一.网络拓扑
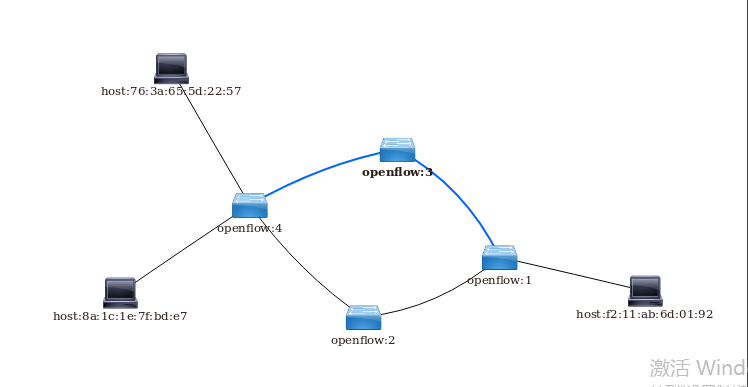
二.拓扑建立
from mininet.topo import Topo
class MyTopo( Topo ):
"Simple topology example."
def __init__( self ):
# Initialize topology
Topo.__init__( self )
s1 = self.addSwitch('s1')
s2 = self.addSwitch('s2')
s3 = self.addSwitch('s3')
s4 = self.addSwitch('s4')
h1 = self.addHost('h1')
h2 = self.addHost('h2')
h3 = self.addHost('h3')
self.addLink(h1,s1)
self.addLink(s1,s2)
self.addLink(s1,s3)
self.addLink(s2,s4)
self.addLink(s3,s4)
self.addLink(h2,s4)
self.addLink(h3,s4)
topos = { 'mytopo': ( lambda: MyTopo() ) }
三.Python代码
import httplib2
import time
class OdlUtil:
url = ''
def __init__(self, host, port):
self.url = 'http://' + host + ':' + str(port)
def install_flow(self, container_name='default',username="admin", password="admin"):
http = httplib2.Http()
http.add_credentials(username, password)
headers = {'Accept': 'application/json'}
flow_name = 'flow_' + str(int(time.time()*1000))
h1h2body1 ='{"flow": [{"id": "1","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type": {"type": "2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination": "10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "2"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "100","cookie": "1","table_id": "0"}]}'
mh1h2body1 ='{"flow": [{"id": "1","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type": {"type": "2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination": "10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "2"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "102","cookie": "1","table_id": "0"}]}'
h1h2body2 ='{"flow": [{"id": "2","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type": {"type": "2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination": "10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "3"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "99","cookie": "2","table_id": "0"}]}'
mh1h2body2 ='{"flow": [{"id": "2","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type": {"type": "2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination": "10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "3"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "102","cookie": "2","table_id": "0"}]}'
headers = {'Content-type': 'application/json'}
num=0
while num < 4 :
response, content = http.request(uri='http://127.0.0.1:8181/restconf/config/opendaylight-inventory:nodes/node/openflow:1/flow-node-inventory:table/0/flow/3', body=mh1h2body1, method='PUT',headers=headers)
time.sleep(0.1)
response, content = http.request(uri='http://127.0.0.1:8181/restconf/config/opendaylight-inventory:nodes/node/openflow:1/flow-node-inventory:table/0/flow/3', body=h1h2body1, method='PUT',headers=headers)
response, content = http.request(uri='http://127.0.0.1:8181/restconf/config/opendaylight-inventory:nodes/node/openflow:1/flow-node-inventory:table/0/flow/2', body=mh1h2body2, method='PUT',headers=headers)
time.sleep(0.1)
response, content = http.request(uri='http://127.0.0.1:8181/restconf/config/opendaylight-inventory:nodes/node/openflow:1/flow-node-inventory:table/0/flow/2', body=h1h2body2, method='PUT',headers=headers)
print(content.decode())
odl = OdlUtil('127.0.0.1','8181')
odl.install_flow()
三.小组分工
负责编写下发流表程序的Python脚本,并使得流表成功下发至流表中。主要考虑用什么样的方法实现负载均衡。
负载均衡实现方法
在规定的时间内,下发新的流表,使得流量流向另一个交换机,从而实现负载均衡。在一定程度上,该算法与轮询算法思想一致。
在该拓扑结构下,则是实现在h1,h2通讯时,他们之间的流量会被s2,s3两个交换机分担,从而达到负载均衡的要求。
在Python脚本中流表:
该流表为h1发送数据向h2时,数据会经过交换机的2端口进行转发,且他的优先级为100
h1h2body1='{"flow": [{"id": "1","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type"{"type":"2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination":"10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "2"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "100","cookie": "2","table_id": "0"}]}'
h1h2body2 ='{"flow": [{"id": "2","match": {"ethernet-match":'
'{"ethernet-type": {"type": "2048"}},'
'"ipv4-source":"10.0.0.1/32","ipv4-destination": "10.0.0.2/32"},'
'"instructions": {"instruction": [{"order": "0",'
'"apply-actions": {"action": [{"output-action": {'
'"output-node-connector": "3"},"order": "0"}]}}]},'
'"priority": "99","cookie": "2","table_id": "0"}]}'
下发流表到S1
response, content = http.request(uri='http://127.0.0.1:8181/restconf/config/opendaylight-inventory:nodes/node/openflow:1/flow-node-inventory:table/0/flow/1', body=mh1h2body1, method='PUT',headers=headers)
利用计时的方式下发流表
time.sleep(0.1)
id不同时,想要运行的流表的优先级应较大,这样才能执行当前流表
id相同时,流表会被覆盖
通过while循环不间断的下发流表,使得s1转发端口不断改变,从而实现负载均衡
最后调用该程序:
odl = OdlUtil('127.0.0.1','8181')
odl.install_flow()
通过ovs查看流表下发成功
四.学习情况
1.初步了解了SDN的含义
软件定义网络(Software Defined Network, SDN ),是Emulex网络一种新型网络创新架构,是网络虚拟化的一种实现方式,其核心技术OpenFlow通过将网络设备控制面与数据面分离开来,从而实现了网络流量的灵活控制,使网络作为管道变得更加智能。
2.mininet的使用
需在管理员权限下使用mininet
我们使用该软件,通过Python脚本的运行,在一台主机上构建所需的网络拓扑结构
from mininet.topo import Topo
class MyTopo( Topo ):
"Simple topology example."
def __init__( self ):
# Initialize topology
Topo.__init__( self )
s = self.addSwitch('s') //创建交换机S
h = self.addHost('h') //创建主机h
self.addLink(h1,s1) //增加交换机和主机之间的链路连接
topos = { 'mytopo': ( lambda: MyTopo() ) }
命令行创建拓扑:
mn --custom --topo mytopo usename.py --controller=remote,ip=127.0.0.1,port=6653
3.floodlight的使用
是一个基于JAVA的软件,通过命令行下发流表
增加ACL规则:
curl -X POST -d '{"src-ip":"10.0.0.1/32","dst-ip":"10.0.0.2/32","action":"deny"}' http://controller_ip:8080/wm/acl/rules/json
显示所有ACL规则:
curl http://controller_ip:8080/wm/acl/rules/json | python -mjson.tool
删除ACL规则:
curl -X DELETE -d '{"ruleid":"1" }' http://controller_ip:8080/wm/acl/rules/json
4.odl的使用
odl控制器,可通过图形化界面下发流表,通过使用API的北向接口下发流表
比起floodlight的使用,更加简便,直观
在此次的最终试验中,使用Python脚本,通过odl控制器下发流表
5.负载均衡
由于目前现有网络的各个核心部分随着业务量的提高,访问量和数据流量的快速增长,其处理能力和计算强度也相应地增大,使得单一的服务器设备根本无法承担。在此情况下,如果扔掉现有设备去做大量的硬件升级,这样将造成现有资源的浪费,而且如果再面临下一次业务量的提升时,这又将导致再一次硬件升级的高额成本投入,甚至性能再卓越的设备也不能满足当前业务量增长的需求。针对此情况而衍生出来的一种廉价有效透明的方法以扩展现有网络设备和服务器的带宽、增加吞吐量、加强网络数据处理能力、提高网络的灵活性和可用性的技术就是负载均衡。
负载均衡算法,可通过下列各算法,对负载均衡进行优化
由于对python是初步接触,下列算法实现采用了JAVA进行编写
1、轮询法
将请求按顺序轮流地分配到后端服务器上,它均衡地对待后端的每一台服务器,而不关心服务器实际的连接数和当前的系统负载。
public class RoundRobin
{
private static Integer pos = 0;
public static String getServer()
{
// 重建一个Map,避免服务器的上下线导致的并发问题
Map<String, Integer> serverMap =
new HashMap<String, Integer>();
serverMap.putAll(IpMap.serverWeightMap);
// 取得Ip地址List
Set<String> keySet = serverMap.keySet();
ArrayList<String> keyList = new ArrayList<String>();
keyList.addAll(keySet);
String server = null;
synchronized (pos)
{
if (pos > keySet.size())
pos = 0;
server = keyList.get(pos);
pos ++;
}
return server;
}
}
2、随机法
通过系统的随机算法,根据后端服务器的列表大小值来随机选取其中的一台服务器进行访问。由概率统计理论可以得知,随着客户端调用服务端的次数增多,其实际效果越来越接近于平均分配调用量到后端的每一台服务器,也就是轮询的结果。
public class Random
{
public static String getServer()
{
// 重建一个Map,避免服务器的上下线导致的并发问题
Map<String, Integer> serverMap =
new HashMap<String, Integer>();
serverMap.putAll(IpMap.serverWeightMap);
// 取得Ip地址List
Set<String> keySet = serverMap.keySet();
ArrayList<String> keyList = new ArrayList<String>();
keyList.addAll(keySet);
java.util.Random random = new java.util.Random();
int randomPos = random.nextInt(keyList.size());
return keyList.get(randomPos);
}
}
3、源地址哈希法
源地址哈希的思想是根据获取客户端的IP地址,通过哈希函数计算得到的一个数值,用该数值对服务器列表的大小进行取模运算,得到的结果便是客服端要访问服务器的序号。采用源地址哈希法进行负载均衡,同一IP地址的客户端,当后端服务器列表不变时,它每次都会映射到同一台后端服务器进行访问。
public class Hash
{
public static String getServer()
{
// 重建一个Map,避免服务器的上下线导致的并发问题
Map<String, Integer> serverMap =
new HashMap<String, Integer>();
serverMap.putAll(IpMap.serverWeightMap);
// 取得Ip地址List
Set<String> keySet = serverMap.keySet();
ArrayList<String> keyList = new ArrayList<String>();
keyList.addAll(keySet);
// 在Web应用中可通过HttpServlet的getRemoteIp方法获取
String remoteIp = "127.0.0.1";
int hashCode = remoteIp.hashCode();
int serverListSize = keyList.size();
int serverPos = hashCode % serverListSize;
return keyList.get(serverPos);
}
}
4、加权轮询法
不同的后端服务器可能机器的配置和当前系统的负载并不相同,因此它们的抗压能力也不相同。给配置高、负载低的机器配置更高的权重,让其处理更多的请;而配置低、负载高的机器,给其分配较低的权重,降低其系统负载,加权轮询能很好地处理这一问题,并将请求顺序且按照权重分配到后端。
public class WeightRoundRobin
{
private static Integer pos;
public static String getServer()
{
// 重建一个Map,避免服务器的上下线导致的并发问题
Map<String, Integer> serverMap =
new HashMap<String, Integer>();
serverMap.putAll(IpMap.serverWeightMap);
// 取得Ip地址List
Set<String> keySet = serverMap.keySet();
Iterator<String> iterator = keySet.iterator();
List<String> serverList = new ArrayList<String>();
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String server = iterator.next();
int weight = serverMap.get(server);
for (int i = 0; i < weight; i++)
serverList.add(server);
}
String server = null;
synchronized (pos)
{
if (pos > keySet.size())
pos = 0;
server = serverList.get(pos);
pos ++;
}
return server;
}
}
5、加权随机法
与加权轮询法一样,加权随机法也根据后端机器的配置,系统的负载分配不同的权重。不同的是,它是按照权重随机请求后端服务器,而非顺序。
public class WeightRandom
{
public static String getServer()
{
// 重建一个Map,避免服务器的上下线导致的并发问题
Map<String, Integer> serverMap =
new HashMap<String, Integer>();
serverMap.putAll(IpMap.serverWeightMap);
// 取得Ip地址List
Set<String> keySet = serverMap.keySet();
Iterator<String> iterator = keySet.iterator();
List<String> serverList = new ArrayList<String>();
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String server = iterator.next();
int weight = serverMap.get(server);
for (int i = 0; i < weight; i++)
serverList.add(server);
}
java.util.Random random = new java.util.Random();
int randomPos = random.nextInt(serverList.size());
return serverList.get(randomPos);
}
}
6、最小连接数法
实现复杂,故在此不提供具体代码实现,只对他的思想进行简介。
最小连接数算法比较灵活和智能,由于后端服务器的配置不尽相同,对于请求的处理有快有慢,它是根据后端服务器当前的连接情况,动态地选取其中当前积压连接数最少的一台服务器来处理当前的请求,尽可能地提高后端服务的利用效率,将负责合理地分流到每一台服务器。
以后端服务器的视角来观察系统的负载,而非请求发起方来观察。最小连接数法便属于此类。