题记
我们为什么需要一个爬虫框架?一个爬虫框架能帮我们做什么事情,减轻我们什么样的一些工作,我们重新梳理爬虫到底是做什么的,哪些工作是重复的工作,我们可以用框架来解决的。
一个简单的爬虫,从一个url开始,从开始的网页里面解析到所有可能的链接,通过这些链接不断的递归,抓取到全网的网页。
在这个过程中,
-
需要考虑抓取的url重复问题,在不断扩张后的网页中,可能包含在我们已经抓取的网页地址,而这些地址我们是不希望他在重新抓取一遍。
-
获取网页模块,一个好的获取网页模块,会影响到这个爬虫的质量,而这一部分可以单独出来,重复使用。
-
抓取的网页后,需要进行对网页进行清洗,得到我们需要的信息。
-
得到了我们需要的信息以后,可能需要把它保存在文件中或者是数据库中等等。
-
有些特定的需求,项目本身对某些网页并不感兴趣,爬虫可以进行对爬取的链接进行过滤。
这就是scrapy 爬虫可以为我们做的事情。
安装scrapy
scrapy是第三方库,安装的时候可以是用pip,如下:
pip install scrapy
创建一个一个项目
执行如下命令创建一个Scrapy项目
scrapy startproject scrapy_cnblogs
创建之后查看项目的目录结构如下:
scrapy_cnblogs
├── botcnblogs
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── items.py #用于定义抓取内容的实体
│ ├── pipelines.py #处理抓取的item的管道
│ ├── settings.py #爬虫需要的配置参数在这里
│ └── spiders
│ └── __init__.py
└── scrapy.cfg #项目的配置文件,可以不去理会,默认即可
对照框架的好处,来理解各个文件的用途。
其中scrapy.cfg所在的目录为项目的根目录,此文件是项目的配置文件,项目建立后,此文件的内容可以不用理会。其内容如下:
[settings]
default = botcnblogs.settings
[deploy]
#url = http://localhost:6800/
project = botcnblogs
在items.py文件里定义在抓取网页内容中抽象出来的数据结构的定义,由于这里需要博客名称、发布日期、阅读量和评论量这四个字段,定义的Item结构如下:
from scrapy import Item,Field #引入Item、Field
class BotcnblogsItem(Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
title = Field() #标题
publishDate = Field() #发布日期
readCount = Field() #阅读量
commentCount = Field() #评论数<br><br>
在pipelines.py里对爬虫抓取到的信息(这里的信息是已经组织好的上面定义的Item对象)进行处理,官方介绍的典型的应用场景为:
-
清理HTML数据
-
验证爬取的数据(检查item包含某些字段)
-
查重(并丢弃)
-
将爬取结果保存到数据库中
它的定义也很简单,只需要实现process_item方法即可,此方法有两个参数,一个是item,即要处理的Item对象,另一个参数是spider,即爬虫。
另外还有open_spider和close_spider两个方法,分别是在爬虫启动和结束时的回调方法。
本例中处理很简单,只是将接收的Item对象写到一个json文件中,在__init__方法中以“w+”的方式打开或创建一个item.json的文件,然后把对象反序列化为字符串,写入到item.json文件中。代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
class BotcnblogsPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
self.file = open("item.json", "w+")
def process_item(self, item, spider):
record = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False)+"
" #此处如果有中文的话,要加上ensure_ascii=False参数,否则可能出现乱码
self.file.write(record)
return item
def open_spider(self, spider):
pass
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.file.close()
setting.py是爬虫的配置文件,配置爬虫的一些配置信息,这里用到的就是设置pipelines的ITEM_PIPELINES参数,此参数配置项目中启用的pipeline及其执行顺序,以字典的形式存在,{“pipeline”:执行顺序整数}
此例中的配置如下:
SPIDER_MODULES = ['botcnblogs.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'botcnblogs.spiders'
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'botcnblogs.pipelines.BotcnblogsPipeline': 1,
}
准备工作都做好了,爬虫呢,爬虫在哪里实现呢,我们看到项目中有个spiders目录,里面只有一个init.py文件,没错,爬虫文件需要自己创建,就在这个目录下,这里创建一个botspider.py的文件,对网页进行解析的工作就要在这里实现了,此例中定义的爬虫类继承自CrawlSpider类。
定义一个Spider需要如下几个变量和方法实现:
name:定义spider名字,这个名字应该是唯一的,在执行这个爬虫程序的时候,需要用到这个名字。
allowed_domains:允许爬取的域名列表,例如现在要爬取博客园,这里要写成cnblogs.com
start_urls:爬虫最开始爬的入口地址列表。
rules:如果要爬取的页面不是单独一个或者几个页面,而是具有一定的规则可循的,例如爬取的博客有连续多页,就可以在这里设置,如果定义了rules,则需要自己定义爬虫规则(以正则表达式的方式),而且需要自定义回调函数。
代码说话:
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'linuxfengzheng'
from scrapy.spiders import Spider, Rule
from scrapy.selector import Selector
from botcnblogs.items import BotcnblogsItem
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
import re
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider
class botspider(CrawlSpider):
name = "cnblogsSpider" #设置爬虫名称
allowed_domains = ["cnblogs.com"] #设置允许的域名
start_urls = [
"http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/default.html?page=3", #设置开始爬取页面
]
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('fengzheng/default.html?page=([d]+)', ),),callback='parse_item',follow=True),
) #制定规则
def parse_item(self, response):
sel = response.selector
posts = sel.xpath('//div[@id="mainContent"]/div/div[@class="day"]')
items = []
for p in posts:
#content = p.extract()
#self.file.write(content.encode("utf-8"))
item = BotcnblogsItem()
publishDate = p.xpath('div[@class="dayTitle"]/a/text()').extract_first()
item["publishDate"] = (publishDate is not None and [publishDate.encode("utf-8")] or [""])[0]
#self.file.write(title.encode("utf-8"))
title = p.xpath('div[@class="postTitle"]/a/text()').extract_first()
item["title"] = (title is not None and [title.encode("utf-8")] or [""])[0]
#re_first("posted @ 2015-11-03 10:32 风的姿态 阅读(d+")
readcount = p.xpath('div[@class="postDesc"]/text()').re_first(u"阅读(d+)")
regReadCount = re.search(r"d+", readcount)
if regReadCount is not None:
readcount = regReadCount.group()
item["readCount"] = (readcount is not None and [readcount.encode("utf-8")] or [0])[0]
commentcount = p.xpath('div[@class="postDesc"]/text()').re_first(u"评论(d+)")
regCommentCount = re.search(r"d+", commentcount)
if regCommentCount is not None:
commentcount = regCommentCount.group()
item["commentCount"] = (commentcount is not None and [commentcount.encode("utf-8")] or [0])[0]
items.append(item)
return items
#self.file.close()
爬虫思路:
首先进入到我的博客页面http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/,这是我的博客首页,以列表形式显示已经发布的博文,这是第一页,点击页面下面的下一页按钮,进入第二页,页面地址为http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/default.html?page=2,由此看出网站以page作为参数来表示页数,这样看来爬虫的规则就很简单了, fengzheng/default.html?page=([d]+),这个就是爬虫的规则,爬取default.html页面,page参数为数字的页面,这样无论有多少页都可以遍历到。当然,如果页面数量很少可以在start_urls列表中,将要爬取的页面都列出来,但是这样当博文数量增多就会出现问题,如下:
start_urls = [
"http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/default.html?page=1",
"http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/default.html?page=2",
"http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/default.html?page=3",
]
当爬取的网页具有规则定义的情况下,要继承CrawlSpider爬虫类,使用Spider就不行了,在规则定义(rules)时,如果要对爬取的网页进行处理,而不是简单的需要Url,这时,需要定义一个回调函数,在爬取到符合条件的网页时调用,并且设置follow=Ture,定义如下:
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('fengzheng/default.html?page=([d]+)', ),),callback='parse_item',follow=True),
)
回调函数名称为parse_item,在parse_item方法中,就是真正要分析网页html,获取需要的内容的时候了。观察页面,查看需要的信息在什么位置,如图:
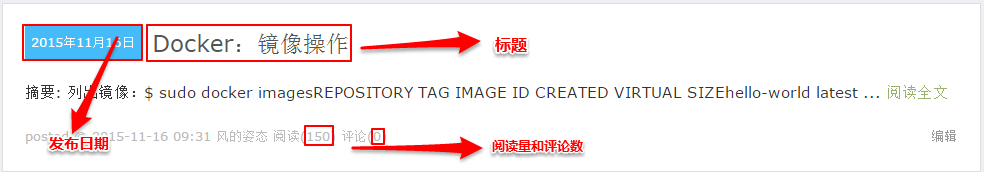
之后,分析网页源码,分析出xpath
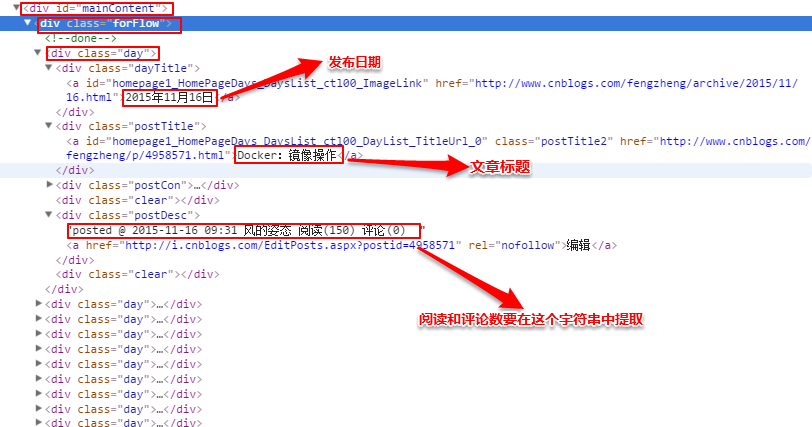
用如下代码找到所有的class为day的div,每一个就是一个博文区域:
posts = sel.xpath('//div[@id="mainContent"]/div/div[@class="day"]')
之后遍历这个集合,获取所需内容,其中注意一下几点:
-
因为有中文内容,要对获取的内容进行encode("utf-8")编码
-
由于评论数和阅读量混在一起,要对那个字符串再进行正则表达式提取
至此,简单的爬虫已经完成,接下来要运行这个爬虫,cd进入到爬虫项目所在的目录,执行以下命令:
scrapy crawl cnblogsSpider
会输出爬取过程信息

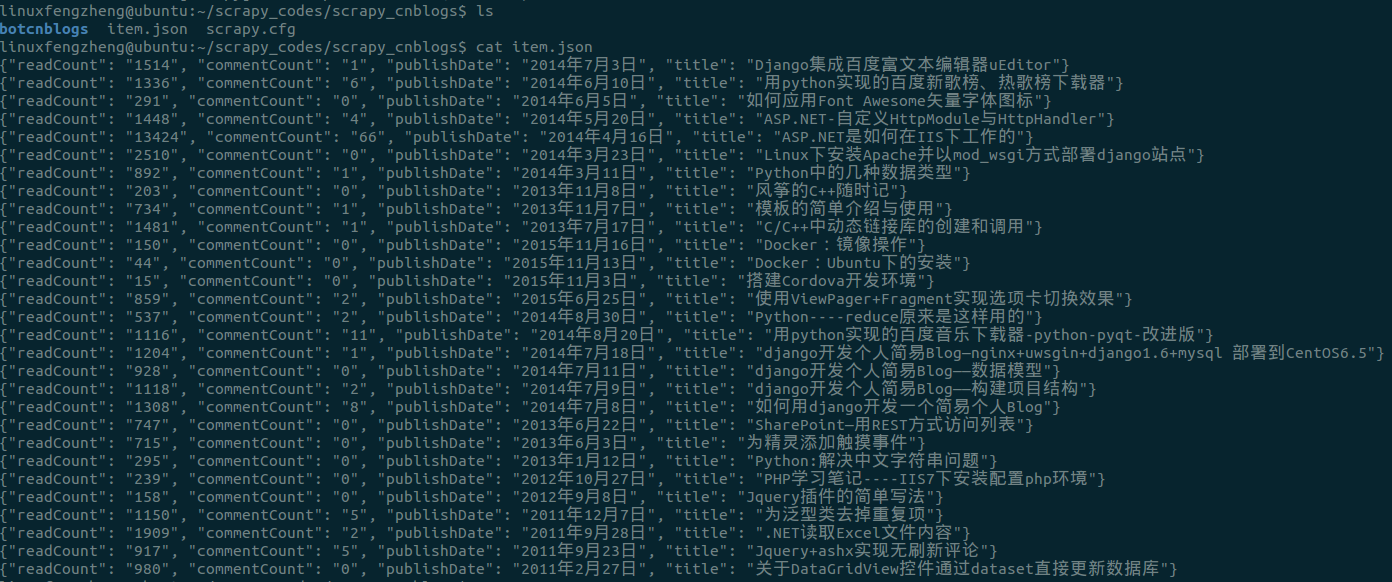
之后会看到,根目录中多了一个item.json文件,cat此文件内容,可以看到信息已经被提取出来:
更多入门教程可以参考 (http://www.bugingcode.com/python_start/)