一、底层结构剖析
我们来自顶向下来分析redis内部字典的数据结构
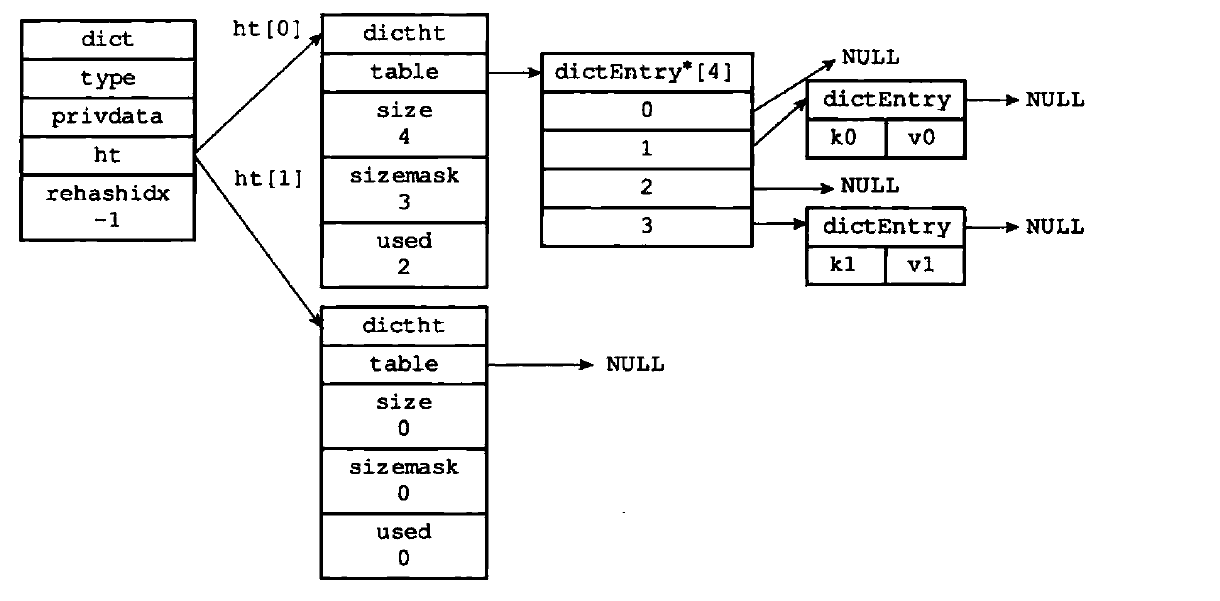
dict
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; //类型函数指针 这个结构体包含了一组处理特定类型的函数
void *privdata; //私有数据 传给特定类型的函数
dictht ht[2]; //哈希表
long rehashidx; //rehash的进度 -1则为没有进行rehash
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
dictht
哈希表,只使用 ht[0] ht[1] 用于 rehash的临时空间
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; //哈希表数组 这是个数组 数组元素为 dictEntry指针 dictEntry保存了键值对
unsigned long size;//table数组的大小
unsigned long sizemask;//用于计算索引 size-1
unsigned long used; //已经分配的键值对数量
} dictht;
计算索引
h = dictHashKey(key) & n.sizemask;
dictEntry
存放键值对的结构体
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; //键
//值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; //下一个节点 因为哈希表用拉链法解决hash碰撞
} dictEntry;
dictType
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);//计算哈希值
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);//复制键
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);//复制值
//比较键
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
//销毁键
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
//销毁值
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
二、拉链法解决hash碰撞
可以参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/biningooginind/p/12522333.html
redis在发生碰撞后,将节点采用 头插法 链接到链表后面,这样就将插入节点的时间复杂度降低到 O(1)
三、关于rehash
为什么要rehash?
键的数量可能会不断改变,增加键值对的话碰撞太多,造成查找效率的底下,如果键值对减少太多,那么空间可能会太大,造成数组空间的浪费。所以应该适当的 rehash ,从新分配空间
何时进行
-
redis会根据 used的值进行rehash,一旦达到了阀值,那么就开始rehash,借助ht[1]来进行
-
在redis创建子进程进行RDB、AOF备份的时候,不会进行rehash
渐进式rehash
为了避免影响主进程处理请求,redis采用 渐进式rehash策略,即在插入或者删除键的时候进行rehash,因此需要rehashidx来表示rehash的进度,
但是这里带来一个问题,渐进式rehash那么如果需要插入或者删除键这么安排呢?
redis在插入的时候不会在旧的ht[0]上操作,并且在删除键的时候需要在ht[0]、ht[1]中都寻找键,这样就保证了ht[0]只减少不增加,直到ht[0]全部rehash到ht[1]
四、重要函数解析
dictAdd
给字典添加键值对
static int dictAdd(dict *ht, void *key, void *val) {
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(ht, key)) == -1) //获取键的hashIndex
return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocates the memory and stores key */
entry = malloc(sizeof(*entry)); //分配键值对空间
entry->next = ht->table[index]; //头插法
ht->table[index] = entry;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
dictSetHashKey(ht, entry, key);
dictSetHashVal(ht, entry, val);
ht->used++;
return DICT_OK;
}