Netty Reator(二)Scalable IO in Java
目录
Netty 系列目录 (https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117436.html)
相关文章:
Doug Lea 大神的《Scalable IO in Java》http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/cpjslides/nio.pdf:可伸缩的 IO 模型
大部分 IO 都是下面这个步骤,
- Read request
- Decode request
- Process service
- Encode reply
- Send reply
一、经典的网络 IO 模型
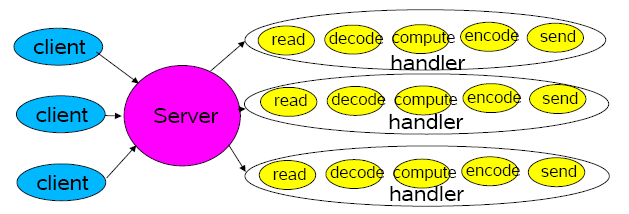
传统的 IO 模型是一个 socket 一个线程,代码如下:
class Server implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(PORT);
while (!Thread.interrupted())
new Thread(new Handler(ss.accept())).start(); //创建新线程来handle
// or, single-threaded, or a thread pool
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
static class Handler implements Runnable {
final Socket socket;
Handler(Socket s) { socket = s; }
public void run() {
try {
byte[] input = new byte[MAX_INPUT];
socket.getInputStream().read(input);
byte[] output = process(input);
socket.getOutputStream().write(output);
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
private byte[] process(byte[] cmd) { /* ... */ }
}
}
显然简单的多线程会带来扩展性问题,当 client 数量变的很多的时候,还其他的可用性、性能的问题。解决方法就是 Divide-and-conquer,分开后,就需要 Event-driven Designs 来串联起来...
二、单线程( BasicReactor Design)
所有事情 read、process、write 都由单个线程完成,完成一步重新设置下一步的 event。问题当然就是,其中任何步骤阻塞其它任务就阻塞了,因为只有一个线程。
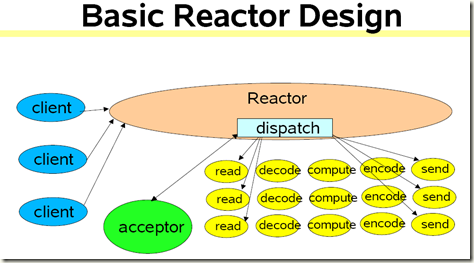
class Reactor implements Runnable {
final Selector selector;
final ServerSocketChannel serverSocket;
Reactor(int port) throws IOException { // Reactor 初始化
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocket.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞
SelectionKey sk = serverSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); // 分步处理,第一步,接收accept事件
sk.attach(new Acceptor()); //attach callback object, Acceptor
}
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
selector.select();
Set selected = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = selected.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
dispatch((SelectionKey)(it.next()); //Reactor负责dispatch收到的事件
selected.clear();
}
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
void dispatch(SelectionKey k) {
Runnable r = (Runnable)(k.attachment()); //调用之前注册的callback对象
if (r != null)
r.run();
}
class Acceptor implements Runnable { // inner
public void run() {
try {
SocketChannel c = serverSocket.accept();
if (c != null)
new Handler(selector, c);
}
catch(IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
}
}
final class Handler implements Runnable {
final SocketChannel socket;
final SelectionKey sk;
ByteBuffer input = ByteBuffer.allocate(MAXIN);
ByteBuffer output = ByteBuffer.allocate(MAXOUT);
static final int READING = 0, SENDING = 1;
int state = READING;
Handler(Selector sel, SocketChannel c) throws IOException {
socket = c; c.configureBlocking(false);
// Optionally try first read now
sk = socket.register(sel, 0);
sk.attach(this); //将Handler作为callback对象
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); //第二步,接收Read事件
sel.wakeup();
}
boolean inputIsComplete() { /* ... */ }
boolean outputIsComplete() { /* ... */ }
void process() { /* ... */ }
public void run() {
try {
if (state == READING) read();
else if (state == SENDING) send();
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
void read() throws IOException {
socket.read(input);
if (inputIsComplete()) {
process();
state = SENDING;
// Normally also do first write now
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); //第三步,接收write事件
}
}
void send() throws IOException {
socket.write(output);
if (outputIsComplete()) sk.cancel(); //write完就结束了, 关闭select key
}
}
//上面 的实现用Handler来同时处理Read和Write事件, 所以里面出现状态判断
//我们可以用State-Object pattern来更优雅的实现
class Handler { // ...
public void run() { // initial state is reader
socket.read(input);
if (inputIsComplete()) {
process();
sk.attach(new Sender()); //状态迁移, Read后变成write, 用Sender作为新的callback对象
sk.interest(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
sk.selector().wakeup();
}
}
class Sender implements Runnable {
public void run(){ // ...
socket.write(output);
if (outputIsComplete()) sk.cancel();
}
}
}
单线程模式的局限还是比较明显的。所以改进是将比较耗时的部分,从 reactor 线程中分离出去,让 reactor 专门负责 IO,而另外创建 Thread Pool 和 queue 来缓存和处理任务。所以其实已经进化成 Proactor 模式,异步模式。
三、多线程(Worker Threads)
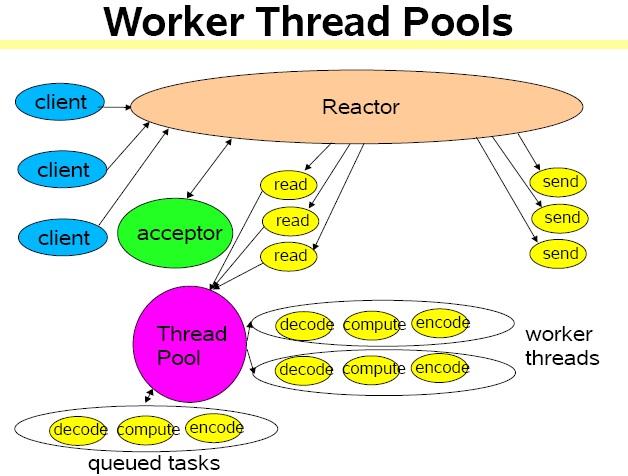
class Handler implements Runnable {
// uses util.concurrent thread pool
static PooledExecutor pool = new PooledExecutor(...);
static final int PROCESSING = 3;
// ...
synchronized void read() { // ...
socket.read(input);
if (inputIsComplete()) {
state = PROCESSING;
pool.execute(new Processer()); //使用线程pool异步执行
}
}
synchronized void processAndHandOff() {
process();
state = SENDING; // or rebind attachment
sk.interest(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); //process完,开始等待write事件
}
class Processer implements Runnable {
public void run() { processAndHandOff(); }
}
}
使用多个 reactor 进程,主 reactor 只负责 accept,然后将接收到的 socketchannel 交给 Thread Pool 去处理。
四、主从(Multiple Reactor Threads)
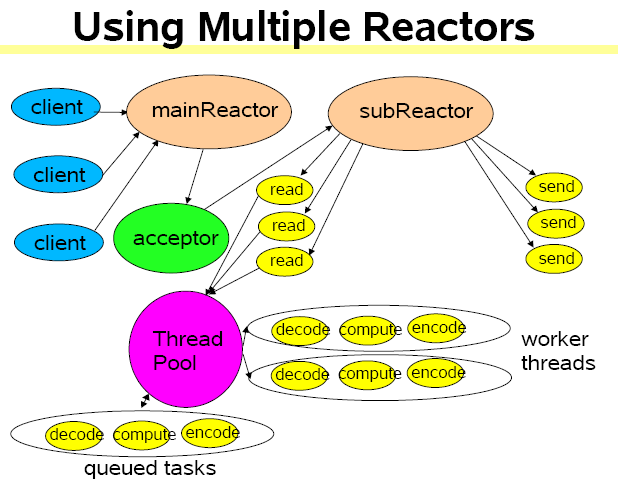
Selector[] selectors; // 一个 selector 代表一个 subReactor
int next = 0;
class Acceptor { // ...
public synchronized void run() { ...
Socket connection = serverSocket.accept(); // 主 selector 负责 accept
if (connection != null)
new Handler(selectors[next], connection); //选个 subReactor 去负责接收到的 connection
if (++next == selectors.length) next = 0;
}
}
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!