<span style="font-size:18px;">/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf.cpp
> Author: acvcla
> QQ:
> Mail: acvcla@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2014年11月17日 星期一 23时34分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 3e3 + 10;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define pb push_back
int A[maxn],B[maxn];
std::vector<int>x,y;
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
int ans=0;
while(cin>>n){
x.clear();y.clear();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>A[i];
B[i]=A[i];
}
sort(B,B+n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(A[i]==B[i])continue;
int M=0;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)if(A[j]==B[i]){
M=j;
if(B[j]==A[i]){
swap(A[i],A[j]);
x.pb(i);y.pb(j);
break;
}
}
if(A[i]==B[i])continue;
swap(A[i],A[M]);
x.pb(i);y.pb(M);
}
cout<<x.size()<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<x.size();i++){
cout<<x[i]<<' '<<y[i]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}</span>
The Berland State University is hosting a ballroom dance in celebration of its 100500-th anniversary! n boys and m girls are already busy rehearsing waltz, minuet, polonaise and quadrille moves.
We know that several boy&girl pairs are going to be invited to the ball. However, the partners' dancing skill in each pair must differ by at most one.
For each boy, we know his dancing skills. Similarly, for each girl we know her dancing skills. Write a code that can determine the largest possible number of pairs that can be formed from n boys and m girls.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of boys. The second line contains sequencea1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100), where ai is the i-th boy's dancing skill.
Similarly, the third line contains an integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 100) — the number of girls. The fourth line contains sequence b1, b2, ..., bm (1 ≤ bj ≤ 100), where bj is the j-th girl's dancing skill.
Print a single number — the required maximum possible number of pairs.
4
1 4 6 2
5
5 1 5 7 9
3
4
1 2 3 4
4
10 11 12 13
0
5
1 1 1 1 1
3
1 2 3
2
<span style="font-size:18px;">/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf.cpp
> Author: acvcla
> QQ:
> Mail: acvcla@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2014年11月17日 星期一 23时34分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1e3 + 10;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define pb push_back
int A[maxn],B[maxn];
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,m;
while(cin>>n){
memset(A,0,sizeof A);
memset(B,0,sizeof B);
int x;
rep(i,1,n){
cin>>x;
++A[x];
}
cin>>m;
rep(i,1,m){
cin>>x;
++B[x];
}
int ans=0;
rep(i,1,100){
if(A[i]<=0)continue;
ans+=min(A[i],B[i-1]+B[i]+B[i+1]);
if(A[i]>=B[i-1]+B[i]+B[i+1])B[i-1]=B[i]=B[i+1]=0;
else{
if(B[i-1]>0&&A[i]>0){
int t=B[i-1];
B[i-1]=max(B[i-1]-A[i],0);
A[i]=max(A[i]-t,0);
}
if(B[i]>0&&A[i]>0){
int t=B[i];
B[i]=max(B[i]-A[i],0);
A[i]=max(A[i]-t,0);
}
if(B[i+1]>0&&A[i]>0){
int t=B[i+1];
B[i+1]=max(B[i+1]-A[i],0);
A[i]=max(A[i]-t,0);
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}</span>
<span style="font-size:18px;">/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf.cpp
> Author: acvcla
> QQ:
> Mail: acvcla@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2014年11月17日 星期一 23时34分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define pb push_back
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int m,s;
char ans1[200],ans2[200];
while(cin>>m>>s){
bool ok=true;
int t1=s/9;
for(int i=0;i<150;i++)ans2[i]=ans1[i]='9';
if(s==0&&m==1){
cout<<"0 0"<<endl;
continue;
}
if(!s&&m>1||s>m*9){
cout<<"-1 -1"<<endl;continue;
}
ans2[m]=ans1[m]=0;
int d=s%9;
if(d==0){
if(t1==m){
cout<<ans1<<' '<<ans2<<endl;
continue;
}
ans1[0]='1';
ans1[m-t1]='8';
for(int i=m-t1-1;i>0;i--)ans1[i]='0';
for(int i=t1;i<m;i++)ans2[i]='0';
}else{
if(t1==m-1){
ans1[0]='0'+d;
ans2[m-1]='0'+d;
}else{
ans1[0]='1';
ans1[m-t1-1]='0'+d-1;
for(int i=m-t1-2;i>0;i--)ans1[i]='0';
ans2[t1]='0'+d;
for(int i=t1+1;i<m;i++)ans2[i]='0';
}
}
cout<<ans1<<' '<<ans2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}</span>Tomash keeps wandering off and getting lost while he is walking along the streets of Berland. It's no surprise! In his home town, for any pair of intersections there is exactly one way to walk from one intersection to the other one. The capital of Berland is very different!
Tomash has noticed that even simple cases of ambiguity confuse him. So, when he sees a group of four distinct intersections a, b, c and d, such that there are two paths from a to c — one through b and the other one through d, he calls the group a "damn rhombus". Note that pairs (a, b), (b, c), (a, d), (d, c) should be directly connected by the roads. Schematically, a damn rhombus is shown on the figure below:
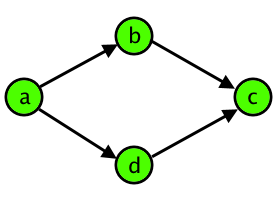
Other roads between any of the intersections don't make the rhombus any more appealing to Tomash, so the four intersections remain a "damn rhombus" for him.
Given that the capital of Berland has n intersections and m roads and all roads are unidirectional and are known in advance, find the number of "damn rhombi" in the city.
When rhombi are compared, the order of intersections b and d doesn't matter.
The first line of the input contains a pair of integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 30000) — the number of intersections and roads, respectively. Next m lines list the roads, one per line. Each of the roads is given by a pair of integers ai, bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n;ai ≠ bi) — the number of the intersection it goes out from and the number of the intersection it leads to. Between a pair of intersections there is at most one road in each of the two directions.
It is not guaranteed that you can get from any intersection to any other one.
Print the required number of "damn rhombi".
5 4 1 2 2 3 1 4 4 3
1
4 12 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 1 2 3 2 4 3 1 3 2 3 4 4 1 4 2 4 3
12
<span style="font-size:18px;">/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf.cpp
> Author: acvcla
> QQ:
> Mail: acvcla@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2014年11月17日 星期一 23时34分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 3e3 + 10;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define pb push_back
int n,m;
std::vector<int> G[maxn];
int d[maxn][maxn];
void dfs(int u,int v,int dist){
if(dist>2)return;
if(dist==2){
++d[u][v];return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<G[v].size();i++){
dfs(u,G[v][i],dist+1);
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
while(cin>>n>>m){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)G[i].clear();
memset(d,0,sizeof d);
int u,v;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>u>>v;
G[u].pb(v);
}
LL ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)dfs(i,i,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(d[i][j]<2||j==i)continue;
//cout<<i<<' '<<j<<' '<<d[i][j]<<endl;
LL t=d[i][j];
ans+=(t*(t-1))/2;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}</span>
直到终于列和所有为2.
详细看代码
<span style="font-size:18px;">/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf.cpp
> Author: acvcla
> QQ:
> Mail: acvcla@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2014年11月17日 星期一 23时34分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 500+10;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define pb push_back
LL d[maxn][maxn],n,m,mod;
bool vis[maxn][maxn];
int col[maxn];
char s[maxn];
LL cn2(LL n){
return n*(n-1)/2;
}
LL dfs(LL x,LL y){//当前还有x列为1,y列为0。到达目标状态的方案种数,之所以是每次选2个是由于每行的和都必须为2
if(x==0&&y==0)return 1;
if(vis[x][y])return d[x][y];
d[x][y]=0;
vis[x][y]=1;
if(x>=2)d[x][y]+=cn2(x)*dfs(x-2,y)%mod;//选出为1的两列让其加上1,此时和为1的为x-2,和为0的为y
if(y>=2)d[x][y]+=cn2(y)*dfs(x+2,y-2)%mod;//选出为0的两列让其加上1,此时和为1的为x+2,和为0的为y-2
if(x>=1&&y>=1)d[x][y]+=x*y*dfs(x,y-1)%mod;//各选一列加上1,此时和为1的为x,和为0的为y-1
return d[x][y]%=mod;
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
while(cin>>n>>m>>mod){
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
memset(col,0,sizeof col);
rep(i,1,m){
cin>>s;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
col[j+1]+=(s[j]=='1');
}
}
LL x=0,y=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(col[i]==1)x++;
if(col[i]==0)y++;
if(col[i]>2){
cout<<0<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<dfs(x,y)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}</span>