是Decommision,大意就是说将1个节点从集群中移除掉,并且不会对集群造成影响.所以很明显的可以看出,下线操作必然会导致集群失去大约1个节点资源的计算能力,但在hadoop中下线操作最重要的还是2个字:数据.如何保证下线节点中的数据能够完全转移到其他机器中,这才是最关键的.所以在DataNode的下线过程中,做的主要操作就是block块的重新复制,来达到HDFS默认的3副本的数据备份,当这些数据都拷贝完毕后,datanode的节点状态就是decommissioned,这个时候就可以stop datanode,彻底将机器关机移除掉.
节点下线中止后大量块复制残留
上一小节其实是一个铺垫,下线操作中出现的问题才是本文所重点强调的.当你在进行普通的机器下线中,当然过程会非常的顺利.但是当你执行完节点下线操作后,出现下面2种情形时:
1.你发现是1个误操作,误将nodeA节点加入到dfs.exclude文件中了
2.你受到上级指示,这个节点暂时不进行下线,重新调回正常服务状态
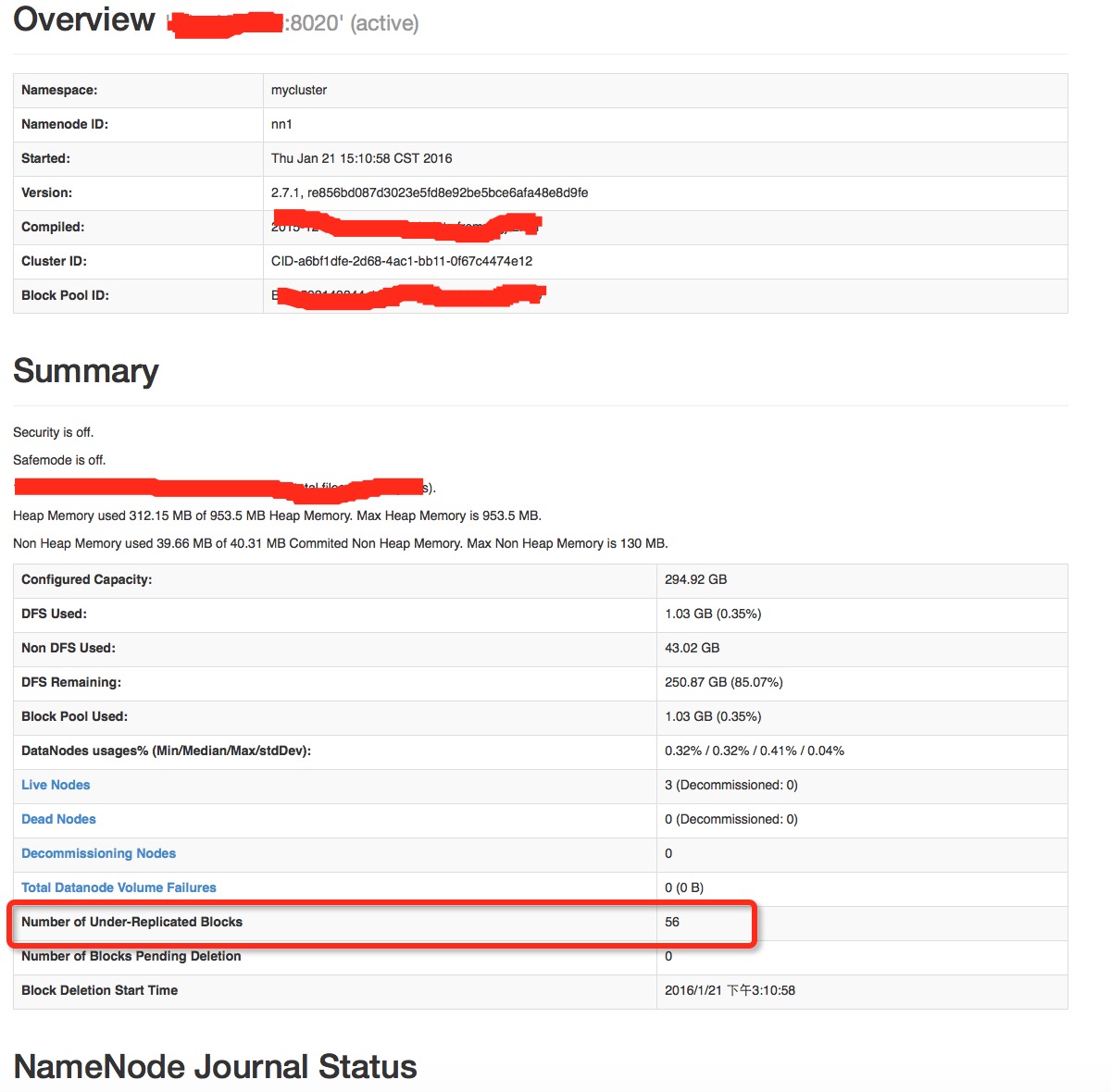
上述2种情况发生后,你的第一反应就是将节点从exclude文件中移掉,并重新dfsadmin -refreshNodes,当然你会很高兴的看到,节点的状态确实重新变为In Service的状态了.但是你如果再仔细一点的话,你会发现namenode主页面上的underReplicatedBlocks块的个数并没有减少,依然是中止下线操作前的数值.这些待复制的块基本就是原下线节点上存储的那些块.就是如下图所示的区域:
显然当下线节点恢复后,这些大量的复制块请求是不需要的,而且会持续占用namenode的时间去处理这些待复制block块,而且最后会频繁的发现,HDFS已经存在足够的块副本了,当有大量的待复制块时,那对namenode来说简直就是灾难,甚至会直接影响到namenode正常的请求处理.OK,从这里可以看出,这绝对不是一个小问题,在后面的篇幅中将会给出一套完整的解决方案,在这之前,为了帮助大家扩展一下视野,在介绍一种类似大量残余复制块的场景.
类似场景:Dead Node"复活"
出现大量复制块的另外一个场景就是出现Dead Node.当一个DataNode出现心跳长时间不汇报,超过心跳检测超时时间后,就会被任务是Dead Node.出现了Dead Node后,为了达到副本块的平衡,同样会进行大量块的拷贝,与Decommision下线操作极为类似.但是这里会有1个主要的不同点,当Dead Node,重启之后,这些残余复制块过一会就会减少到Dead Node之前的正常值.(不相信的同学可以执行这个操作进行验证).2种场景,相似的现象,不同的结果.Dead Node恢复的情况才是我们想看到的结果.那么为什么Dead Node的恢复会使得复制块的减少,而下线恢复操作则不会呢,解决这个问题的唯一办法还是从源码中寻找,光猜是永远解决不了问题的,一旦这个答案发现,一定有助于我们用相同的办法解决下线操作时大量复制块残留的问题.
Dead Node复活-"复制块消除"
本篇文章中的角色始终在围绕着"复制块",那么在HDFS的代码中,这个变量到底是被对象类所控制的呢,找到这个变量,方法很关键.答案在FSNamesystem类中,代码如下:
@Override // FSNamesystemMBean
@Metric
public long getUnderReplicatedBlocks() {
return blockManager.getUnderReplicatedBlocksCount();
}/** Used by metrics */
public long getUnderReplicatedBlocksCount() {
return underReplicatedBlocksCount;
}void updateState() {
pendingReplicationBlocksCount = pendingReplications.size();
underReplicatedBlocksCount = neededReplications.size();
corruptReplicaBlocksCount = corruptReplicas.size();
}/**
* Main loop for each BP thread. Run until shutdown,
* forever calling remote NameNode functions.
*/
private void offerService() throws Exception {
LOG.info("For namenode " + nnAddr + " using"
+ " DELETEREPORT_INTERVAL of " + dnConf.deleteReportInterval + " msec "
+ " BLOCKREPORT_INTERVAL of " + dnConf.blockReportInterval + "msec"
+ " CACHEREPORT_INTERVAL of " + dnConf.cacheReportInterval + "msec"
+ " Initial delay: " + dnConf.initialBlockReportDelay + "msec"
+ "; heartBeatInterval=" + dnConf.heartBeatInterval);
//
// Now loop for a long time....
//
while (shouldRun()) {
try {
final long startTime = scheduler.monotonicNow();
//
// Every so often, send heartbeat or block-report
//
final boolean sendHeartbeat = scheduler.isHeartbeatDue(startTime);
if (sendHeartbeat) {
...
}
if (sendImmediateIBR ||
(startTime - lastDeletedReport > dnConf.deleteReportInterval)) {
reportReceivedDeletedBlocks();
lastDeletedReport = startTime;
}
List<DatanodeCommand> cmds = blockReport();
processCommand(cmds == null ? null : cmds.toArray(new DatanodeCommand[cmds.size()]));
... /**
* Report the list blocks to the Namenode
* @return DatanodeCommands returned by the NN. May be null.
* @throws IOException
*/
List<DatanodeCommand> blockReport() throws IOException {
...
// Send the reports to the NN.
int numReportsSent = 0;
int numRPCs = 0;
boolean success = false;
long brSendStartTime = monotonicNow();
long reportId = generateUniqueBlockReportId();
try {
if (totalBlockCount < dnConf.blockReportSplitThreshold) {
// Below split threshold, send all reports in a single message.
DatanodeCommand cmd = bpNamenode.blockReport(
bpRegistration, bpos.getBlockPoolId(), reports,
new BlockReportContext(1, 0, reportId));
...@Override // DatanodeProtocol
public DatanodeCommand blockReport(DatanodeRegistration nodeReg,
String poolId, StorageBlockReport[] reports,
BlockReportContext context) throws IOException {
checkNNStartup();
verifyRequest(nodeReg);
...
//
// BlockManager.processReport accumulates information of prior calls
// for the same node and storage, so the value returned by the last
// call of this loop is the final updated value for noStaleStorage.
//
noStaleStorages = bm.processReport(nodeReg, reports[r].getStorage(),
blocks, context, (r == reports.length - 1));
metrics.incrStorageBlockReportOps();
}
.../**
* Modify (block-->datanode) map. Remove block from set of
* needed replications if this takes care of the problem.
* @return the block that is stored in blockMap.
*/
private Block addStoredBlock(final BlockInfoContiguous block,
DatanodeStorageInfo storageInfo,
DatanodeDescriptor delNodeHint,
boolean logEveryBlock)
throws IOException {
...
// handle underReplication/overReplication
short fileReplication = bc.getBlockReplication();
if (!isNeededReplication(storedBlock, fileReplication, numCurrentReplica)) {
neededReplications.remove(storedBlock, numCurrentReplica,
num.decommissionedReplicas(), fileReplication);
} else {
...Decommission下线操作如何运作
这个部分可以作为本文的一个"分水岭",上半部是渐渐通过现象找出问题的根源,而下半部则是学习原理解决问题.所以要解决Decommision下线操作中大量块的问题,就要首先明白他的运作逻辑.我们都知道,下线相关动作都是通过-refreshNodes的命令触发的,对应到下面的方法:
/**
* 1. Added to hosts --> no further work needed here.
* 2. Removed from hosts --> mark AdminState as decommissioned.
* 3. Added to exclude --> start decommission.
* 4. Removed from exclude --> stop decommission.
*/
private void refreshDatanodes() {
for(DatanodeDescriptor node : datanodeMap.values()) {
// Check if not include.
if (!hostFileManager.isIncluded(node)) {
node.setDisallowed(true); // case 2.
} else {
if (hostFileManager.isExcluded(node)) {
decomManager.startDecommission(node); // case 3.
} else {
decomManager.stopDecommission(node); // case 4.
}
}
}
}Start Decommissioning
在开始下线操作后,待复制块是如何被加入到needReplications这个对象里去的.
/**
* Start decommissioning the specified datanode.
* @param node
*/
@VisibleForTesting
public void startDecommission(DatanodeDescriptor node) {
if (!node.isDecommissionInProgress()) {
if (!node.isAlive) {
LOG.info("Dead node {} is decommissioned immediately.", node);
node.setDecommissioned();
} else if (!node.isDecommissioned()) {
for (DatanodeStorageInfo storage : node.getStorageInfos()) {
LOG.info("Starting decommission of {} {} with {} blocks",
node, storage, storage.numBlocks());
}
// Update DN stats maintained by HeartbeatManager
hbManager.startDecommission(node);
node.decommissioningStatus.setStartTime(monotonicNow());
pendingNodes.add(node);
}
}
.../**
* Checks to see if DNs have finished decommissioning.
* <p/>
* Since this is done while holding the namesystem lock,
* the amount of work per monitor tick is limited.
*/
private class Monitor implements Runnable {
...
@Override
public void run() {
if (!namesystem.isRunning()) {
LOG.info("Namesystem is not running, skipping decommissioning checks"
+ ".");
return;
}
...@Override
public void run() {
...
try {
processPendingNodes();
check();
} finally {
namesystem.writeUnlock();
}
if (numBlocksChecked + numNodesChecked > 0) {
LOG.info("Checked {} blocks and {} nodes this tick", numBlocksChecked,
numNodesChecked);
}
}/**
* Pop datanodes off the pending list and into decomNodeBlocks,
* subject to the maxConcurrentTrackedNodes limit.
*/
private void processPendingNodes() {
while (!pendingNodes.isEmpty() &&
(maxConcurrentTrackedNodes == 0 ||
decomNodeBlocks.size() < maxConcurrentTrackedNodes)) {
decomNodeBlocks.put(pendingNodes.poll(), null);
}
}private void check() {
final Iterator<Map.Entry<DatanodeDescriptor, AbstractList<BlockInfoContiguous>>>
it = new CyclicIteration<>(decomNodeBlocks, iterkey).iterator();
final LinkedList<DatanodeDescriptor> toRemove = new LinkedList<>();
while (it.hasNext()
&& !exceededNumBlocksPerCheck()
&& !exceededNumNodesPerCheck()) {
...
if (blocks == null) {
// This is a newly added datanode, run through its list to schedule
// under-replicated blocks for replication and collect the blocks
// that are insufficiently replicated for further tracking
LOG.debug("Newly-added node {}, doing full scan to find " +
"insufficiently-replicated blocks.", dn);
blocks = handleInsufficientlyReplicated(dn);
decomNodeBlocks.put(dn, blocks);
fullScan = true;
} else {
// This is a known datanode, check if its # of insufficiently
// replicated blocks has dropped to zero and if it can be decommed
LOG.debug("Processing decommission-in-progress node {}", dn);
pruneSufficientlyReplicated(dn, blocks);
}
...private void processBlocksForDecomInternal(
final DatanodeDescriptor datanode,
final Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous> it,
final List<BlockInfoContiguous> insufficientlyReplicated,
boolean pruneSufficientlyReplicated) {
...
while (it.hasNext()) {
...
final NumberReplicas num = blockManager.countNodes(block);
final int liveReplicas = num.liveReplicas();
final int curReplicas = liveReplicas;
// Schedule under-replicated blocks for replication if not already
// pending
if (blockManager.isNeededReplication(block, bc.getBlockReplication(),
liveReplicas)) {
if (!blockManager.neededReplications.contains(block) &&
blockManager.pendingReplications.getNumReplicas(block) == 0 &&
namesystem.isPopulatingReplQueues()) {
// Process these blocks only when active NN is out of safe mode.
blockManager.neededReplications.add(block,
curReplicas,
num.decommissionedReplicas(),
bc.getBlockReplication());
}
}
...
}
Stop Decommission
那停止下线操作又做了什么操作呢,至少有1点我们可以确定的是,他没有将原本存在与下线节点中的block块从neededReplications对象中移除掉.
/**
* Stop decommissioning the specified datanode.
* @param node
*/
void stopDecommission(DatanodeDescriptor node) {
if (node.isDecommissionInProgress() || node.isDecommissioned()) {
LOG.info("Stopping decommissioning of node {}", node);
// Update DN stats maintained by HeartbeatManager
hbManager.stopDecommission(node);
// Over-replicated blocks will be detected and processed when
// the dead node comes back and send in its full block report.
// The original blocks in decomNodes will be removing from
// neededReplications if node is decommission-in-progress.
if (node.isAlive) {
blockManager.processOverReplicatedBlocksOnReCommission(node);
}
// Remove from tracking in DecommissionManager
pendingNodes.remove(node);
decomNodeBlocks.remove(node);
} else {
LOG.trace("stopDecommission: Node {} is not decommission in progress " +
"or decommissioned, nothing to do.", node);
}
}中止下线操作后移除残余副本块解决方案
我们首先在DecommissionManager这个类中定义一个新的方法,如下:
private void removeNeededReplicatedBlocksInDecomNodes(
final DatanodeDescriptor datanode) {
final Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous> it = datanode.getBlockIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BlockInfoContiguous block = it.next();
BlockCollection bc = blockManager.blocksMap.getBlockCollection(block);
if (bc == null) {
// Orphan block, will be invalidated eventually. Skip.
continue;
}
final NumberReplicas num = blockManager.countNodes(block);
final int liveReplicas = num.liveReplicas();
final int curReplicas = liveReplicas;
if (!blockManager.isNeededReplication(block, bc.getBlockReplication(),
liveReplicas)) {
blockManager.neededReplications.remove(block, curReplicas,
num.decommissionedReplicas(), bc.getBlockReplication());
}
}
}/**
* Stop decommissioning the specified datanode.
* @param node
*/
void stopDecommission(DatanodeDescriptor node) {
if (node.isDecommissionInProgress() || node.isDecommissioned()) {
LOG.info("Stopping decommissioning of node {}", node);
AdminStates adminState = node.getAdminState();
// Update DN stats maintained by HeartbeatManager
hbManager.stopDecommission(node);
// Over-replicated blocks will be detected and processed when
// the dead node comes back and send in its full block report.
// The original blocks in decomNodes will be removing from
// neededReplications if node is decommission-in-progress.
if (node.isAlive) {
blockManager.processOverReplicatedBlocksOnReCommission(node);
if (adminState == AdminStates.DECOMMISSION_INPROGRESS) {
removeNeededReplicatedBlocksInDecomNodes(node);
}
}
// Remove from tracking in DecommissionManager
pendingNodes.remove(node);
decomNodeBlocks.remove(node);
} else {
LOG.trace("stopDecommission: Node {} is not decommission in progress " +
"or decommissioned, nothing to do.", node);
}
}@Test
public void testDecommissionRemovingNeededReplicatedBlocks()
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int underReplicatedBlocksNum;
int neededReplicatedBlocksNum;
int sleepIntervalTime = 5000;
int numNamenodes = 1;
int numDatanodes = 2;
// Set replications num equal to datanode's num
// So the blocks's num of each node is actually the file blocks's num
int replicas = numDatanodes;
conf.setInt(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_REPLICATION_KEY, replicas);
startCluster(numNamenodes, numDatanodes, conf);
ArrayList<ArrayList<DatanodeInfo>> namenodeDecomList =
new ArrayList<ArrayList<DatanodeInfo>>(numNamenodes);
for (int i = 0; i < numNamenodes; i++) {
namenodeDecomList.add(i, new ArrayList<DatanodeInfo>(numDatanodes));
}
// Calculate total blocks num of file
neededReplicatedBlocksNum = (int) Math.ceil(1.0 * fileSize / blockSize);
Path file = new Path("testDecommission.dat");
for (int iteration = 0; iteration < numDatanodes - 1; iteration++) {
// Start decommissioning one namenode
for (int i = 0; i < numNamenodes; i++) {
FileSystem fileSys = cluster.getFileSystem(i);
FSNamesystem ns = cluster.getNamesystem(i);
BlockManager blcokManager = ns.getBlockManager();
writeFile(fileSys, file, replicas);
DFSClient client = getDfsClient(cluster.getNameNode(i), conf);
DatanodeInfo[] info = client.datanodeReport(DatanodeReportType.LIVE);
ArrayList<String> decommissionedNodes = new ArrayList<String>();
decommissionedNodes.add(info[0].getXferAddr());
writeConfigFile(excludeFile, decommissionedNodes);
refreshNodes(cluster.getNamesystem(i), conf);
// Return the datanode descriptor for the given datanode.
NameNodeAdapter.getDatanode(cluster.getNamesystem(i), info[0]);
// Sleep some time to let DecommissionManager Monitor thread to scan the
// blocks
Thread.sleep(sleepIntervalTime);
underReplicatedBlocksNum =
blcokManager.getUnderReplicatedNotMissingBlocks();
assertEquals(neededReplicatedBlocksNum, underReplicatedBlocksNum);
// Remove decommissionedNodes from exclude file
// The blocks of neededReplications will be removed
decommissionedNodes.clear();
writeConfigFile(excludeFile, decommissionedNodes);
refreshNodes(cluster.getNamesystem(i), conf);
underReplicatedBlocksNum =
blcokManager.getUnderReplicatedNotMissingBlocks();
assertEquals(0, underReplicatedBlocksNum);
cleanupFile(fileSys, file);
}
}
// Restart the cluster and ensure decommissioned datanodes
// are allowed to register with the namenode
cluster.shutdown();
startCluster(numNamenodes, numDatanodes, conf);
cluster.shutdown();
}相关链接
Issue链接: https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HDFS-9685
Github patch链接: https://github.com/linyiqun/open-source-patch/blob/master/hdfs/HDFS-9685/HDFS-9685.001.patch