前言
在Hadoop Job的各个运行过程中,Shuffle阶段一直是一个比较神秘的过程.因为Shuffle阶段是隶属于Reduce过程的子过程,所以很多时候会被人所忽略.但是Shffle的整个过程在map reduce的整个过程中起到1个数据过渡的作用.正因为这个模块的重要性,Hadoop把这个模块设置成了可插拔的模块,用户可以根据自己应用的类型特点,定制自己的Shuffle模块代码.之前粗粗的阅读了一下相关的代码,于是写一些内容记录一下所学的.
Shuffle过程
Shuffle过程是Reduce阶段的初始操作阶段,过程简单的理解就是"远程数据拷贝"的过程,拷贝的目标数据源就是map的中间输出结果.reduce过程要想进一步进行处理操作,首先必须要做的就是拿到这批数据.一般map的中间结果文件是写出在当前的Task运行的节点上,所以reduce task拷贝数据会经过走网络的过程.而且如果这其中的量比较大的话,会消耗掉一定的网络带宽.
Shuffle模块源码分析
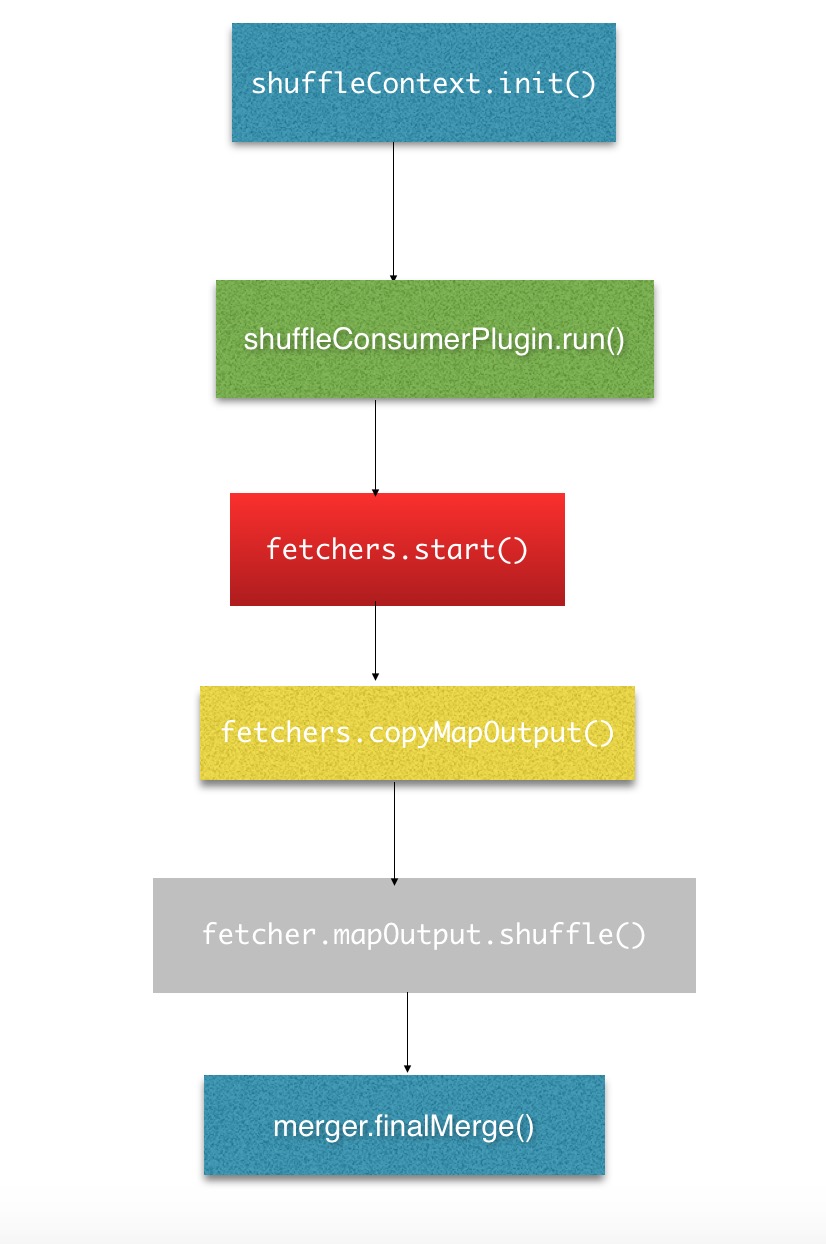
下面从源代码层面浅析此模块部分的代码,首先这个阶段是属于Reduce的过程中的,所以定位到Reduce Task的代码上.
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void run(JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
if (isMapOrReduce()) {
copyPhase = getProgress().addPhase("copy");
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort");
reducePhase = getProgress().addPhase("reduce");
}
....
// Initialize the codec
codec = initCodec();
RawKeyValueIterator rIter = null;
ShuffleConsumerPlugin shuffleConsumerPlugin = null;
Class combinerClass = conf.getCombinerClass();
CombineOutputCollector combineCollector =
(null != combinerClass) ?
new CombineOutputCollector(reduceCombineOutputCounter, reporter, conf) : null;
Class<? extends ShuffleConsumerPlugin> clazz =
job.getClass(MRConfig.SHUFFLE_CONSUMER_PLUGIN, Shuffle.class, ShuffleConsumerPlugin.class);
shuffleConsumerPlugin = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, job);
LOG.info("Using ShuffleConsumerPlugin: " + shuffleConsumerPlugin);
ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context shuffleContext =
new ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context(getTaskID(), job, FileSystem.getLocal(job), umbilical,
super.lDirAlloc, reporter, codec,
combinerClass, combineCollector,
spilledRecordsCounter, reduceCombineInputCounter,
shuffledMapsCounter,
reduceShuffleBytes, failedShuffleCounter,
mergedMapOutputsCounter,
taskStatus, copyPhase, sortPhase, this,
mapOutputFile, localMapFiles);
shuffleConsumerPlugin.init(shuffleContext);
rIter = shuffleConsumerPlugin.run();
....@InterfaceAudience.LimitedPrivate("mapreduce")
@InterfaceStability.Unstable
public static class Context<K,V> {
private final org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptID reduceId;
private final JobConf jobConf;
private final FileSystem localFS;
private final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical;
private final LocalDirAllocator localDirAllocator;
private final Reporter reporter;
private final CompressionCodec codec;
private final Class<? extends Reducer> combinerClass;
private final CombineOutputCollector<K, V> combineCollector;
//与Shuffle过程相关计数器
private final Counters.Counter spilledRecordsCounter;
private final Counters.Counter reduceCombineInputCounter;
private final Counters.Counter shuffledMapsCounter;
private final Counters.Counter reduceShuffleBytes;
private final Counters.Counter failedShuffleCounter;
private final Counters.Counter mergedMapOutputsCounter;
private final TaskStatus status;
private final Progress copyPhase;
private final Progress mergePhase;
private final Task reduceTask;
private final MapOutputFile mapOutputFile;
private final Map<TaskAttemptID, MapOutputFile> localMapFiles;shuffleConsumerPlugin.init(shuffleContext);@InterfaceAudience.LimitedPrivate({"MapReduce"})
@InterfaceStability.Unstable
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public class Shuffle<K, V> implements ShuffleConsumerPlugin<K, V>, ExceptionReporter {
private static final int PROGRESS_FREQUENCY = 2000;
private static final int MAX_EVENTS_TO_FETCH = 10000;
private static final int MIN_EVENTS_TO_FETCH = 100;
private static final int MAX_RPC_OUTSTANDING_EVENTS = 3000000;
private ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context context;
.....
@Override
public void init(ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context context) {
this.context = context;
this.reduceId = context.getReduceId();
this.jobConf = context.getJobConf();
this.umbilical = context.getUmbilical();
this.reporter = context.getReporter();
this.metrics = new ShuffleClientMetrics(reduceId, jobConf);
this.copyPhase = context.getCopyPhase();
this.taskStatus = context.getStatus();
this.reduceTask = context.getReduceTask();
this.localMapFiles = context.getLocalMapFiles();
scheduler = new ShuffleSchedulerImpl<K, V>(jobConf, taskStatus, reduceId,
this, copyPhase, context.getShuffledMapsCounter(),
context.getReduceShuffleBytes(), context.getFailedShuffleCounter());
merger = createMergeManager(context);
}rIter = shuffleConsumerPlugin.run();@Override
public RawKeyValueIterator run() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
......
// Start the map-completion events fetcher thread
final EventFetcher<K,V> eventFetcher =
new EventFetcher<K,V>(reduceId, umbilical, scheduler, this,
maxEventsToFetch);
eventFetcher.start();
// Start the map-output fetcher threads
boolean isLocal = localMapFiles != null;
final int numFetchers = isLocal ? 1 :
jobConf.getInt(MRJobConfig.SHUFFLE_PARALLEL_COPIES, 5);
Fetcher<K,V>[] fetchers = new Fetcher[numFetchers];
if (isLocal) {
fetchers[0] = new LocalFetcher<K, V>(jobConf, reduceId, scheduler,
merger, reporter, metrics, this, reduceTask.getShuffleSecret(),
localMapFiles);
fetchers[0].start();
} else {
for (int i=0; i < numFetchers; ++i) {
fetchers[i] = new Fetcher<K,V>(jobConf, reduceId, scheduler, merger,
reporter, metrics, this,
reduceTask.getShuffleSecret());
fetchers[i].start();
}
}
......public void run() {
try {
while (!stopped && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
MapHost host = null;
try {
// If merge is on, block
merger.waitForResource();
// Get a host to shuffle from
host = scheduler.getHost();
metrics.threadBusy();
// Shuffle
copyFromHost(host);
} finally {
if (host != null) {
scheduler.freeHost(host);
metrics.threadFree();
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
return;
} catch (Throwable t) {
exceptionReporter.reportException(t);
}
} @VisibleForTesting
protected void copyFromHost(MapHost host) throws IOException {
// reset retryStartTime for a new host
retryStartTime = 0;
// Get completed maps on 'host'
List<TaskAttemptID> maps = scheduler.getMapsForHost(host);
....// List of maps to be fetched yet
Set<TaskAttemptID> remaining = new HashSet<TaskAttemptID>(maps); // Construct the url and connect
URL url = getMapOutputURL(host, maps);
DataInputStream input = openShuffleUrl(host, remaining, url);
if (input == null) {
return;
}
TaskAttemptID[] failedTasks = null;
while (!remaining.isEmpty() && failedTasks == null) {
try {
failedTasks = copyMapOutput(host, input, remaining, fetchRetryEnabled);
} catch (IOException e) {
//
// Setup connection again if disconnected by NM
connection.disconnect();
// Get map output from remaining tasks only.
url = getMapOutputURL(host, remaining);
input = openShuffleUrl(host, remaining, url);
if (input == null) {
return;
}
}
}在拷贝操作之前,会进行拷贝总大小的计算,从输入流中读取.
private TaskAttemptID[] copyMapOutput(MapHost host,
DataInputStream input,
Set<TaskAttemptID> remaining,
boolean canRetry) throws IOException {
MapOutput<K,V> mapOutput = null;
TaskAttemptID mapId = null;
long decompressedLength = -1;
long compressedLength = -1;
try {
long startTime = Time.monotonicNow();
int forReduce = -1;
//Read the shuffle header
try {
ShuffleHeader header = new ShuffleHeader();
header.readFields(input);
mapId = TaskAttemptID.forName(header.mapId);
compressedLength = header.compressedLength;
decompressedLength = header.uncompressedLength;
forReduce = header.forReduce;
.....// Do some basic sanity verification
if (!verifySanity(compressedLength, decompressedLength, forReduce,
remaining, mapId)) {
return new TaskAttemptID[] {mapId};
}
if(LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("header: " + mapId + ", len: " + compressedLength +
", decomp len: " + decompressedLength);
}
// Get the location for the map output - either in-memory or on-disk
try {
mapOutput = merger.reserve(mapId, decompressedLength, id);
.... @Override
public synchronized MapOutput<K,V> reserve(TaskAttemptID mapId,
long requestedSize,
int fetcher
) throws IOException {
if (!canShuffleToMemory(requestedSize)) {
LOG.info(mapId + ": Shuffling to disk since " + requestedSize +
" is greater than maxSingleShuffleLimit (" +
maxSingleShuffleLimit + ")");
return new OnDiskMapOutput<K,V>(mapId, reduceId, this, requestedSize,
jobConf, mapOutputFile, fetcher, true);
}
.....
if (usedMemory > memoryLimit) {
LOG.debug(mapId + ": Stalling shuffle since usedMemory (" + usedMemory
+ ") is greater than memoryLimit (" + memoryLimit + ")." +
" CommitMemory is (" + commitMemory + ")");
return null;
}
// Allow the in-memory shuffle to progress
LOG.debug(mapId + ": Proceeding with shuffle since usedMemory ("
+ usedMemory + ") is lesser than memoryLimit (" + memoryLimit + ")."
+ "CommitMemory is (" + commitMemory + ")");
return unconditionalReserve(mapId, requestedSize, true);
}/**
* Unconditional Reserve is used by the Memory-to-Memory thread
* @return
*/
private synchronized InMemoryMapOutput<K, V> unconditionalReserve(
TaskAttemptID mapId, long requestedSize, boolean primaryMapOutput) {
usedMemory += requestedSize;
return new InMemoryMapOutput<K,V>(jobConf, mapId, this, (int)requestedSize,
codec, primaryMapOutput);
} ....
// The codec for lz0,lz4,snappy,bz2,etc. throw java.lang.InternalError
// on decompression failures. Catching and re-throwing as IOException
// to allow fetch failure logic to be processed
try {
// Go!
LOG.info("fetcher#" + id + " about to shuffle output of map "
+ mapOutput.getMapId() + " decomp: " + decompressedLength
+ " len: " + compressedLength + " to " + mapOutput.getDescription());
mapOutput.shuffle(host, is, compressedLength, decompressedLength,
metrics, reporter);
} catch (java.lang.InternalError e) {
LOG.warn("Failed to shuffle for fetcher#"+id, e);
throw new IOException(e);
}// Start the map-output fetcher threads
boolean isLocal = localMapFiles != null;
final int numFetchers = isLocal ? 1 :
jobConf.getInt(MRJobConfig.SHUFFLE_PARALLEL_COPIES, 5);
Fetcher<K,V>[] fetchers = new Fetcher[numFetchers];
if (isLocal) {
fetchers[0] = new LocalFetcher<K, V>(jobConf, reduceId, scheduler,
merger, reporter, metrics, this, reduceTask.getShuffleSecret(),
localMapFiles);
fetchers[0].start();
} else {
for (int i=0; i < numFetchers; ++i) {
fetchers[i] = new Fetcher<K,V>(jobConf, reduceId, scheduler, merger,
reporter, metrics, this,
reduceTask.getShuffleSecret());
fetchers[i].start();
}
}
.....
// Finish the on-going merges...
RawKeyValueIterator kvIter = null;
try {
kvIter = merger.close();
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ShuffleError("Error while doing final merge " , e);
}@Override
public RawKeyValueIterator close() throws Throwable {
// Wait for on-going merges to complete
if (memToMemMerger != null) {
memToMemMerger.close();
}
inMemoryMerger.close();
onDiskMerger.close();
List<InMemoryMapOutput<K, V>> memory =
new ArrayList<InMemoryMapOutput<K, V>>(inMemoryMergedMapOutputs);
inMemoryMergedMapOutputs.clear();
memory.addAll(inMemoryMapOutputs);
inMemoryMapOutputs.clear();
List<CompressAwarePath> disk = new ArrayList<CompressAwarePath>(onDiskMapOutputs);
onDiskMapOutputs.clear();
return finalMerge(jobConf, rfs, memory, disk);
}其他方面代码的分析请点击链接https://github.com/linyiqun/hadoop-yarn,后续将会继续更新YARN其他方面的代码分析。
参考源码
Apach-hadoop-2.7.1(hadoop-hdfs-project)