我们的日常开发几乎离不开Spring,他为我们的开发带来了很大的便捷,那么Spring框架是如何做到方便他人的呢。今天就来说说bean如何被加载加载。
我们在xml文件中写过太多类似这样的bean声明
<bean id="jsonParser" class="com.jackie.json.FastjsonJsonParser" />
那么这样的声明是如果被Spring读取并加载的呢?
DefaultListableBeanFactory
继承关系
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable
上面是DefaultListableBeanFactory类源码的声明,集成了父类AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory以及实现了接口
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable(且不管这些又长有难懂的父类和父接口都是干什么的)
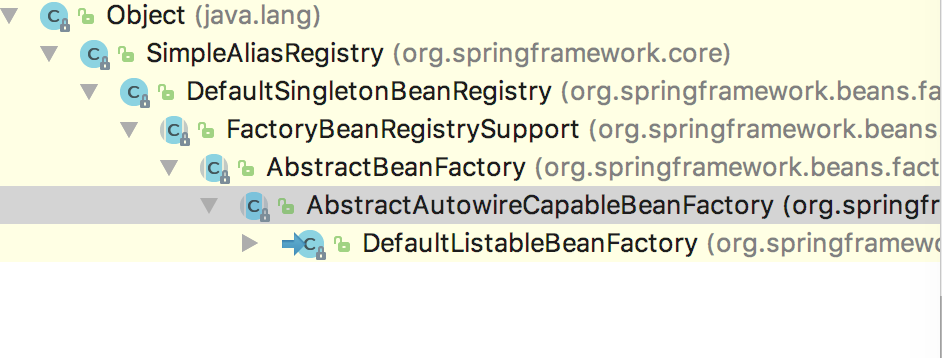
上面是DefaultListableBeanFactory的所有依赖父类,可以看到最顶层使我们熟悉的Object类。
地位
DefaultListableBeanFactory类是整个bean加载的核心部分。后面我们要说到的XmlBeanFactory就是DefaultListableBeanFactory的子类。
XmlBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory的子类。其与DefaultListableBeanFactory类的不同之处通过看源码就会发现,XmlBeanFactory使用了自定义的XmlBeanDefinitionReader用于读取xml文件内容。
XmlBeanFactory的源码并不复杂
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
/**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
/**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
- 有两个构造函数
- 两个构造函数都有参数Resource,我们在调用前可以通过各种实现比如
new ClassPathResource("application-context.xml")的方式传值 - Resource有很多实现比如 文件(FileSystemResource)、URL资源(UrlResource)、InputStream资源(InputStreamResource)、Byte数组(ByteArrayResource)等
- 使用Resource是因为该接口抽象出了Spring用到的各种底层资源比如File、Url、Classpath等
bean加载过程
说到这里的bean加载就离不开我们上面提到的XmlBeanFactory类。
一切的加载XML以及解析bean的操作都要从XmlBeanFactory的
XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory)
说起。
步骤分析
- 理所当然,我们首先点击进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader类的loadBeanDefinitions方法。整个过程简单说就是:
1.首先对传入的Resouce进行封装,成为EncodeResource对象(之所以这么做,是考虑可以对于资源文件进行编码)。
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
- 得到Resource的输入流
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
3.调用doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
- 进入doLoadBeanDefinitions方法,我们可以看到方法实现也很简单
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
主要做了三件事
得到XML文件的验证模式
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
2.加载XML文件,得到对应的Document对象(这里可以发现是调用了this.documentLoader即DefaultDocmentLoader类)
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
这里的解析成Document其实就是常规的SAX解析XML的操作。
3.根据得到的Document对象注册Bean
registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)
解析注册BeanDefinitions
上面的在得到Docment对象后,就是需要解析注册BeanDefinitions了。
进入registerBeanDefinitions方法我们可以看到其实现为
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
我们继续深入,则进入到类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReaderregisterBeanDefinitions方法的doRegisterBeanDefinitions实现。
在这个方法里实现了对于XML中的bean真正的解析
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "Environment must be set for evaluating profiles");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createHelper(this.readerContext, root, parent);
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
追踪该方法中的每一个方法就是具体执行解析xml并加载bean的过程,有兴趣可以打断点调试一遍。
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!如果您想持续关注我的文章,请扫描二维码,关注JackieZheng的微信公众号,我会将我的文章推送给您,并和您一起分享我日常阅读过的优质文章。
