结构设计
Channel的NIO实现位于io.netty.channel.nio包和io.netty.channel.socket.nio包中,其中io.netty.channel.nio是抽象实现,io.netty.channel.socket.nio最终实现。下面是Channel NIO相关类的派生图:
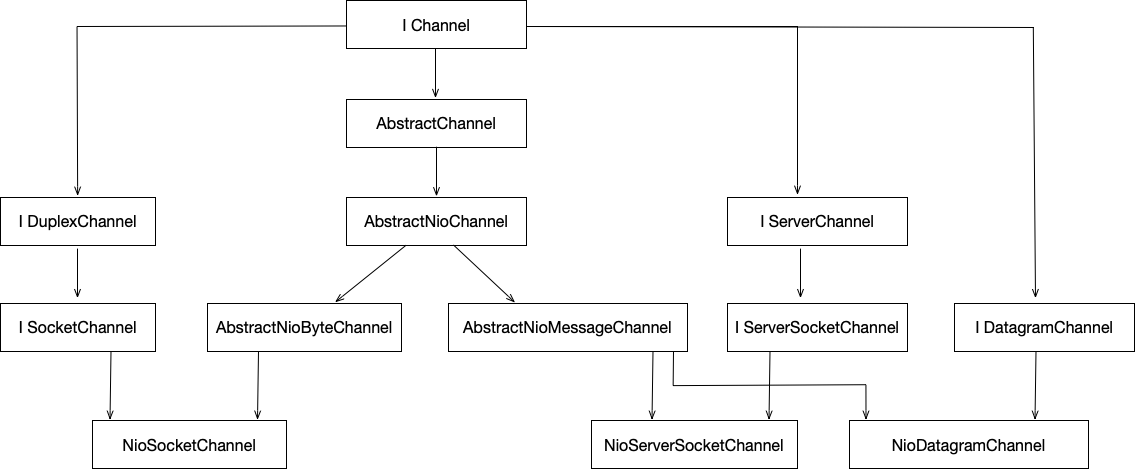
NIO实现最终派生出3个类型NioServerSocketChannel实现了tcp server, NioSocketChannel实现了tcp client, NioDatagramChannel实现了udp socket。
整个NIO实现分为三个层次:
AbstractNioChannel抽象层
对channel进行基本的初始化工作,把channel设置成非阻塞模式。
实现Channel.Unsafe的connect方法框架,提供给了doConnection, doFinishConnect两个抽象方法,把真正的连接操作交给子类实现。
覆盖了AbstractChannel的doRegister,doDeregister方法,正两个方法实现了Channel的selectionKey的注册和注销。
实现AbstractChannel的doClose, 这个方法并没有真正关闭channel动作。
形如doXXX的方法是,AbstractChannel提供的扩展点,在<<netty源码解解析(4.0)-3 Channel的抽象实现>>的末尾,给出了这些扩展点的详细列表。
AbstractNioByteChannel, AbstractNioMessageChannel抽象层
这两个类主要实现read和write的框架,它们的实现大致相同AbstractNioByteChannel读写的是byte array,而AbstractNioMessageChannel读的时候会把byte array转换成结构化的对象,写的时候把结构化对象序列化成byte array。
AbstractNioByteChannel定义了3个抽象方法用来实现真正的读写操作: doReadBytes, doWriteBytes, doWriteFileRegion。
AbstractNioMessageChannel第了两个2个抽象方法用来实现真正的结构化数据类型的读写: doReadMessages, doWriteMessage。
NioServerSocketChannel, NioSocketChannel, NioDatagramChannel最终实现
封装NIO API调用,真正的I/O操操作和socket相关的api调用都在这一层实现。
使用方式
使用过netty的人都知道,netty提供了ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap类帮助用户方便地创建服务器端和客户端应用,但这不是必须的。仅仅使用NioServerSocketChannel, NioSocketChannel, NioDatagramChannel和NioEventLoopGroup就可以用开发tcp的server和client, 及udp应用。
为了能让读者能够更清晰地理解NioEventLoopGroup和Channel直接的关系,下面给出了最原始的使用使用netty框架的代码。
tcp server实现
1 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 2 import io.netty.channel.*; 3 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 4 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 5 6 import java.net.InetSocketAddress; 7 import java.nio.charset.Charset; 8 9 public class TcpServer { 10 private NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 11 12 public static void main(String[] argc){ 13 TcpServer server = new TcpServer(); 14 server.start(); 15 16 while(true){ 17 try{ 18 Thread.sleep(1000); 19 }catch (Exception e){ 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 24 server.stop(); 25 } 26 27 public void start(){ 28 NioServerSocketChannel server = new NioServerSocketChannel(); 29 30 ChannelPipeline pipleline = server.pipeline(); 31 pipleline.addFirst(new ServerHandler()); 32 33 group.register(server).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { 34 @Override 35 public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { 36 server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9001)); 37 System.out.println("server listen add:"+9001); 38 } 39 }); 40 } 41 public void stop(){ 42 group.shutdownGracefully(); 43 } 44 45 private class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{ 46 47 @Override 48 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ 49 Channel child = (Channel)msg; 50 51 child.pipeline().addLast(new ChildHandler()); 52 53 group.register(child); 54 55 } 56 } 57 58 private class ChildHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{ 59 60 @Override 61 public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 62 System.out.println("connected"); 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 67 System.out.println("closed"); 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ 72 Channel chnl = ctx.channel(); 73 ByteBuf data = (ByteBuf)msg; 74 75 System.out.println("recv: "+data.toString(Charset.forName("utf-8"))); 76 chnl.write(msg); 77 } 78 79 @Override 80 public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 81 ctx.channel().flush(); 82 } 83 84 } 85 }
一个channel创建之后,首先要做的事就是向pipleline中添加handler,然后才是把它注册到NioEventLoopGroup中(第31,33行)。这个顺序不能错,否则,handler的handlerAdded,channelRegistered和channelActive将不会被调用。当NioServerSocketChannel收到一个连接时,ServerHandler的的channelRead方法将会被调用,的新建好的连接当成参数传递进来,第49-53行是对新连接的初始化代码。
tcp client实现
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class TcpClient { public static void main(String[] args){ NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); NioSocketChannel client = new NioSocketChannel(); client.pipeline().addLast(new ClientInboundHandler()); group.register(client); client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(9001)); try{ Thread.sleep(3000); }catch (Exception e){ } group.shutdownGracefully(); } private static class ClientInboundHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{ @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("connected"); Channel chnl = ctx.channel(); ByteBuf buf = chnl.alloc().buffer(); buf.writeBytes( "this is test".getBytes()); chnl.writeAndFlush(buf); } @Override public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("closed"); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ ByteBuf data = (ByteBuf)msg; System.out.println("recv: "+data.toString(Charset.forName("utf-8"))); ctx.channel().close(); } } }
client的实现比server实现相对简单,添加handler,register顺序和server一致。只有把一个channel注册到gruop中之后才能调用它的方法,应为channel的大多数方法都需要通过pipleline调用,而pipleline需要在eventLoop中执行。
udp没有server和client的区别,这里为了使代码更加清晰,把server和client代码区分开来。
udp server
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.DatagramPacket; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioDatagramChannel; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class UdpServer { public static void main(String[] args){ NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); NioDatagramChannel chnl = new NioDatagramChannel(); chnl.pipeline().addLast(new UdpHandler()); group.register(chnl).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { chnl.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9002)); System.out.println("udp bind at:"+9002); } }); while(true){ try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (Exception e){ break; } } group.shutdownGracefully(); } private static class UdpHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.print("udp channel active"); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ Channel chnl = ctx.channel(); DatagramPacket pkg = (DatagramPacket)msg; ByteBuf content = pkg.content(); InetSocketAddress from = pkg.sender(); System.out.println("recv: "+content.toString(Charset.forName("utf-8"))+" from:"+from.toString()); pkg = new DatagramPacket(content, from); chnl.write(pkg); } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.channel().flush(); } } }
udp client
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.DatagramPacket; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioDatagramChannel; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class UdpClient { public static void main(String[] args){ NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); NioDatagramChannel chnl = new NioDatagramChannel(); chnl.pipeline().addLast(new UdpHandler()); group.register(chnl).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { chnl.bind(new InetSocketAddress(0)); } }); try{ Thread.sleep(3000); }catch (Exception e){ } group.shutdownGracefully(); } private static class UdpHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.print("udp channel active"); Channel chnl = ctx.channel(); ByteBuf content = chnl.alloc().buffer(); content.writeBytes("udp message".getBytes()); chnl.writeAndFlush(new DatagramPacket(content, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9002))); System.out.println("send message"); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ DatagramPacket pkg = (DatagramPacket)msg; ByteBuf content = pkg.content(); InetSocketAddress from = pkg.sender(); System.out.println("recv: "+content.toString(Charset.forName("utf-8"))+" from:"+from.toString()); } } }
NioDatagramChannel和NioSocketChannel的初始化过程大致相同。它们的不同点是,NioSocketChannel在connect之后处于active状态,NioDatagramChannel是在bind之后处于才处于active状态。