一、SpringBoot全局配置文件
SpringBoot两个全局配置文件,application.properties和application.yml

例如端口号配置
(1)application.properties文件

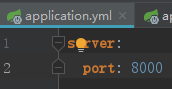
(2)application.yml文件格式
二、yaml文件格式语法
1.大小写敏感
2.属性: 值 之间必须有空格
3.值如果是字符串 默认不用加引号。加单引号转义字符功能失效原样输出,加双引号转义字符有转义功能,
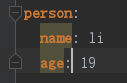
4.对象
(1)
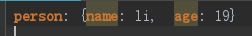
(2)或者
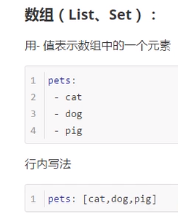
5.
三、调用yaml
1.pom.xml添加
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
2.

package com.example.demo.bean; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String username) { this.name = username; } }
单元测试
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.bean.Person; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class DemoApplicationTests { @Autowired // Person person; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(person.getName()); } }
测试文件运行

四、application.properties配置
书写方式
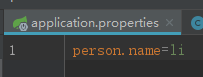
运行同理
注意如果是有中文
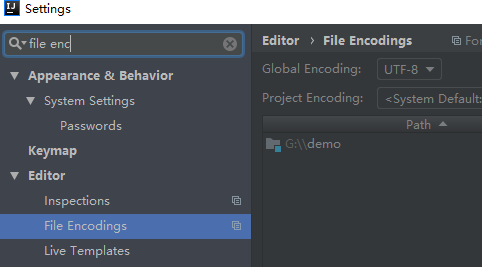
properties文件 需要转成ascii

六、用value注解方式单个读取配置文件


七、 加载非全局配置文件
创建一个
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"}) public class Person { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String username) { this.name = username; } }
八、导入Spring 配置文件
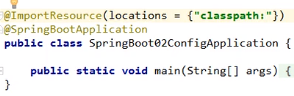
九、占位符
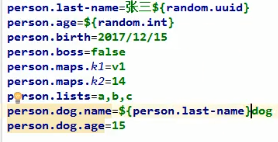
十、激活指定profile
快速切换开发、测试、生产的配置环境
1. properties的激活

一个开发环境,一个生产环境的配置文件
在application.properties 中激活开发环境的配置
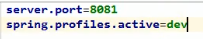
2.yml的激活
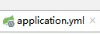
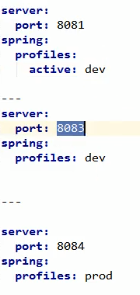
3.命令行方式激活

4.虚拟机参数

十一、配置顺序
1.

2.外部加载配置
