合成模式:有时又叫做部分-整体模式(Part-Whole)。合成模式将对象组织到树结构中,可以用来描述整体与部分的关系。合成模式可以使客户端将单纯元素与复合元素同等看待。
合成模式分为安全式和透明式
安全式合成模式类图:
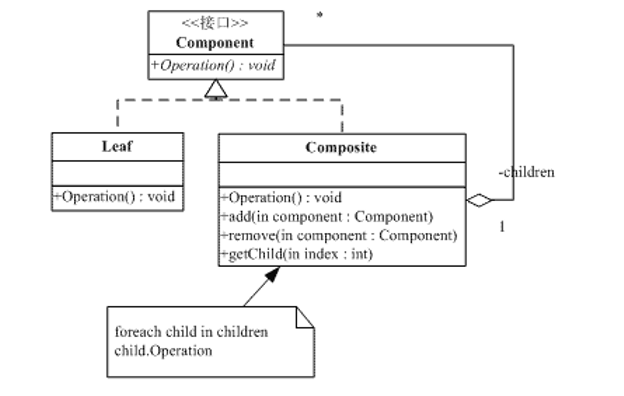
抽象构件(Component)角色:这是一个抽象角色,它给参加组合的对象定义出公共的接口及其默认行为,可以用来管理所有的子对象。在安全式的合成模式里,构件角色并不是定义出管理子对象的方法,这一定义由树枝构件对象给出。
树叶构件(Leaf)角色:树叶对象是没有下级子对象的对 象,定义出参加组合的原始对象的行为。
树枝构件(Composite)角色:代表参加组合的有下级子对象的对象。树枝对象给出所有的管理子对象的方法,如 add()、remove()、getChild()等。
示例代码:

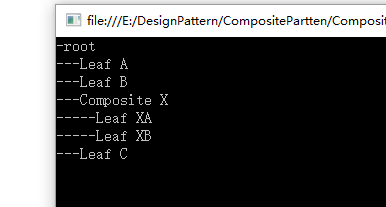
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Composite root = new Composite("root"); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf A")); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf B")); Composite comp = new Composite("Composite X"); comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XA")); comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XB")); root.Add(comp); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf C")); Leaf Leaf1 = new Leaf("Leaf D"); root.Add(Leaf1); root.Remove(Leaf1); root.Display(1); Console.ReadKey(); } } public abstract class Component { protected string name; public Component(string name) { this.name = name; } public abstract void Display(int depth); } public class Composite : Component { private ArrayList children = new ArrayList(); public Composite(string name) : base(name) { } public void Add(Component component) { children.Add(component); } public void Remove(Component component) { children.Remove(component); } public override void Display(int depth) { Console.WriteLine(new string('-', depth) + name); foreach (Component item in children) { item.Display(depth + 2); } } } class Leaf : Component { public Leaf(string name) : base(name) { } public override void Display(int depth) { Console.WriteLine(new String('-', depth) + name); } }
运行结果:
透明式合成模式类图:
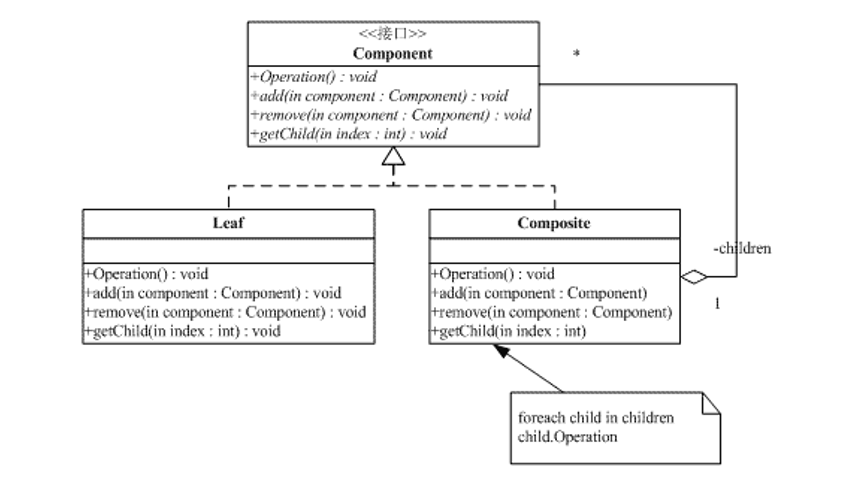
透明式的合成模式要求所有的具体构件类,不论树枝构件还是树叶构件,均符合一个固定的接口。
抽象构件(Component)角色:这是一个抽象角色,它给参加组合的对象规定一个接口,规范共有的接口及默认行为。
树叶构件(Leaf)角色:代表参加组合的树叶对象,定义 出参加组合的原始对象的行为。树叶类会给出 add()、 remove()以及 getChild()之类的用来管理子类对 对象的方法的平庸实现。
树枝构件(Composite)角色:代表参加组合的有子对 象的对象,定义出这样的对象的行为。
示例代码:

class CompositePartten2 { public static void Main(string[] args) { Composite root = new Composite("rood"); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf A")); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf b")); Composite comp = new Composite("Composite X"); comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XA")); comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XB")); root.Add(comp); root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf C")); // Add and remove a leaf Leaf l = new Leaf("Leaf D"); root.Add(l); root.Remove(l); // Recursively display nodes root.Display(1); Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class Component { protected string name; public Component(string name) { this.name = name; } public abstract void Add(Component c); public abstract void Remove(Component c); public abstract void Display(int c); } class Composite : Component { private ArrayList children = new ArrayList(); public Composite(string name) : base(name) { } public override void Add(Component c) { children.Add(c); } public override void Remove(Component c) { children.Remove(c); } public override void Display(int depth) { Console.WriteLine(new String('-', depth) + name); foreach (Component item in children) { item.Display(depth + 2); } } } class Leaf : Component { public Leaf(string name) : base(name) { } public override void Add(Component c) { Console.WriteLine("Connot add to leaf"); } public override void Remove(Component c) { Console.WriteLine("Connot remove from a leaf"); } public override void Display(int c) { Console.WriteLine(new String('-', c) + name); } }
运行结果:

使用时注意问题:
1、明显的给出父对象的引用。在子对象里面给出父对象的引用,可以很容易的遍历所有父对象。有了这个引用,可以方便的应用责任链模式。
2、在通常的系统里,可以使用享元模式实现构件的共享,但是由于合成模式的对象经常要有对父对象的引用,因此共享不容易实现。
3、有时候系统需要遍历一个树枝结构的子构件很多次,这 时候 可以考虑把遍历子构件的结果暂时存储在父构件里面作为缓存。
4、关于使用什么数据类型来存储子对象的问题,在示意性的 代码中使用了 ArrayList,在实际系统中可以使用其它聚 集或数组等。
5、客户端尽量不要直接调用树叶类中的方法,而是借助其父 类(Component)的多态性完成调用,这样可以增加代 码的复用性
