You are given n magical numbers a1, a2, ..., an, such that the length of each of these numbers is 20 digits.
You can move from the ith number to the jth number, if the number of common digits between ai and aj is exactly 17 digits.
The number of common digits between two numbers x and y is computed is follow:
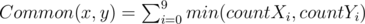 .
.Where countXi is the frequency of the ith digit in the number x, and countYi is the frequency of the ith digit in the number y.
You are given two integers s and e, your task is to find the minimum numbers of moves you need to do, in order to finish at number aestarting from number as.
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 250), where T is the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains three integers n, s, and e (1 ≤ n ≤ 250) (1 ≤ s, e ≤ n), where n is the number of magical numbers, s is the index of the number to start from it, and e is the index of the number to finish at it.
Then n lines follow, giving the magical numbers. All numbers consisting of digits, and with length of 20 digits. Leading zeros are allowed.
For each test case, print a single line containing the minimum numbers of moves you need to do, in order to finish at number ae starting from number as. If there is no answer, print -1.
1 5 1 5 11111191111191111911 11181111111111818111 11811171817171181111 11111116161111611181 11751717818314111118
3
In the first test case, you can move from a1 to a2, from a2 to a3, and from a3 to a5. So, the minimum number of moves is 3 moves.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 255;
int n;
int e[maxn][maxn];
const int inf = 99999999;
void initial() {
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i < maxn; ++i) {
for (j = 1; j < maxn; ++j) {
if (i == j) {
e[i][j] = 0;
}
else {
e[i][j] = inf;
}
}
}
}
/**
*floyd算法
*/
void floyd() {
int i, j, k;
for (k = 1; k <= n; ++k) {//遍历所有的中间点
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {//遍历所有的起点
for (j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {//遍历所有的终点
if (e[i][j] > e[i][k] + e[k][j]) {//如果当前i-->j的距离大于i-->k--->j的距离之和
e[i][j] = e[i][k] + e[k][j];//更新从i--->j的最短路径
}
}
}
}
}
int num[maxn][12];
char s[25];
void init(int i)
{
for(int k=0;k<20;k++)
num[i][s[k]-'0']++;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int T,x,y,i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
initial();
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&x,&y);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",&s);
init(i);
}
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
{
int com=0;
for(k=0;k<=9;k++)
{
com+=min(num[i][k],num[j][k]);
}
if(com==17)
{//加边
e[i][j] = 1;
e[j][i] = 1;
// cout<<i<<" "<<j<<endl;
}
}
floyd();
if(e[x][y]==inf)
printf("-1
");
else
printf("%d
",e[x][y]);
//通过x,y来计算最短路径
}
}