一、线程的定义
进程(Process)是Windows系统中的一个基本概念,它包含着一个运行程序所需要的资源。进程之间是相对独立的,一个进程无法访问另一个进程的数据(除非利用分布式计算方式),一个进程运行的失败也不会影响其他进程的运行,Windows系统就是利用进程把工作划分为多个独立的区域的。进程可以理解为一个程序的基本边界。
线程(Thread)是进程中的基本执行单元,在进程入口执行的第一个线程被视为这个进程的主线程。在.NET应用程序中,都是以Main()方法作为入口的,当调用此方法时系统就会自动创建一个主线程。线程主要是由CPU寄存器、调用栈和线程本地存储器(Thread Local Storage,TLS)组成的。CPU寄存器主要记录当前所执行线程的状态,调用栈主要用于维护线程所调用到的内存与数据,TLS主要用于存放线程的状态信息。
多线程,在单CPU系统的一个单位时间( time slice)内,CPU只能运行单个线程,运行顺序取决于线程的优先级别。如果在单位时间内线程未能完成执行,系统就会把线程的状态信息保存到线程的本地存储器(TLS)中,以便下次执行时恢复执行。而多线程只是系统带来的一个假象,它在多个单位时间内进行多个线程的切换。因为切换频密而且单位时间非常短暂,所以多线程可以被视作同时运行。
适当使用多线程能提高系统的性能,比如:在系统请求大容量的数据时使用多线程,把数据输出工作交给异步线程,使主线程保持其稳定性去处理其他问题。但需要注意一点,因为CPU需要花费不少的时间在线程的切换上,所以过多地使用多线程反而会导致性能下降。(用量要适中)
二、线程的基础知识
2.1 System.Threading.Thread类
System.Threadubg.Thread是用于控制线程的基础类,通过Thread可以控制当前医用程序域中线程的创建、挂起、停止、销毁。它包括以下常用公共属性:
属性名称:
CurrentContext: 获取线程正在其中执行的当前上下文
CurrentThread: 获取当前正在运行的线程
ExecutionContext: 获取一个ExecutionContext对象,该对象包含有关当前线程的各种上下文的信息。
IsAlive: 获取一个值,该值指示当前线程的执行状态
IsBackground: 获取或设置一个值,该值指示某个线程是否为后台线程
IsThreadPoolThread: 获取一个值,该值指示线程是否属于托管线程池
ManagedThreadId: 获取当前托管线程的唯一标识符
Name: 获取或设置线程的名称
Priority: 获取或设置一个值,该值指示线程的调度优先级
ThreadState: 获取一个值,该值包含当前线程的状态
2.1.1线程的标识符
ManagedThreadId是确认线程的唯一标识符,程序在大部分情况下都是通过Thread.ManagedThreadId来辨别线程的。而Name是一个可变值,在默认时候,Name为一个空值Null,开发人员可以通过程序设置线程的名字,但这知识一个辅助功能。
2.1.2线程的优先级别
.NET为线程设置Priority属性来定义线程执行的优先级别。里面包含5个选项,其中NORMAL是默认值。除非系统有特殊要求,否则不应该随便设置线程的优先级别。
成员名称
Lowerst: 可以将Thread安排在具有任何其他优先级的线程之后
BelowNormal: 可以将Thread安排在具有Normal优先级的线程之后,在具有Lowest优先级的线程之前
Normal: 默认选择。可以将Thread安排在具有AboveNormal优先级的线程之后,在具有BelowNormal优先级的线程之前
AboveNormal: 可以将Thread安排在具有Highest优先级的线程之后,在具有Normal优先级的线程之前
Highest:可以将Thread安排在具有任何其他优先级的线程之前
2.1.3 线程的状态
通过ThreadState可以检测线程使处于Unstarted、sleeping、running等等状态,它比IsAlive属性能提供更多的特定信息。前面说过,一个应用程序中可能包括多个上下文,而通过CurrentContext可以获取线程当前的上下文,CurrentThread是最常用的一个属性,它是用于获取当前运行的线程。
2.1.4 System.Threading.Thread的方法
Thread中包括了多个方法来控制线程的创建、挂起、停止、销毁,以后来的例子中会经常使用。
方法名称
Abort(): 终止本线程
GetDomain(): 返回当前线程正在其中运行的当前域
GetDomainId(): 返回当前线程正在其中运行的当前域Id
Interrupt(): 中断处于WaitSleepJoin线程状态的线程
Join(): 已重载。阻塞调用线程,直到某个线程终止时为止(让某个线程运行结束再开始执行其他的线程)
Resume(): 继续运行已挂起的线程
Start(): 执行本线程
Suspend(): 挂起当前的线程,如果当前线程属于挂起状态则此不起作用
Sleep(): 把正在运行的线程挂起一段时间
2.1.5 开发实例
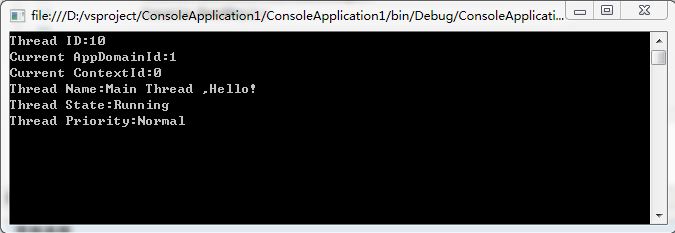
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 namespace ConsoleApplication1 7 { 8 class Program 9 { 10 static void Main(string[] args) 11 { 12 Thread thread = Thread.CurrentThread; 13 thread.Name = "Main Thread ,Hello!"; 14 string threadMessage = string.Format("Thread ID:{0} "+"Current AppDomainId:{1} "+ 15 "Current ContextId:{2} "+"Thread Name:{3} "+ 16 "Thread State:{4} "+"Thread Priority:{5} ",thread.ManagedThreadId,Thread.GetDomainID(),Thread.CurrentContext.ContextI D,thread.Name,thread.ThreadState,thread.Priority); 18 Console.WriteLine(threadMessage); 19 Console.ReadKey(); 20 21 } 22 } 23 }
运行结果:
2.2 System.Threading 命名空间
在System.Threading命名空间内提供多少个方法来构建多线程应用程序,其中ThreadPool与Thread是多线程开发中最常用到的,在.NET中专门设定了一个CLR线程池专门用于管理线程的运行,这个CLR线程池证实通过ThreadPool类来管理。而Thread是管理线程的最直接方式,下面几节将详细介绍有关内容。
| 类 | 说明 |
| AutoResetEvent | 通知正在等待的线程已发生事件。无法继承此类。 |
| ExecutionContext | 管理当前线程的执行上下文。无法继承此类。 |
| Interlocked | 为多个线程共享的变量提供原子操作 |
| Monitor | 提供同步对对象的访问的机制 |
| Mutex | 一个同步基元,也可用于进程间同步 |
| Thread | 创建并控制线程,设置其优先级并获取其状态 |
| ThreadAbortException | 在对Abort方法进行调用时引发的异常。无法继承此类 |
| ThreadPool | 提供一个线程池,该线程也可用于发送工作项、处理异步I/O、代表其他线程等待以及处理计时器 |
| Timeout | 包含用于指定无限长的时间的常数。无法继承此类 |
| Timer | 提供以指定的时间间隔执行方法的机制。无法继承此类 |
| WaitHandle | 封装等待对共享资源的独占访问的操作系统特定的对象 |
2.3 线程的管理方式
通过ThreadStart来创建一个新的线程是最直接的方法,但这样创建出来的线程比较难管理,如果创建过多的线程反而会让系统的性能下降。有见及此,NET为线程管理专门设置了一个CLR线程池,使用CLR线程池系统可以更合理地管理线程的使用。所有请求的服务都能运行与线程池中,当运行结束时线程便会回归到线程池。通过设置,能控制线程池的最大线程数量,在请求超出线程最大值时,线程池能按照操作的优先级基础知识就为大家介绍到这里,下面将消息介绍多线程的开发。
三、以ThreadStart方式实现多线程
3.1 使用ThreadStart委托
这里先以一个例子体现以下多线程带来的好处,首先在Message类中建立一个方法ShowMessage(),里面显示了当前运行线程的Id,并使用Thread.Sleep(int)方法模拟部分工作。在main()中通过ThreadStart委托绑定Message对象的ShowMessage()方法,然后通过Thread.Start()执行异步方法。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class Message { public void ShowMessage1() { string message = string.Format("Async1 threadId is :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.WriteLine(message); for(int n = 0;n < 12;n++) { Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine("The number1 is:"+n.ToString()); } } public void ShowMessage2() { string message = string.Format("Async2 threadId is:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.WriteLine(message); for (int n = 0; n < 12; n++) { Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine("The number2 is:" + n.ToString()); } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args)//主线程 { Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Message message = new Message(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(message.ShowMessage1));//ThreadStart:在线程上执行方法 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(message.ShowMessage2)); thread1.Start();//启动子线程 thread2.Start(); Console.WriteLine("Do something......!"); Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!"); Console.ReadKey();//为了让控制台停住而加,主线程运行到这一句停住,等待用户的输入任意键结束主线程 } } }
得到下面的运行结果
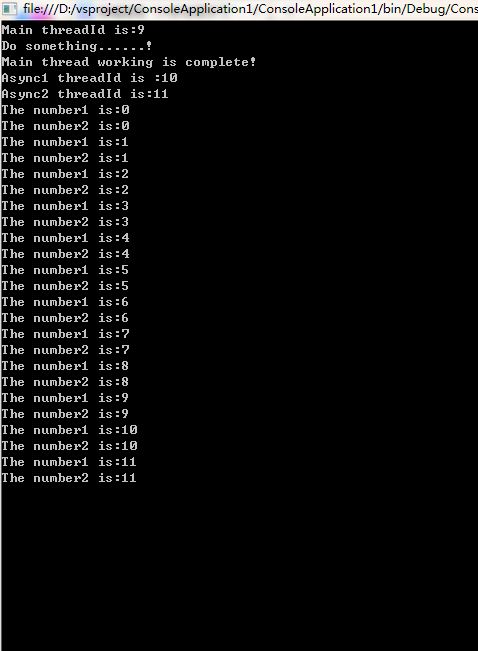
注意运行结果,在调用Thread.Start()方法后,系统以异步方式运行Message.ShowMessage1()和Message.ShowMessage2(), 而主线程的操作是继续执行的,在Message.ShowMessage1()和Message.ShowMessage2()完成前,主线程已经完成所有输出的操作,进入了等待用户输入的状态(主程序最后一句Console.ReadKey()的作用),如果你在两个子线程没结束之前用户按下了任意键,会发现窗口也不会停留,因为由于你的按键主线程已经提早结束了。
多线程的存在,让程序至少看上去不是按顺序执行,仿佛是多个程序在同时进行。
3.2 使用ParameterizedThreadStart委托
ParameterizedThreadStart委托与ThreadStart委托非常相似,但ParameterizedThreadStart委托是面向带参数方法的。注意ParameterizeThreadStart对应方法(放在线程里准备运行的方法)的参数为object,此参数可以为一个值对象,也可以为一个自定义对象。
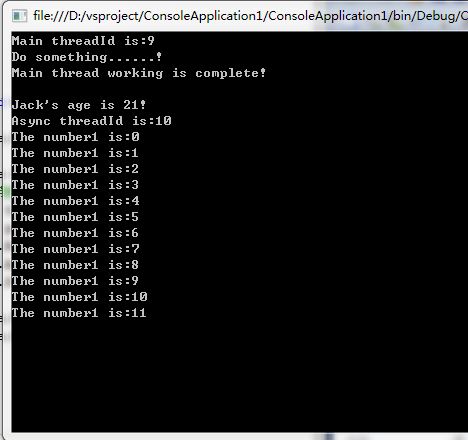
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } } public class Message { public void ShowMessage(object person) { if (person != null) { Person _person = (Person)person; string message = string.Format(" {0}'s age is {1}! Async threadId is:{2}", _person.Name, _person.Age, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.WriteLine(message); } for(int n = 0;n < 12;n++) { Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine("The number1 is:"+n.ToString()); } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args)//主线程 { Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Message message = new Message(); Thread thread = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(message.ShowMessage));//ThreadStart:在线程上执行方法 Person person = new Person(); person.Name = "Jack"; person.Age = 21; thread.Start(person);//启动子线程 Console.WriteLine("Do something......!"); Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!"); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果如下
3.3 前台线程与后台线程
在以上两个例子中主线程最后一句程序是Console.ReadKey(),这样窗口可以在子线程结束后停住,如果两个例子都没有这句程序的话,可以发现系统依然会等待异步线程完成后才会结束。这是因为使用Thread.Start()启动的线程默认为前台线程,而系统必须等待所有前台线程运行结束后,应用程序域才会自动卸载。
在第二节曾将介绍过线程Thread有一个属性IsBacground,通过把此属性设置为true,就可以把线程设置为后台线程!这时应用程序域将在主线程完成时就被卸载,而不会等待异步线程的运行。
3.4 挂起线程
为了等待其他后台线程完成后再结束主线程,就可以使用Thread.Sleep()方法
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 namespace ConsoleApplication1 7 { 8 public class Message 9 { 10 public void ShowMessage() 11 { 12 string message = string.Format(" Async threadId is :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 13 Console.WriteLine(message); 14 for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++) 15 { 16 Thread.Sleep(100); 17 Console.WriteLine("The number is:" + n.ToString()); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 class Program 22 { 23 static void Main(string[] args)//主线程 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 26 Message message = new Message(); 27 Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(message.ShowMessage)); 28 thread.IsBackground = true; 29 thread.Start(); 30 31 Console.WriteLine("Do something ..........!"); 32 Console.WriteLine("Main thread working is complete!"); 33 Console.WriteLine("Main thread sleep!"); 34 Thread.Sleep(5000); 35 } 36 37 } 38 }
运行结果
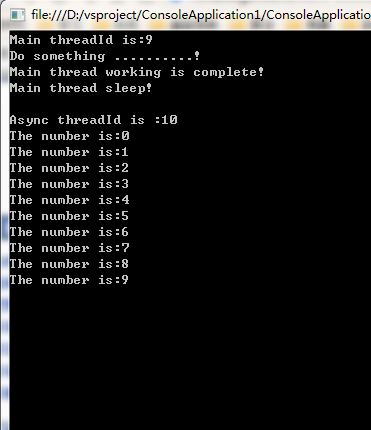
3.5 Suspend与Resume(慎用)
Thread.Suspend()与Thread.Resume()是在Framework1.0就已经存在的老方法了,它们分别可以挂起、恢复线程。但在Framework2.0中就已经明确排斥这两个方法。这是因为一旦某个线程占用了已有的资源,再使用Suspend()使线程长期处于挂起状态,当在其他线程调用这些资源的时候就会引起死锁!所以在没有必要的情况下应该避免使用这两个方法。
3.6 终止线程
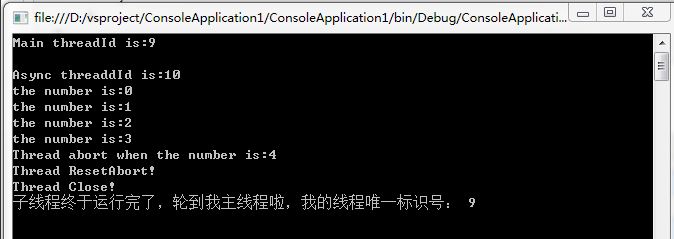
若想终止正在运行的线程,可以使用Abort()方恢复线程的执行,可以在捕获异常后,在catch(ThreadAbortException ex){...}中调用Thread.ResetAbort()取消终止。
而使用Thread.Join()可以保证应用程序域等待异步线程结束后才终止运行。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args)//主线程 { Console.WriteLine("Main threadId is:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(AsyncThread)); thread.IsBackground = true; thread.Start(); thread.Join();//知道thread线程结束再运行别的线程 Console.WriteLine("子线程终于运行完了,轮到我主线程啦,我的线程唯一标识号: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.ReadKey(); } static void AsyncThread() { try { string message = string.Format(" Async threaddId is:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.WriteLine(message); for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++) { if (n >= 4) { //n = 4时,终止线程 Thread.CurrentThread.Abort(n); } Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine("the number is:" + n.ToString()); } } catch (ThreadAbortException ex) { //输出终止线程时n的值 if (ex.ExceptionState != null) Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Thread abort when the number is:{0}",ex.ExceptionState.ToString())); //取消终止,继续执行线程 Thread.ResetAbort(); Console.WriteLine("Thread ResetAbort!"); } //线程结束 Console.WriteLine("Thread Close!"); } } }
运行结果