Netty 源码 Channel(二)核心类
Netty 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117436.html)
相关文章:
1. Channel 类图
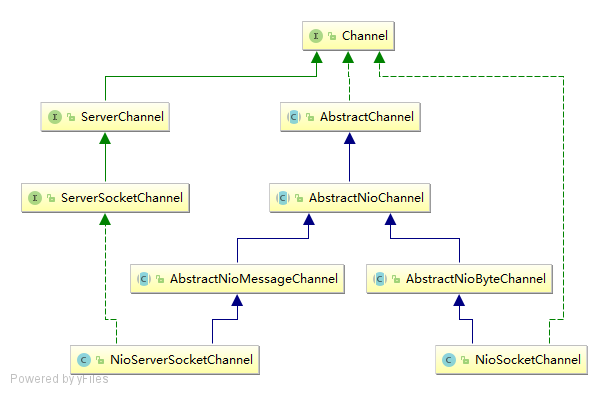
2. AbstractChannel
2.1 几个重要属性
// SocketChannel 的 parent 是 ServerSocketChannel
private final Channel parent;
// 唯一标识
private final ChannelId id;
// Netty 内部使用
private final Unsafe unsafe;
// pipeline
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
// 绑定的线程
private volatile EventLoop eventLoop;
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent, ChannelId id) {
this.parent = parent;
this.id = id;
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
2.2 核心 API
read、write、connect、bind 都委托给了 pipeline 处理。
3. AbstractNioChannel
3.1 几个重要属性
// NIO 底层 Channel
private final SelectableChannel ch;
// 感兴趣的事件
protected final int readInterestOp;
// 绑定的 SelectionKey,当 selectionKey 修改后其它线程可以感知
volatile SelectionKey selectionKey;
3.2 核心 API
(1) doRegister
将 channel 注册到 eventLoop 线程上,此时统一注册的感兴趣的事件类型为 0。
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
// 1. 将 channel 注册到 eventLoop 线程上
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// 2. 对注册失败的 channel,JDK 将在下次 select 将其删除
// 然而此时还没有调用 select,当然也可以调用 selectNow 强删
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// 3. JDK API 描述不会有异常,实际上...
throw e;
}
}
}
}
(2) doBeginRead
doBeginRead 只做了一件事就是注册 channel 感兴趣的事件。此至就可以监听网络事件了。
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
4. AbstractNioByteChannel
AbstractNioByteChannel 中最重要的方法是 doWrite,我们一起来看一下:
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
// 1. spin 是自旋的意思,也就是最多循环的次数
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
// 2. 从 ChannelOutboundBuffer 弹出一条消息
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
// 3. 写完了就要清除半包标记
clearOpWrite();
// 4. 直接返回,不调用 incompleteWrite 方法
return;
}
// 5. 正确处理了一条 msg 消息,循环次数就减 1
writeSpinCount -= doWriteInternal(in, msg);
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
// 6. writeSpinCount < 0 认为有半包需要继续处理
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
为什么要设置最大自旋次数,一次把 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中的所有 msg 处理完了不是更好吗?如果不设置的话,线程会一直尝试进行网络 IO 写操作,此时线程无法处理其它网络 IO 事件,可能导致线程假死。
下面我们看一下 msg 消息是如何处理的,这里以 ByteBuf 消息为例:
private int doWriteInternal(ChannelOutboundBuffer in, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 1. 不可读则丢弃这条消息,继续处理下一条消息
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
// 2. 由具体的子类重写 doWriteBytes 方法,返回处理了多少字节
final int localFlushedAmount = doWriteBytes(buf);
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
// 3. 更新进度
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
// 文件处理,这里略过,类似 ByteBuf
} else if (msg instanceof FileRegion) {
// 省略 ...
} else {
throw new Error();
}
return WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL; // WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL=Integer.MAX_VALUE
}
doWriteBytes 进行消息发送,它是一个抽象方法,由具体的子类实现。如果本次发送的字节数为 0,说明发送的 TCP 缓冲区已满,发生了 ZERO_WINDOW。此时再次发送可能仍是 0,空循环会占用 CPU 资源。因此返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE。直接退出循环,设置半包标识,下次继续处理。
// 没有写完,有两种情况:
// 一是 TCP 缓冲区已满,doWriteBytes 定入 0 个字节,导致 doWriteInternal 返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE,
// 这时设置了半包标识,会自动轮询写事件
// 二是自旋的次数已到,将线程交给其它任务执行,未写完的数据通过 flushTask 继续写
protected final void incompleteWrite(boolean setOpWrite) {
// Did not write completely.
if (setOpWrite) {
setOpWrite();
} else {
// Schedule flush again later so other tasks can be picked up in the meantime
Runnable flushTask = this.flushTask;
if (flushTask == null) {
flushTask = this.flushTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
flush();
}
};
}
eventLoop().execute(flushTask);
}
}
最后我们来看一下半包是如何处理的,可以看到所谓的半包标记其实就是是否取 OP_WRITE 事件。
protected final void clearOpWrite() {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
protected final void setOpWrite() {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
5. AbstractNioMessageChannel
AbstractNioMessageChannel#doWrite 方法和 AbstractNioByteChannel#doWrite 类似,前者可以写 POJO 对象,后者只能写 ByteBuf 和 FileRegion。
6. NioServerSocketChannel
NioServerSocketChannel 通过 doReadMessages 接收客户端的连接请求:
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
if (ch != null) {
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
7. NioSocketChannel
(1) doConnect
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
if (!connected) {
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
连接时有三种情况:
- 直接就连接成功,返回 true
- 如果没有连接成功,就注册 OP_CONNECT 事件进行监听,返回 false
- 发生异常
(2) doWriteBytes
向 ServerSocket 中写入数据。
@Override
protected int doWriteBytes(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception {
final int expectedWrittenBytes = buf.readableBytes();
return buf.readBytes(javaChannel(), expectedWrittenBytes);
}
(3) doReadBytes
从 ServerSocket 中读取数据。
@Override
protected int doReadBytes(ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead(byteBuf.writableBytes());
return byteBuf.writeBytes(javaChannel(), allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead());
}
最底层还是调用 Channel 的 read 方法。
// AbstractByteBuf#writeBytes
public int writeBytes(ScatteringByteChannel in, int length) throws IOException {
ensureWritable(length);
int writtenBytes = setBytes(writerIndex, in, length);
if (writtenBytes > 0) {
writerIndex += writtenBytes;
}
return writtenBytes;
}
// UnpooledHeapByteBuf#setBytes
public int setBytes(int index, ScatteringByteChannel in, int length) throws IOException {
ensureAccessible();
try {
return in.read((ByteBuffer) internalNioBuffer().clear().position(index).limit(index + length));
} catch (ClosedChannelException ignored) {
return -1;
}
}
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!