一、pymysql模块
pymysql模块是python中连接数据库的一个常用第三方库
2.1 pymysql.connect() 通过该方法连接数据库
import pymysql # 打开数据库连接 db = pymysql.connect(host="XX.XXX.XXX.XXX",user='testuser',passwd:'test123',"TESTDB",charset='UTF8',autocommit=True)
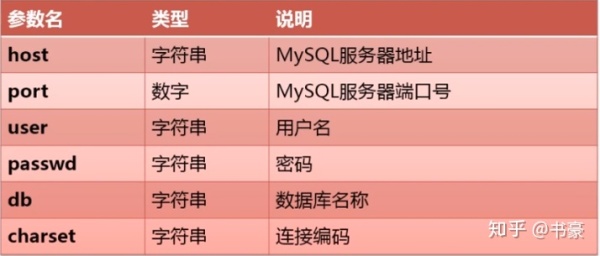
参数:
localhost:需要填写你的MYSQL服务器地址 例如,host="http://XX.XXX.XXX.XXX",加端口号port=XXXX
testuser:是你的用户名 user='testuser',即连接数据库TESTDB使用的用户名为 "testuser"
passwd:是你的用户密码 passwd:test123
TESTDB:连接的数据库为 TESTDB
charset:charset='UTF8'为UTF8编码
autocommit:当修改数据时,自动提交数据
2、connection连接支持的方法
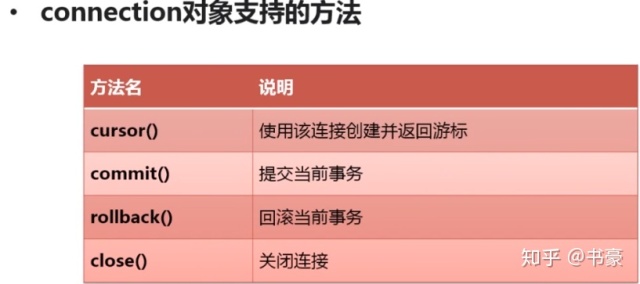
Python查询Mysql使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据, 使用fetchall() 方法获取所有数据,使用fetchmany获取多条数据
注意:使用该方法时,注意和游标的位置有关,当游标处于末尾时,就无法获取数据
- fetchone(): 该方法获取下一个查询结果集。结果集是一个对象
- fetchall(): 接收全部的返回结果行.
- fetchmany(): 接收多条返回结果行.
3、使用cursor.execute("SELECT * from students"),使用execute执行sql语句
2.2、来,使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据.
data = cursor.fetchone()
print ("Database version : %s " % data)
# 关闭数据库连接,释放资源!!!
db.close()
2.3、来,创建数据库表
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# 使用 execute() 方法执行 SQL,如果表存在则删除
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
# 使用预处理语句创建表
sql = """CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE (
FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(20),
AGE INT,
SEX CHAR(1),
INCOME FLOAT )"""
cursor.execute(sql)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
2.4、来,数据库插入操作
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# SQL 插入语句
sql = """INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME,
LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Mac', 'Mohan', 20, 'M', 2000)"""
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
except:
# 如果发生错误则回滚
db.rollback()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
db.commit() 命令很重要,执行此方法,方可提交到数据库执行更新!
2.5、来,数据库查询操作
查询EMPLOYEE表中salary(工资)字段大于1000的所有数据:
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost","testuser","test123","TESTDB" )
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# SQL 查询语句
sql = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE INCOME > %s" % (1000)
try:
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取所有记录列表
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
fname = row[0]
lname = row[1]
age = row[2]
sex = row[3]
income = row[4]
# 打印结果
print ("fname=%s,lname=%s,age=%s,sex=%s,income=%s" %
(fname, lname, age, sex, income ))
except:
print ("Error: unable to fetch data")
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
实例:
import pymysql
connect = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='user', password="123456",
db='user', port=3306,charset='utf8',autocommit=True)#建立数据库链接,autocommit每次修改后自动提交
cur = connect.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)#建立游标,并申明字典类型
sql = 'select * from students'
cur.execute(sql)#执行sql语句
# connect.commit()#在修改数据库时,需要提交数据
# connect.rollback()#遇到事务失败时,需要回滚数据
print(cur.fetchone())#返回字典类型的单条数据
print(cur.fetchmany(2))#返回一个由2条字典构成的列表
print(cur.fetchall())#获取所有结果,默认以元组方式返回,可通过转换为字典以列表返回
cur.close()
connect.close()
print(cur.description)#返回游标的描述信息
1、使用%符号占位写法
#查询语句
sql = "select * from GOODS_TYL where NAME='%s';"%name
#更新语句
sql = "update GOODS_TYL set price = %f,count = %d,color = '%s' where name = '%s';"%(price,count,color,name)
#插入语句
sql = "insert into GOODS_TYL (name,price,count,color) VALUES('%s',%f,%d,'%s');"%(name,price,count,color)
#删除语句
sql = "delete from GOODS_TYL where name = '%s';"% name