CSharpGL(35)用ViewPort实现类似3DMax那样的把一个场景渲染到4个视口
开始
像下面这样的四个视口的功能是很常用的,所以我花了几天时间在CSharpGL中集成了这个功能。

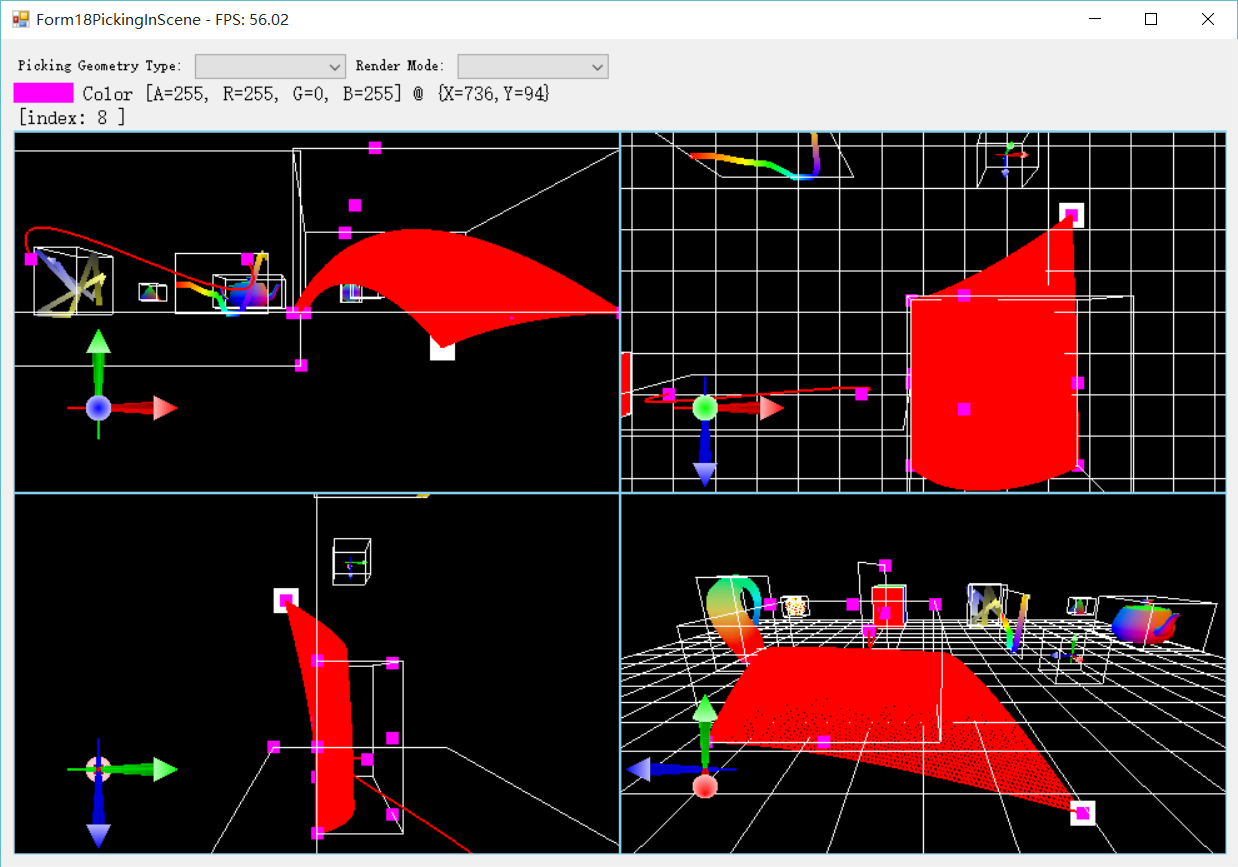
在CSharpGL中的多视口效果如下。效果图是粗糙了些,但是已经实现了拖拽图元时4个视口同步更新的功能,算是一个3D模型编辑器的雏形了。
原理
ViewPort
多视口的任务,是在不同的区域用不同的摄像机渲染同一个场景。这个“区域”我们称其为 ViewPort 。(实际上 ViewPort 是强化版的 glViewport() ,它附带了摄像机等其他成员)
为了渲染多个视口,就应该有一个 ViewPort 列表,保存所有的视口。这就是 Scene 里新增的RootViewPort属性。
1 public class Scene : IDisposable 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// Root object of all viewports to be rendered in the scene. 5 /// </summary> 6 [Category(strScene)] 7 [Description("Root object of all viewports to be rendered in the scene.")] 8 [Editor(typeof(PropertyGridEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))] 9 public ViewPort RootViewPort { get; private set; } 10 // other stuff … 11 }
为了让视口也能像UIRenderer那样使用ILayout接口的树型布局功能,我们也让ViewPort实现ILayout接口。
1 public partial class ViewPort : ILayout<ViewPort> 2 { 3 private const string viewport = "View Port"; 4 5 /// <summary> 6 /// 7 /// </summary> 8 [Category(viewport)] 9 [Description("camera of the view port.")] 10 [Editor(typeof(PropertyGridEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))] 11 public ICamera Camera { get; private set; } 12 13 /// <summary> 14 /// background color. 15 /// </summary> 16 [Category(viewport)] 17 [Description("background color.")] 18 public Color ClearColor { get; set; } 19 20 /// <summary> 21 /// Rectangle area of this view port. 22 /// </summary> 23 [Category(viewport)] 24 [Description("Rectangle area of this view port.")] 25 public Rectangle Rect { get { return new Rectangle(this.location, this.size); } } 26 27 public ViewPort(ICamera camera, AnchorStyles anchor, Padding margin, Size size) 28 { 29 this.Children = new ChildList<ViewPort>(this); 30 31 this.Camera = camera; 32 this.Anchor = anchor; 33 this.Margin = margin; 34 this.Size = size; 35 } 36 }
有了这样的设计,CSharpGL在渲染上述效果图时就有了5个视口。如下图所示,其中根结点上的ViewPort.Visible属性为false,表示这个ViewPort不会参与渲染,即不会显示到最终的窗口上。而此根结点下属的4个子结点,各自代表一个ViewPort,他们分别以TopFrontLeftPerspecitve的角度渲染了一次整个场景,并将渲染结果放置到自己的范围内。
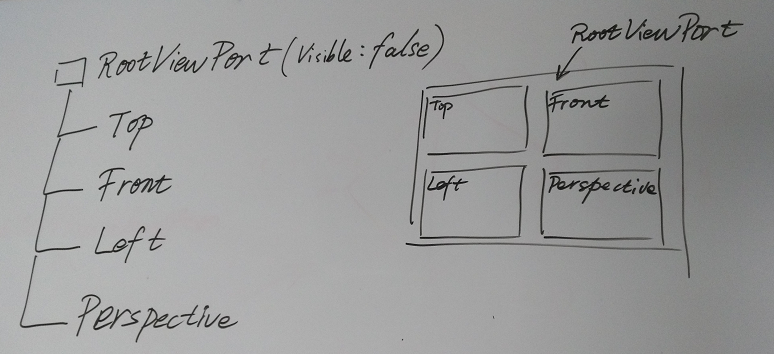
树型结构的ViewPort,其布局就和UIRenderer、Winform控件的布局方式是一样的。你可以像安排控件一样安排ViewPort的Location和Size。因此ViewPort是支持重叠、支持任意多个的。
渲染
有多少个ViewPort,就要渲染多少次。同时,ViewPort修改了glViewport()的值,这个情况也要反映到每个Renderer的渲染过程。
1 public partial class Scene 2 { 3 private object synObj = new object(); 4 5 // Render this scene. 6 public void Render(RenderModes renderMode, 7 bool autoClear = true, 8 GeometryType pickingGeometryType = GeometryType.Point) 9 { 10 lock (this.synObj) 11 { 12 // update view port's location and size. 13 this.rootViewPort.Layout(); 14 // render scene in every view port. 15 this.RenderViewPort(this.rootViewPort, this.Canvas.ClientRectangle, renderMode, autoClear, pickingGeometryType); 16 } 17 } 18 19 // Render scene in every view port. 20 private void RenderViewPort(ViewPort viewPort, Rectangle clientRectangle, RenderModes renderMode, bool autoClear, GeometryType pickingGeometryType) 21 { 22 if (viewPort.Enabled) 23 { 24 // render in this view port. 25 if (viewPort.Visiable) 26 { 27 viewPort.On();// limit rendering area. 28 // render scene in this view port. 29 this.Render(viewPort, clientRectangle, renderMode, autoClear, pickingGeometryType); 30 viewPort.Off();// cancel limitation. 31 } 32 33 // render children viewport. 34 foreach (ViewPort item in viewPort.Children) 35 { 36 this.RenderViewPort(item, clientRectangle, renderMode, autoClear, pickingGeometryType); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 }
坐标系
再次强调一个问题,Winform的坐标系,是以左上角为(0, 0)原点的。OpenGL的窗口坐标系,是以左下角为(0, 0)原点的。
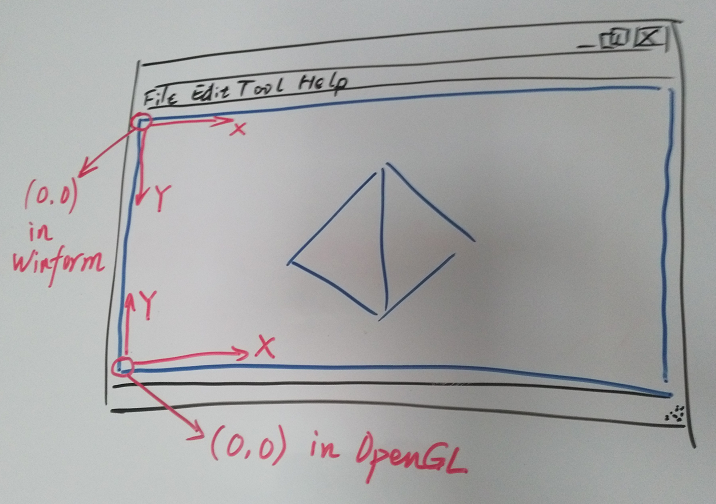
那么一个良好的习惯就是,通过Winform获取的鼠标坐标,应该第一时间转换为OpenGL下的坐标,然后再参与OpenGL的后续计算。等OpenGL部分的计算完毕时,应立即转换回Winform下的坐标。
保持这个好习惯,再遇到鼠标坐标时就不会有便秘的感觉了。
拾取
为了适应新出现的ViewPort功能,原有的Picking功能也要调整了。
之前没有ViewPort树的时候,其本质上是只有一个覆盖整个窗口的'ViewPort'。现在,新出现的ViewPort可能只覆盖窗口的一部分,那么拾取时也要修改为只在这部分内进行。
只在一个ViewPort内拾取
现在有了多个ViewPort。很显然,即使ViewPort之间有重叠,也只应在一个ViewPort内执行Picking操作。因为鼠标不会同时出现在2个地方。即使鼠标位于重叠的部分,也只应在最先(后序优先搜索顺序)接触到的ViewPort上执行Picking操作。
注意,这里先用 int y = clientRectangle.Height - mousePosition.Y - 1; 得到了OpenGL坐标系下的鼠标位置,然后才开始OpenGL方面的计算。
1 public partial class Scene 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// Get geometry at specified <paramref name="mousePosition"/> with specified <paramref name="pickingGeometryType"/>. 5 /// <para>Returns null when <paramref name="mousePosition"/> is out of this scene's area or there's no active(visible and enabled) viewport.</para> 6 /// </summary> 7 /// <param name="mousePosition">mouse position in Windows coordinate system.(Left Up is (0, 0))</param> 8 /// <param name="pickingGeometryType">target's geometry type.</param> 9 /// <returns></returns> 10 public List<Tuple<Point, PickedGeometry>> Pick(Point mousePosition, GeometryType pickingGeometryType) 11 { 12 Rectangle clientRectangle = this.Canvas.ClientRectangle; 13 // if mouse is out of window's area, nothing picked. 14 if (mousePosition.X < 0 || clientRectangle.Width <= mousePosition.X || mousePosition.Y < 0 || clientRectangle.Height <= mousePosition.Y) { return null; } 15 16 int x = mousePosition.X; 17 int y = clientRectangle.Height - mousePosition.Y - 1; 18 // now (x, y) is in OpenGL's window cooridnate system. 19 Point position = new Point(x, y); 20 List<Tuple<Point, PickedGeometry>> allPickedGeometrys = null; 21 var pickingRect = new Rectangle(x, y, 1, 1); 22 foreach (ViewPort viewPort in this.rootViewPort.DFSEnumerateRecursively()) 23 { 24 if (viewPort.Visiable && viewPort.Enabled && viewPort.Contains(position)) 25 { 26 allPickedGeometrys = ColorCodedPicking(viewPort, pickingRect, clientRectangle, pickingGeometryType); 27 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 32 return allPickedGeometrys; 33 } 34 }
Picking的过程
Picking的步骤比较长,分支情况也超级多。这里只大体认识一下即可。
首先,如果depth buffer在鼠标所在的像素点上的深度为1(最深),就说明鼠标没有点中任何东西,因此直接返回即可。
然后,我们在给定的 ViewPort 范围内,用color-coded方式渲染一遍整个场景。
然后,用 glReadPixels() 获取鼠标所在位置的颜色值。
最后,由于这个颜色值是与图元的编号一一对应的,我们就可以通过这个颜色值辨认出它到底是属于哪个Renderer里的哪个图元。

1 /// <summary> 2 /// Pick primitives in specified <paramref name="viewPort"/>. 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="viewPort"></param> 5 /// <param name="pickingRect">rect in OpenGL's window coordinate system.(Left Down is (0, 0)), size).</param> 6 /// <param name="clientRectangle">whole canvas' rectangle.</param> 7 /// <param name="pickingGeometryType"></param> 8 /// <returns></returns> 9 private List<Tuple<Point, PickedGeometry>> ColorCodedPicking(ViewPort viewPort, Rectangle pickingRect, Rectangle clientRectangle, GeometryType pickingGeometryType) 10 { 11 var result = new List<Tuple<Point, PickedGeometry>>(); 12 13 // if depth buffer is valid in specified rect, then maybe something is picked. 14 if (DepthBufferValid(pickingRect)) 15 { 16 lock (this.synObj) 17 { 18 var arg = new RenderEventArgs(RenderModes.ColorCodedPicking, clientRectangle, viewPort, pickingGeometryType); 19 // Render all PickableRenderers for color-coded picking. 20 List<IColorCodedPicking> pickableRendererList = Render4Picking(arg); 21 // Read pixels in specified rect and get the VertexIds they represent. 22 List<Tuple<Point, uint>> stageVertexIdList = ReadPixels(pickingRect); 23 // Get all picked geometrys. 24 foreach (Tuple<Point, uint> tuple in stageVertexIdList) 25 { 26 int x = tuple.Item1.X; 27 int y = tuple.Item1.Y; 28 29 uint stageVertexId = tuple.Item2; 30 PickedGeometry pickedGeometry = GetPickGeometry(arg, 31 x, y, stageVertexId, pickableRendererList); 32 if (pickedGeometry != null) 33 { 34 result.Add(new Tuple<Point, PickedGeometry>(new Point(x, y), pickedGeometry)); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 return result; 41 }
这其中包含了太多的细节,关键详情可参看这6篇介绍(这里,这里,这里,这里,这里,还有这里)
自定义布局方式
虽然ViewPort实现了ILayout接口,但是这难以完成按比例布局的功能。(即:当窗口Size改变时,TopFrontLeftPerspective始终保持各占窗口1/4大小)
这时可以通过自定义布局的方式来实现这个功能。
具体方法就是自定义 ViewPort.BeforeLayout 和 ViewPort.AfterLayout 事件。
例如,对于Top,我们想让它始终保持在窗口的左上角,且占窗口1/4大小。
private void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { // other stuff ... // ‘top’ view port var camera = new Camera( new vec3(0, 0, 15), new vec3(0, 0, 0), new vec3(0, 1, 0), CameraType.Perspecitive, this.glCanvas1.Width, this.glCanvas1.Height); ViewPort viewPort = new ViewPort(camera, AnchorStyles.None, new Padding(), new Size()); viewPort.BeforeLayout += viewPort_BeforeLayout; viewPort.AfterLayout += topViewPort_AfterLayout; this.scene.RootViewPort.Children.Add(viewPort); // other stuff ... } private void viewPort_BeforeLayout(object sender, System.ComponentModel.CancelEventArgs e) { // cancel ILayout's layout action for this view port. e.Cancel = true; } private void topViewPort_AfterLayout(object sender, EventArgs e) { var viewPort = sender as ViewPort; ViewPort parent = viewPort.Parent; viewPort.Location = new Point(0 + 1, parent.Size.Height / 2 + 1); viewPort.Size = new Size(parent.Size.Width / 2 - 2, parent.Size.Height / 2 - 2); }
如果你查看一下实现了布局机制的 ILayoutHelper 的代码,会发现 e.Cancel = true; 这句话取消了 ILayout 对此 ViewPort 的布局操作。(我们要自定义布局操作,因此ILayout原有的布局操作就没有必要实施了。)
1 public static void Layout<T>(this ILayout<T> node) where T : ILayout<T> 2 { 3 ILayout<T> parent = node.Parent; 4 if (parent != null) 5 { 6 bool cancelTreeLayout = false; 7 8 var layoutEvent = node.Self as ILayoutEvent; 9 if (layoutEvent != null) 10 { cancelTreeLayout = layoutEvent.DoBeforeLayout(); } 11 12 if (!cancelTreeLayout) 13 { NonRootNodeLayout(node, parent); } 14 15 if (layoutEvent != null) 16 { layoutEvent.DoAfterLayout(); } 17 } 18 19 foreach (T item in node.Children) 20 { 21 item.Layout(); 22 } 23 24 if (parent != null) 25 { 26 node.ParentLastSize = parent.Size; 27 } 28 }
总结
ViewPort在Scene里是一个树型结构,支持ILayout布局和Before/AfterLayout自定义布局。有一个Visible的ViewPort,场景就要渲染一次。
