线性回归是分析一个变量与另外一个或多个变量(自变量)之间,关系强度的方法。
线性回归的标志,如名称所暗示的那样,即自变量与结果变量之间的关系是线性的,也就是说变量关系可以连城一条直线。
模型评估:量化预测的质量
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/model_evaluation.html#model-evaluation
线性回归的 7种 预测质量方法,

1、导包,
# 导包 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression import sklearn.datasets as datasets
2、加载数据集, 糖尿病数据
# 获取数据集 diabetes data = datasets.load_diabetes() data

{'data': array([[ 0.03807591, 0.05068012, 0.06169621, ..., -0.00259226,
0.01990842, -0.01764613],
[-0.00188202, -0.04464164, -0.05147406, ..., -0.03949338,
-0.06832974, -0.09220405],
[ 0.08529891, 0.05068012, 0.04445121, ..., -0.00259226,
0.00286377, -0.02593034],
...,
[ 0.04170844, 0.05068012, -0.01590626, ..., -0.01107952,
-0.04687948, 0.01549073],
[-0.04547248, -0.04464164, 0.03906215, ..., 0.02655962,
0.04452837, -0.02593034],
[-0.04547248, -0.04464164, -0.0730303 , ..., -0.03949338,
-0.00421986, 0.00306441]]),
'target': array([151., 75., 141., 206., 135., 97., 138., 63., 110., 310., 101.,
69., 179., 185., 118., 171., 166., 144., 97., 168., 68., 49.,
68., 245., 184., 202., 137., 85., 131., 283., 129., 59., 341.,
87., 65., 102., 265., 276., 252., 90., 100., 55., 61., 92.,
259., 53., 190., 142., 75., 142., 155., 225., 59., 104., 182.,
128., 52., 37., 170., 170., 61., 144., 52., 128., 71., 163.,
150., 97., 160., 178., 48., 270., 202., 111., 85., 42., 170.,
200., 252., 113., 143., 51., 52., 210., 65., 141., 55., 134.,
42., 111., 98., 164., 48., 96., 90., 162., 150., 279., 92.,
83., 128., 102., 302., 198., 95., 53., 134., 144., 232., 81.,
104., 59., 246., 297., 258., 229., 275., 281., 179., 200., 200.,
173., 180., 84., 121., 161., 99., 109., 115., 268., 274., 158.,
107., 83., 103., 272., 85., 280., 336., 281., 118., 317., 235.,
60., 174., 259., 178., 128., 96., 126., 288., 88., 292., 71.,
197., 186., 25., 84., 96., 195., 53., 217., 172., 131., 214.,
59., 70., 220., 268., 152., 47., 74., 295., 101., 151., 127.,
237., 225., 81., 151., 107., 64., 138., 185., 265., 101., 137.,
143., 141., 79., 292., 178., 91., 116., 86., 122., 72., 129.,
142., 90., 158., 39., 196., 222., 277., 99., 196., 202., 155.,
77., 191., 70., 73., 49., 65., 263., 248., 296., 214., 185.,
78., 93., 252., 150., 77., 208., 77., 108., 160., 53., 220.,
154., 259., 90., 246., 124., 67., 72., 257., 262., 275., 177.,
71., 47., 187., 125., 78., 51., 258., 215., 303., 243., 91.,
150., 310., 153., 346., 63., 89., 50., 39., 103., 308., 116.,
145., 74., 45., 115., 264., 87., 202., 127., 182., 241., 66.,
94., 283., 64., 102., 200., 265., 94., 230., 181., 156., 233.,
60., 219., 80., 68., 332., 248., 84., 200., 55., 85., 89.,
31., 129., 83., 275., 65., 198., 236., 253., 124., 44., 172.,
114., 142., 109., 180., 144., 163., 147., 97., 220., 190., 109.,
191., 122., 230., 242., 248., 249., 192., 131., 237., 78., 135.,
244., 199., 270., 164., 72., 96., 306., 91., 214., 95., 216.,
263., 178., 113., 200., 139., 139., 88., 148., 88., 243., 71.,
77., 109., 272., 60., 54., 221., 90., 311., 281., 182., 321.,
58., 262., 206., 233., 242., 123., 167., 63., 197., 71., 168.,
140., 217., 121., 235., 245., 40., 52., 104., 132., 88., 69.,
219., 72., 201., 110., 51., 277., 63., 118., 69., 273., 258.,
43., 198., 242., 232., 175., 93., 168., 275., 293., 281., 72.,
140., 189., 181., 209., 136., 261., 113., 131., 174., 257., 55.,
84., 42., 146., 212., 233., 91., 111., 152., 120., 67., 310.,
94., 183., 66., 173., 72., 49., 64., 48., 178., 104., 132.,
220., 57.]),
'DESCR': '.. _diabetes_dataset:
Diabetes dataset
----------------
Ten baseline variables, age, sex, body mass index, average blood
pressure, and six blood serum measurements were obtained for each of n =
442 diabetes patients, as well as the response of interest, a
quantitative measure of disease progression one year after baseline.
**Data Set Characteristics:**
:Number of Instances: 442
:Number of Attributes: First 10 columns are numeric predictive values
:Target: Column 11 is a quantitative measure of disease progression one year after baseline
:Attribute Information:
- Age
- Sex
- Body mass index
- Average blood pressure
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
- S5
- S6
Note: Each of these 10 feature variables have been mean centered and scaled by the standard deviation times `n_samples` (i.e. the sum of squares of each column totals 1).
Source URL:
https://www4.stat.ncsu.edu/~boos/var.select/diabetes.html
For more information see:
Bradley Efron, Trevor Hastie, Iain Johnstone and Robert Tibshirani (2004) "Least Angle Regression," Annals of Statistics (with discussion), 407-499.
(https://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/Papers/LARS/LeastAngle_2002.pdf)',
'feature_names': ['age',
'sex',
'bmi',
'bp',
's1',
's2',
's3',
's4',
's5',
's6'],
'data_filename': 'c:\python37\lib\site-packages\sklearn\datasets\data\diabetes_data.csv.gz',
'target_filename': 'c:\python37\lib\site-packages\sklearn\datasets\data\diabetes_target.csv.gz'}
3、将数据分为 训练数据 和 测试数据
# 导包, 将数据分为 训练数据 和 测试数据 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1) display (X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_test.shape)

(397, 10) (397,) (45, 10) (45,)
4、建模
# 使用线性回归算法 训练数据 lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
5、预测数据
# 开始预测数据 lr.predict(X_test)

array([230.00915863, 109.37448796, 135.55277842, 151.10470676, 112.50492861, 60.06173076, 185.98893008, 154.37782567, 226.83758259, 35.04571744, 72.66756812, 58.39584888, 174.04109657, 236.22478163, 140.04573477, 179.59637478, 290.40096377, 232.79655649, 127.57606558, 155.94225585, 233.96170807, 122.18494431, 124.57198973, 97.73726963, 261.60495587, 170.48284605, 128.85673176, 93.16011898, 198.08756371, 179.37427503, 199.42069686, 106.91159532, 114.42691898, 215.81999925, 200.58503886, 168.46631094, 123.85604486, 118.02004664, 189.81321827, 80.30230583, 108.35537981, 80.98007737, 180.839016 , 83.22091387, 117.70861488])
6、查看真实数据
# 查看真实的 结果值, 与上面测试结果 对比 y_test

array([246., 69., 40., 150., 107., 70., 67., 252., 236., 104., 48., 77., 311., 270., 187., 200., 270., 217., 135., 144., 280., 191., 65., 170., 303., 138., 42., 158., 222., 85., 173., 129., 68., 279., 248., 235., 111., 153., 101., 77., 72., 42., 107., 102., 183.])
7、回归评价得分 (R²得分,决定系数)
回归评价7种方法,
# 调用算法, 算出 评价分, 负无穷 到 1 的范围, 1为最好 lr.score(X_test, y_test)

0.5103097598041384
8、代码实现 预测评价(R²得分,决定系数)
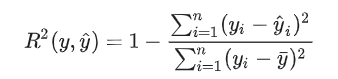

''' The coefficient R^2 is defined as (1 - u/v), where u is the residual sum of squares ((y_true - y_pred) ** 2).sum() and v is the total sum of squares ((y_true - y_true.mean()) ** 2).sum(). '''
y_pred = lr.predict(X_test).round(2) y_true = y_test # 代码实现 评价标准 # 真实结果: y_true # 测试结果: y_pred
u = ((y_true - y_pred)**2).sum()
v = ((y_true - y_true.mean())**2).sum()
score = (1 - u/v)
score
0.5103097598041384
