一、Pandas的数据操作
0.DataFrame的数据结构
1.Series索引操作
(0)Series
class Series(base.IndexOpsMixin, generic.NDFrame): """ One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels (including time series). #带轴标签的一维ndarray(包括时间序列)。 Labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object #标签不一定是唯一的,但必须是可清洗的类型 supports both integer- and label-based indexing and provides a host of methods for performing operations involving the index. Statistical methods from ndarray have been overridden to automatically exclude missing data (currently represented as NaN). Operations between Series (+, -, /, *, **) align values based on their associated index values-- they need not be the same length. The result index will be the sorted union of the two indexes. Parameters ---------- data : array-like, dict, or scalar value Contains data stored in Series .. versionchanged :: 0.23.0 If data is a dict, argument order is maintained for Python 3.6 and later. index : array-like or Index (1d) Values must be hashable and have the same length as `data`. Non-unique index values are allowed. Will default to RangeIndex (0, 1, 2, ..., n) if not provided. If both a dict and index sequence are used, the index will override the keys found in the dict. dtype : numpy.dtype or None If None, dtype will be inferred copy : boolean, default False Copy input data """
(1)Series索引,ser_obj['label'],ser_obj[pos],通过字符串的标签或者索引位置进行索引
import pandas as pd ser_obj = pd.Series(range(5,10),index=['a','b','c','d','e']) #将索引设置为['a','b','c','d','e'] print(ser_obj) # 进行行索引 print(ser_obj['a']) #这里索引的是标签本身 print(ser_obj[0]) #注意这里索引的是标签的位置
返回值都是5
(2)切片索引
#切片索引 print(ser_obj[2:4]) #按照索引位置进行切片操作的时候,是不包含最后一个元素的返回第2个索引以及第3个索引 c 7; d 8
print(ser_obj['b':'d']) #按照索引名切片操作的时候,最后一个元素是包含在其中的,返回的是b 6,c 7,d 8
(3)不连续的索引,ser_obj[['label1','label3','label3']] 或者ser_obj[[pos1,pos2,pos3]],注意ser_obj[]中放的的是一个list列表,列表中放的是lab或者position,第一个[]表示需要对列表进行索引
print(ser_obj[[0,2,4]])
a 5
c 7
e 9
dtype: int64
print(ser_obj[['a','e']])
a 5
e 9
dtype: int64
(4)布尔索引
#布尔索引 ser_bool = ser_obj>7 #判断值是否大于7 print(ser_bool) #打印出判断的结果
a False
b False
c False
d True
e True
dtype: bool
print(ser_obj[ser_bool]) #找出ser_obj>7的情况并打印
d 8
e 9
dtype: int64
print(ser_obj[ser_obj>7]) #找出ser_obj大于7的情况
d 8
e 9
dtype: int64
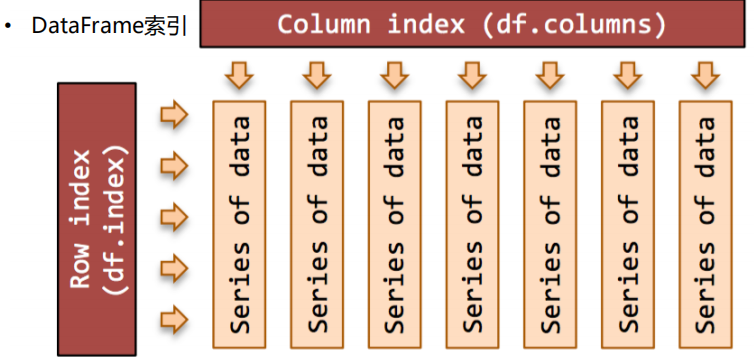
2.DataFrame索引,分为行索引和列索引,DataFrame是优先访问列索引的,如果访问不连续的列索引,那就将索引写进列表中,然后将列表进行索引操作。
class DataFrame(NDFrame): """ Two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data #两维的大小可变的,可能异构的表格数据标记轴(行和列)的结构
structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). Arithmetic operations #算术运算:在行标签和列标签上对齐。 可以被认为是一个像字典一样,Series对象的容器。 主要的pandas数据结构。
align on both row and column labels. Can be thought of as a dict-like container for Series objects. The primary pandas data structure. Parameters ---------- data : numpy ndarray (structured or homogeneous), dict, or DataFrame Dict can contain Series, arrays, constants, or list-like objects .. versionchanged :: 0.23.0 If data is a dict, argument order is maintained for Python 3.6 and later. index : Index or array-like Index to use for resulting frame. Will default to RangeIndex if no indexing information part of input data and no index provided columns : Index or array-like Column labels to use for resulting frame. Will default to RangeIndex (0, 1, 2, ..., n) if no column labels are provided dtype : dtype, default None Data type to force. Only a single dtype is allowed. If None, infer copy : boolean, default False Copy data from inputs. Only affects DataFrame / 2d ndarray input Examples -------- Constructing DataFrame from a dictionary. >>> d = {'col1': [1, 2], 'col2': [3, 4]} >>> df = pd.DataFrame(data=d) >>> df col1 col2 0 1 3 1 2 4 Notice that the inferred dtype is int64. >>> df.dtypes col1 int64 col2 int64 dtype: object To enforce a single dtype: >>> df = pd.DataFrame(data=d, dtype=np.int8) >>> df.dtypes col1 int8 col2 int8 dtype: object Constructing DataFrame from numpy ndarray: >>> df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(low=0, high=10, size=(5, 5)), ... columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) >>> df2 a b c d e 0 2 8 8 3 4 1 4 2 9 0 9 2 1 0 7 8 0 3 5 1 7 1 3 4 6 0 2 4 2 See also -------- DataFrame.from_records : constructor from tuples, also record arrays DataFrame.from_dict : from dicts of Series, arrays, or dicts DataFrame.from_items : from sequence of (key, value) pairs pandas.read_csv, pandas.read_table, pandas.read_clipboard """
df_obj =pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(5,4),columns=['a','b','c','d']) #生成一个5行4列的随机矩阵 print(df_obj)
a b c d
0 0.996924 0.681100 0.866762 0.379989
1 0.351276 0.661369 0.679242 0.099117
2 0.668854 0.023886 0.074815 0.745030
3 0.527927 0.200501 0.439957 0.486921
4 0.011786 0.303719 0.521673 0.821344
(1)列索引:df_obj['label']
#创建DataFrame的数据结构 import numpy as np df_obj =pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(5,4),columns=['a','b','c','d']) #生成一个5行4列的随机矩阵 print(df_obj) #列索引 print('列索引') print(df_obj['a']) #打印出a这一列的数据 print(type(ser_obj['a'])) #这个地方返回的数据类型是Series数据类型 print(ser_obj[[0]]) #返回的是a 5 print(type(ser_obj[[0]])) #返回class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
(2)不连续索引df_obj[['label1','label2']]
#不连续的索引 print('不连续索引') print(df_obj[['a','c']]) #打印出a列和c列的数据
a c
0 0.706947 0.668036
1 0.248566 0.602534
2 0.659694 0.816147
3 0.659362 0.271291
4 0.951508 0.435010
3.Pandas的索引可以归纳为3种
(1):loc,标签索引,使用的是索引的名称,就是标签,标签索引是包含末尾位置的
# 标签索引loc #Series print(ser_obj['b':'d']) #使用标签索引是包含最后一个元素的 print(ser_obj.loc['b':'d']) #标签索引是包含最后一个元素的 #上面两个最后输出的都是:
b 6
c 7
d 8
dtype: int6
#DataFrame print(df_obj['b']) #打印出b这一列所有的值
0 0.007736
1 0.099958
2 0.974213
3 0.289881
4 0.106485
Name: b, dtype: float64
print(df_obj.loc[0:2,'b']) #z注意这里是loc标签索引是包含最后一个元素的,输出的是0,1,2这3个
0 0.007736
1 0.099958
2 0.974213
Name: b, dtype: float64
(2)iloc,位置索引,按照标签的位置进行索引
(3)ix ,标签于位置的混合索引,如果标签和位置是一样的,就先按照标签尝试操作,然后按照位置尝试操作(这个目前的版本中已经过期了)
注意:DataFramen索引的时候,可以将其看做ndarray的操作
标签的切片索引是包含末尾位置的
4.运算与对齐
(0)np.ones()函数
def ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C'): """
返回一个给定类型和大小的新的数组,其中填充值为1 Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones. Parameters ----------
大小:整数值或者整数序列值
shape : int or sequence of ints
新数组的大小,例如(2,3)或者2 Shape of the new array, e.g., ``(2, 3)`` or ``2``. dtype : data-type, optional
数据类型:可选,一个数组期望的数据类型 The desired data-type for the array, e.g., `numpy.int8`. Default is `numpy.float64`. order : {'C', 'F'}, optional, default: C Whether to store multi-dimensional data in row-major (C-style) or column-major (Fortran-style) order in memory. Returns ------- out : ndarray Array of ones with the given shape, dtype, and order. See Also -------- ones_like : Return an array of ones with shape and type of input. empty : Return a new uninitialized array. zeros : Return a new array setting values to zero. full : Return a new array of given shape filled with value. Examples -------- >>> np.ones(5) array([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]) >>> np.ones((5,), dtype=int) array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) >>> np.ones((2, 1)) array([[ 1.], [ 1.]]) >>> s = (2,2) >>> np.ones(s) array([[ 1., 1.], [ 1., 1.]]) """ a = empty(shape, dtype, order) multiarray.copyto(a, 1, casting='unsafe') return a
(1)按照索引对齐运算,没对齐的位置NaN
Series按照行索引对齐
s1 = pd.Series(range(10,20),index=range(10)) s2 = pd.Series(range(20,25),index=range(5)) print('s1= ',s1) print('s2= ',s2) #按索引对齐运算,没有对齐的位置补空,如下s1的索引是0-9,而s2的索引是0-4, #最后计算的时候将0-4的数据进行相加,剩下的5-9的数据直接补空就可以 print(s1+s2)
DataFrame按照行、列索引对齐
(2)填充未对齐的数据进行运算
使用add,sub,div,mul
同时通过fill_value指定填充值
充未对齐的数据进行运算 # print(s1) # print(s2) #将s2中未对齐的数据填充为-1,然后再进行匀速那 print('s1+s2',s1.add(s2,fill_value=-1))
#对未对齐的数据进行运算
print('df1+df2= ',df1+df2)
#加法运算,未对齐的值填充-1
print(df1.add(df2,fill_value=-1))
# 减法运算,未对齐的值填充2.0
print(df1.sub(df2,fill_value=2))
(3)填充NaN
fillna
#填充NaN s3 =s1 + s2 print(s3)
#将填充的NaN值填充为-1
s3_filled =s3.fillna(-1)
print(s3_filled)
#加法运算,未对齐的部分填充NaN
df3 =df1+df2
print('df3= ',df3)
#加法运算,未对齐的部分填充NaN
df3 =df1+df2
print('df3= ',df3)
df3.fillna(100,inplace=True)
print(df3)
5.函数应用
(1)可直接使用Numpy的ufunc函数,如abs等
#numpy的ufunc函数,创建一个5行4列的随机数矩阵 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(5,4)) print(df) # # print('绝对值为:',np.abs(df))
(2)通过apply应用到行或者列上
注意指定轴的方向,默认axis=0,axis=0表示在列的方向上
#使用apply方法应用行或者列数据,这里注意x= 0 是用在列的方向上,x=1是在行的方向上 f = lambda x:x.max() print('在axis=0即列的方向上:',df.apply(f,axis=0)) print('在axis=1即行的方向上:',df.apply(f,axis=1)) #指定轴的方向,x=1表示在行的方向上 print(df.apply(lambda x:x.max(),axis=1))
(3)通过applymap将函数应用到每个数据上
# 使用applymap应用到每个数据上面 f2 = lambda x:'%2f' %x print(df.applymap(f2))
6.排序
(1)sort_index,索引排序
对 DataFrame操作的时候注意轴的方向
#索引排序 s4.sort_index(ascending=False) #按照索引降序排列 df4 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(3,4), index=np.random.randint(3,size=3), #行索引,3行 columns=np.random.randint(4,size=4) #列索引,4个数 ) print(df4) # 对索引进行排序 print(df4.sort_index(axis=1))
(2)按值排序
sort_values(by='label')