Description
gty又虐了一场比赛,被虐的蒟蒻们决定吊打gty。gty见大势不好机智的分出了n个分身,但还是被人多势众的蒟蒻抓住了。蒟蒻们将
n个gty吊在n根绳子上,每根绳子穿过天台的一个洞。这n根绳子有一个公共的绳结x。吊好gty后蒟蒻们发现由于每个gty重力不同,绳
结x在移动。蒟蒻wangxz脑洞大开的决定计算出x最后停留处的坐标,由于他太弱了决定向你求助。
不计摩擦,不计能量损失,由于gty足够矮所以不会掉到地上。
Input
输入第一行为一个正整数n(1<=n<=10000),表示gty的数目。
接下来n行,每行三个整数xi,yi,wi,表示第i个gty的横坐标,纵坐标和重力。
对于20%的数据,gty排列成一条直线。
对于50%的数据,1<=n<=1000。
对于100%的数据,1<=n<=10000,-100000<=xi,yi<=100000
接下来n行,每行三个整数xi,yi,wi,表示第i个gty的横坐标,纵坐标和重力。
对于20%的数据,gty排列成一条直线。
对于50%的数据,1<=n<=1000。
对于100%的数据,1<=n<=10000,-100000<=xi,yi<=100000
Output
输出1行两个浮点数(保留到小数点后3位),表示最终x的横、纵坐标。
Sample Input
3
0 0 1
0 2 1
1 1 1
0 0 1
0 2 1
1 1 1
Sample Output
0.577 1.000
解题思路:
来,我们盗一张Google的图。
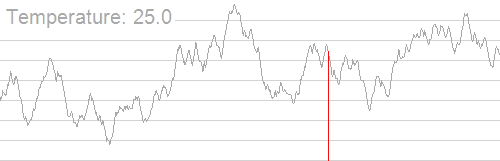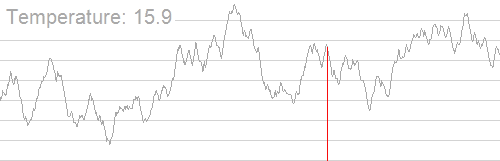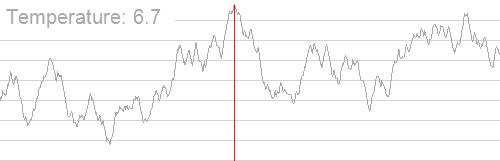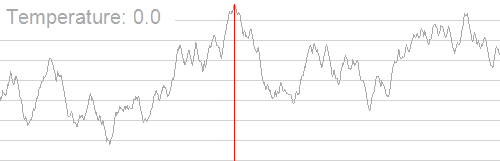
大概就是这样。
模拟退火,就是某位天才在AK了IPHO以后准备AKIOI时发明的 ,模仿物理中晶体缓慢降温时最后稳定的过程。
由于最后排列位置是不确定的,但能量比较低,分子热运动时会趋向于稳定时的位置,但也会有几率走到更不
稳定的位置。
大概就是这样的,只要让步幅与温度正相关就可以像温度降低时热运动变缓了。
这道题就让机械能最小就好了。
代码:
1 #include<ctime> 2 #include<cmath> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 const double delt=0.99; 8 struct hole{ 9 double x,y,w; 10 void Ins(void) 11 { 12 scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&x,&y,&w); 13 return ; 14 } 15 }h[20000]; 16 int n; 17 double ansx,ansy; 18 double ans=1e18; 19 double squ(double x) 20 { 21 return x*x; 22 } 23 double dist(int a,int b) 24 { 25 return sqrt(squ(h[a].x-h[b].x)+squ(h[a].y-h[b].y)); 26 } 27 double Ep(double xx,double yy) 28 { 29 double ans=0.00; 30 h[n+1].x=xx; 31 h[n+1].y=yy; 32 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 33 ans+=dist(i,n+1)*h[i].w; 34 return ans; 35 } 36 void Simulate_Anneal(void) 37 { 38 double Tpt=4600; 39 while(Tpt>1e-15) 40 { 41 double tmpx=ansx+(rand()*2-RAND_MAX)*Tpt; 42 double tmpy=ansy+(rand()*2-RAND_MAX)*Tpt; 43 double tmpans=Ep(tmpx,tmpy); 44 if(tmpans-ans<0) 45 { 46 ansx=tmpx; 47 ansy=tmpy; 48 ans=tmpans; 49 }else if(exp((-tmpans+ans)/Tpt)*RAND_MAX>rand()) 50 { 51 ansx=tmpx; 52 ansy=tmpy; 53 ans=tmpans; 54 } 55 Tpt*=delt; 56 } 57 return ; 58 } 59 int main() 60 { 61 srand(time(NULL)); 62 scanf("%d",&n); 63 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 64 h[i].Ins(); 65 Simulate_Anneal(); 66 printf("%.3lf %.3lf ",ansx,ansy); 67 return 0; 68 }