介绍
KNN算法全名为k-Nearest Neighbor,就是K最近邻的意思。KNN也是一种分类算法。但是与之前说的决策树分类算法相比,这个算法算是最简单的一个了。算法的主要过程为:
1、给定一个训练集数据,每个训练集数据都是已经分好类的。
2、设定一个初始的测试数据a,计算a到训练集所有数据的欧几里得距离,并排序。
3、选出训练集中离a距离最近的K个训练集数据。
4、比较k个训练集数据,选出里面出现最多的分类类型,此分类类型即为最终测试数据a的分类。
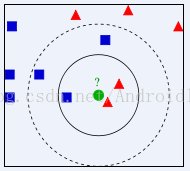
下面百度百科上的一张简图:
KNN算法实现
首先测试数据需要2块,1个是训练集数据,就是已经分好类的数据,比如上图中的非绿色的点。还有一个是测试数据,就是上面的绿点,当然这里的测试数据不会是一个,而是一组。这里的数据与数据之间的距离用数据的特征向量做计算,特征向量可以是多维度的。通过计算特征向量与特征向量之间的欧几里得距离来推算相似度。定义训练集数据trainInput.txt:
a 1 2 3 4 5
b 5 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 3 3
d -3 -3 -3 -3 -3
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
1 2 3 2 4
2 3 4 2 1
8 7 2 3 5
-3 -2 2 4 0
-4 -4 -4 -4 -4
1 2 3 4 4
4 4 3 2 1
3 3 3 2 4
0 0 1 1 -2 package DataMing_KNN;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.activemq.filter.ComparisonExpression;
/**
* k最近邻算法工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class KNNTool {
// 为4个类别设置权重,默认权重比一致
public int[] classWeightArray = new int[] { 1, 1, 1, 1 };
// 测试数据地址
private String testDataPath;
// 训练集数据地址
private String trainDataPath;
// 分类的不同类型
private ArrayList<String> classTypes;
// 结果数据
private ArrayList<Sample> resultSamples;
// 训练集数据列表容器
private ArrayList<Sample> trainSamples;
// 训练集数据
private String[][] trainData;
// 测试集数据
private String[][] testData;
public KNNTool(String trainDataPath, String testDataPath) {
this.trainDataPath = trainDataPath;
this.testDataPath = testDataPath;
readDataFormFile();
}
/**
* 从文件中阅读测试数和训练数据集
*/
private void readDataFormFile() {
ArrayList<String[]> tempArray;
tempArray = fileDataToArray(trainDataPath);
trainData = new String[tempArray.size()][];
tempArray.toArray(trainData);
classTypes = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] s : tempArray) {
if (!classTypes.contains(s[0])) {
// 添加类型
classTypes.add(s[0]);
}
}
tempArray = fileDataToArray(testDataPath);
testData = new String[tempArray.size()][];
tempArray.toArray(testData);
}
/**
* 将文件转为列表数据输出
*
* @param filePath
* 数据文件的内容
*/
private ArrayList<String[]> fileDataToArray(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
return dataArray;
}
/**
* 计算样本特征向量的欧几里得距离
*
* @param f1
* 待比较样本1
* @param f2
* 待比较样本2
* @return
*/
private int computeEuclideanDistance(Sample s1, Sample s2) {
String[] f1 = s1.getFeatures();
String[] f2 = s2.getFeatures();
// 欧几里得距离
int distance = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < f1.length; i++) {
int subF1 = Integer.parseInt(f1[i]);
int subF2 = Integer.parseInt(f2[i]);
distance += (subF1 - subF2) * (subF1 - subF2);
}
return distance;
}
/**
* 计算K最近邻
* @param k
* 在多少的k范围内
*/
public void knnCompute(int k) {
String className = "";
String[] tempF = null;
Sample temp;
resultSamples = new ArrayList<>();
trainSamples = new ArrayList<>();
// 分类类别计数
HashMap<String, Integer> classCount;
// 类别权重比
HashMap<String, Integer> classWeight = new HashMap<>();
// 首先讲测试数据转化到结果数据中
for (String[] s : testData) {
temp = new Sample(s);
resultSamples.add(temp);
}
for (String[] s : trainData) {
className = s[0];
tempF = new String[s.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(s, 1, tempF, 0, s.length - 1);
temp = new Sample(className, tempF);
trainSamples.add(temp);
}
// 离样本最近排序的的训练集数据
ArrayList<Sample> kNNSample = new ArrayList<>();
// 计算训练数据集中离样本数据最近的K个训练集数据
for (Sample s : resultSamples) {
classCount = new HashMap<>();
int index = 0;
for (String type : classTypes) {
// 开始时计数为0
classCount.put(type, 0);
classWeight.put(type, classWeightArray[index++]);
}
for (Sample tS : trainSamples) {
int dis = computeEuclideanDistance(s, tS);
tS.setDistance(dis);
}
Collections.sort(trainSamples);
kNNSample.clear();
// 挑选出前k个数据作为分类标准
for (int i = 0; i < trainSamples.size(); i++) {
if (i < k) {
kNNSample.add(trainSamples.get(i));
} else {
break;
}
}
// 判定K个训练数据的多数的分类标准
for (Sample s1 : kNNSample) {
int num = classCount.get(s1.getClassName());
// 进行分类权重的叠加,默认类别权重平等,可自行改变,近的权重大,远的权重小
num += classWeight.get(s1.getClassName());
classCount.put(s1.getClassName(), num);
}
int maxCount = 0;
// 筛选出k个训练集数据中最多的一个分类
for (Map.Entry entry : classCount.entrySet()) {
if ((Integer) entry.getValue() > maxCount) {
maxCount = (Integer) entry.getValue();
s.setClassName((String) entry.getKey());
}
}
System.out.print("测试数据特征:");
for (String s1 : s.getFeatures()) {
System.out.print(s1 + " ");
}
System.out.println("分类:" + s.getClassName());
}
}
}
package DataMing_KNN;
/**
* 样本数据类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Sample implements Comparable<Sample>{
// 样本数据的分类名称
private String className;
// 样本数据的特征向量
private String[] features;
//测试样本之间的间距值,以此做排序
private Integer distance;
public Sample(String[] features){
this.features = features;
}
public Sample(String className, String[] features){
this.className = className;
this.features = features;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public String[] getFeatures() {
return features;
}
public void setFeatures(String[] features) {
this.features = features;
}
public Integer getDistance() {
return distance;
}
public void setDistance(int distance) {
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Sample o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.getDistance().compareTo(o.getDistance());
}
}
/**
* k最近邻算法场景类型
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
String trainDataPath = "C:\Users\lyq\Desktop\icon\trainInput.txt";
String testDataPath = "C:\Users\lyq\Desktop\icon\testinput.txt";
KNNTool tool = new KNNTool(trainDataPath, testDataPath);
tool.knnCompute(3);
}
}
测试数据特征:1 2 3 2 4 分类:a
测试数据特征:2 3 4 2 1 分类:c
测试数据特征:8 7 2 3 5 分类:b
测试数据特征:-3 -2 2 4 0 分类:a
测试数据特征:-4 -4 -4 -4 -4 分类:d
测试数据特征:1 2 3 4 4 分类:a
测试数据特征:4 4 3 2 1 分类:b
测试数据特征:3 3 3 2 4 分类:c
测试数据特征:0 0 1 1 -2 分类:d程序的输出结果如上所示,如果不相信的话可以自己动手计算进行验证。
KNN算法的注意点:
1、knn算法的训练集数据必须要相对公平,各个类型的数据数量应该是平均的,否则当A数据由1000个B数据由100个,到时无论如何A数据的样本还是占优的。
2、knn算法如果纯粹凭借分类的多少做判断,还是可以继续优化的,比如近的数据的权重可以设大,最后根据所有的类型权重和进行比较,而不是单纯的凭借数量。
3、knn算法的缺点是计算量大,这个从程序中也应该看得出来,里面每个测试数据都要计算到所有的训练集数据之间的欧式距离,时间复杂度就已经为O(n*n),如果真实数据的n非常大,这个算法的开销的确态度,所以KNN不适合大规模数据量的分类。
KNN算法编码时遇到的困难:
按理来说这么简单的KNN算法本应该是没有多少的难度,但是在多欧式距离的排序上被深深的坑了一段时间,本人起初用Collections.sort(list)的方式进行按距离排序,也把Sample类实现了Compareable接口,但是排序就是不变,最后才知道,distance的int类型要改为Integer引用类型,在compareTo重载方法中调用distance的.CompareTo()方法就成功了,这个小细节平时没注意,难道属性的比较最终一定要调用到引用类型的compareTo()方法?这个小问题竟然花费了我一段时间,最后仔细的比较了一下网上的例子最后才发现......