
从本文章开始,参考结城浩的《图解设计模式》写23种设计模式的系列介绍文章,结合网络上其他的设计模式的内容,使用C++的语言编写这些设计模式,记录自己的设计模式的心得。
使用情景
迭代器的作用是遍历某一类相同元素的集合,所以迭代器模式是一种行为设计模式,该模式的作用是在不改变底层元素的前提下,按照某种方式遍历集合中元素的值。其中,在C++中比较典型类似与std的vector的前向迭代器begin()和end(),以及后向迭代器rbegin()和rend()。
问题引入
可以设想元素聚合成集合的方式,最简单的方式是顺序存储的数组或者列表,但是也有例如树、图和其他复杂的数据结构。所以,如果要遍历集合中的元素,有下面的两个问题需要解决:
- 如何在不改变元素的前提下,遍历各种不同的集合?
- 同一个集合如果有不同的遍历方式(比如树有前中后序3种不同的遍历顺序),如果在不改变集合的前提下,比较容易扩展这些功能呢?
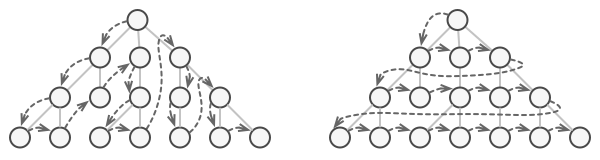
解决方案
为了满足开闭原则,我们将定义一个迭代器的类,将迭代从集合种抽象出来,作为一个行为的迭代器处理。如下图所示,对于一个树结构,我们定义了两个迭代器的类,DFS和BFS两个迭代器,这样可以将元素遍历和树本身进行解耦。
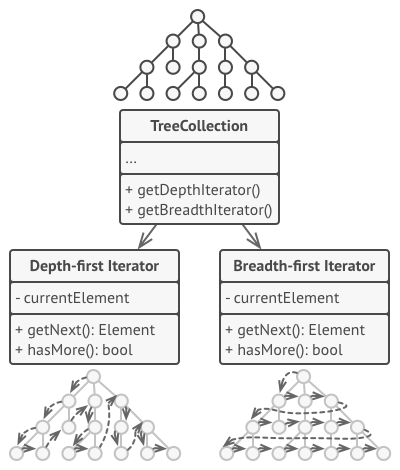
UML表示
我们以《图解设计模式》中遍历书架中的书本为例,有如下的UML图
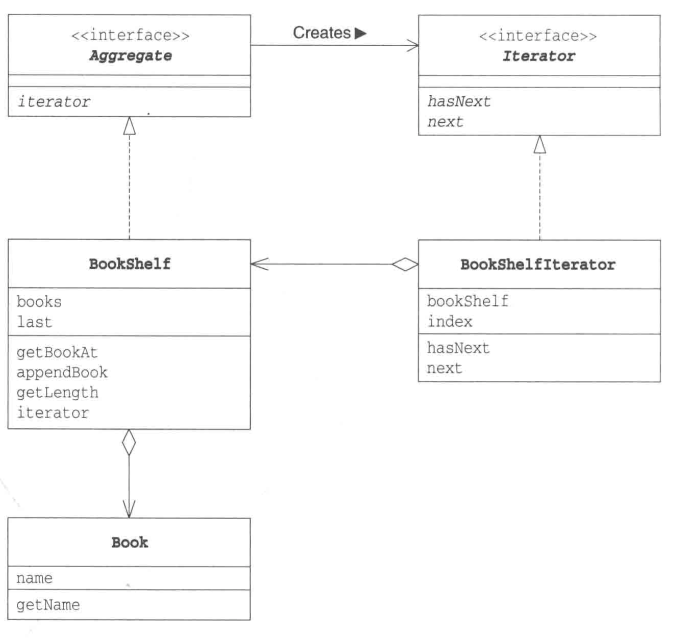
对上面的这幅图做进一步的说明,
- Aggregate表示集合的接口,书架实现该接口,所以书架必须要有迭代器的方法;
- Iterator表示集合的迭代器的接口,书架的迭代器实现它;
需要说明的是,此处的迭代器只有一种前向的迭代器,也可以定义后向遍历的迭代器。
C++代码
我们使用C++按照上面的UML图片实现这个设计模式。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum State {
RIGHT = 0,
WRONG,
RESERVED = 22
};
// 书本的类
class Book {
public:
Book(std::string name = "") : name_(name) {};
std::string getName() const { return name_; };
~Book() = default;
private:
std::string name_;
};
// 抽象的迭代器类,包括获得下一本书,以及是否有下一本书的判断
class Iterator {
public:
virtual Book Next() = 0;
virtual bool HasNext() const = 0;
virtual ~Iterator() = default;
};
// 抽象的聚合类,该类有创建迭代器、取得某个位置的书本,弹出书本,计数,加入书本等功能
class Aggregate {
public:
virtual Iterator* CreateIterator() = 0;
virtual State getBookAt(const int index, Book& book) = 0;
virtual int Count() const = 0;
virtual ~Aggregate() = default;
};
// 书架的具体迭代器,实现上面的抽象类的虚函数
class BookShelfIterator : public Iterator {
public:
BookShelfIterator(Aggregate* aggregate) : aggregate_(aggregate), loc_(0) {};
~BookShelfIterator() {
if (aggregate_ != nullptr) {
delete aggregate_;
aggregate_ = nullptr;
}
loc_ = 0;
}
Book Next() {
Book book;
aggregate_->getBookAt(loc_, book);
loc_++;
return book;
}
bool HasNext() const {
return loc_ < aggregate_->Count();
}
private:
int loc_;
Aggregate* aggregate_;
};
// 具体的聚合类——书架,实现上面的功能
class BookShelf : public Aggregate {
public:
BookShelf(const int maxSize) :maxSize_(maxSize), count_(0), iterator_(nullptr) {
books_.clear();
}
Iterator* CreateIterator() {
if (iterator_ == nullptr) {
iterator_ = new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
return iterator_;
}
State getBookAt(const int index, Book& book) {
if (index >= count_) {
std::cout << "Wrong index
";
return WRONG;
}
book = books_[index];
return RIGHT;
}
void Pop() {
books_.pop_back();
count_--;
}
int Count() const {
return count_;
}
void Push(const Book& book) {
if (count_ == maxSize_) {
std::cout << "bookshelf is full
";
return;
}
books_.push_back(book);
count_++;
}
~BookShelf() {
if (iterator_ != nullptr) {
delete iterator_;
iterator_ = nullptr;
}
maxSize_ = 0;
count_ = 0;
books_.clear();
}
private:
int maxSize_;
int count_;
std::vector<Book> books_;
Iterator* iterator_;
};
// client
int main()
{
BookShelf* myShelf = new BookShelf(5);
myShelf->Push(Book("《重构》"));
myShelf->Push(Book("《图解设计模式》"));
myShelf->Push(Book("《黎曼猜想》"));
Iterator* iter = myShelf->CreateIterator();
cout << "书架上有" << myShelf->Count() << "本书:
";
while (iter->HasNext() == true) {
cout << iter->Next().getName() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
具体的运行结果如下
书架上有3本书:
《重构》
《图解设计模式》
《黎曼猜想》
分析角色
这个模式有实际上由两个角色,集合以及集合的迭代器,这两个事物由分为抽象和具体两种。我们所举的例子中
BookShelf就是具体的集合,它实现自抽象的集合接口Aggregate;BookShelfIterator是具体的迭代器,它实现自抽象的迭代器接口Iterator。
迭代器接口中定义了迭代器的遍历的所有方法,HasNext以及Next。
这里需要注意的是,在C++的版本里面集合的接口中不仅定义了创建迭代器的方法CreateIterator,而且定义了集合的个数Count和集合获取当前元素的方法getBookAt,这是因为迭代器中的方法实现依赖这些接口。
扩展修改
大家可以思考一下为什么我们需要这个模式呢?设计模式的初衷是实现代码的复用和可扩展,这个模式体现在哪里呢?
遍历方法和集合本身解耦
迭代器模式的重要作用是将集合的遍历和实现分离开来,换句话说,无论实现如何变化,我依然可以使用原来的方法进行遍历,也就是说遍历这个动作本身不会因为书架的实现发生变化而变化,所以下面的代码是不变的
while (iter->HasNext() == true) {
cout << iter->Next().getName() << endl;
}
我们依然仅仅依靠HasNext以及Next接口就可以完成对于书架本身的遍历。
遍历需求易于扩展
不妨设想一下,假如我们需要在原来的书架上新增一种遍历方式,从后向前实现后向遍历,这个代码该怎么修改呢?应该完成如下的工作:
- 在原来的书架类中新增后向遍历的iter指针;
- 书架类中包含创建后向迭代器的方法;
- 后向迭代器继承自迭代器类别,实现后向迭代器
然后就可以继续使用原来的遍历方式遍历集合了,具体的代码如下
enum State {
RIGHT = 0,
WRONG,
RESERVED = 22
};
// concrete book
class Book {
public:
Book(std::string name = "") : name_(name) {};
std::string getName() const { return name_; };
~Book() = default;
private:
std::string name_;
};
class Iterator {
public:
virtual Book Next() = 0;
virtual bool HasNext() const = 0;
virtual ~Iterator() = default;
};
class Aggregate {
public:
virtual Iterator* CreateForwardIterator() = 0;
virtual Iterator* CreateBackwardIterator() = 0;
virtual State getBookAt(const int index, Book& book) = 0;
virtual int Count() const = 0;
virtual ~Aggregate() = default;
};
class BookShelfBackwardIterator : public Iterator {
public:
BookShelfBackwardIterator(Aggregate* aggregate) : aggregate_(aggregate) {
loc_ = aggregate_->Count() - 1;
};
~BookShelfBackwardIterator() {
if (aggregate_ != nullptr) {
aggregate_ = nullptr;
}
loc_ = -1;
}
Book Next() {
Book book;
aggregate_->getBookAt(loc_, book);
loc_--;
return book;
}
bool HasNext() const {
return loc_ >= 0;
}
private:
int loc_;
Aggregate* aggregate_;
};
class BookShelfForwardIterator : public Iterator {
public:
BookShelfForwardIterator(Aggregate* aggregate) : aggregate_(aggregate), loc_(0) {};
~BookShelfForwardIterator() {
if (aggregate_ != nullptr) {
aggregate_ = nullptr;
}
loc_ = -1;
}
Book Next() {
Book book;
aggregate_->getBookAt(loc_, book);
loc_++;
return book;
}
bool HasNext() const {
return loc_ < aggregate_->Count();
}
private:
int loc_;
Aggregate* aggregate_;
};
class BookShelf : public Aggregate {
public:
BookShelf(const int maxSize) :maxSize_(maxSize), count_(0), iterator_(nullptr), backiter_(nullptr) {
books_.clear();
}
Iterator* CreateBackwardIterator() {
if (backiter_ == nullptr) {
backiter_ = new BookShelfBackwardIterator(this);
}
return backiter_;
}
Iterator* CreateForwardIterator() {
if (iterator_ == nullptr) {
iterator_ = new BookShelfForwardIterator(this);
}
return iterator_;
}
State getBookAt(const int index, Book& book) {
if (index >= count_) {
std::cout << "Wrong index
";
return WRONG;
}
book = books_[index];
return RIGHT;
}
void Pop() {
books_.pop_back();
count_--;
}
int Count() const {
return count_;
}
void Push(const Book& book) {
if (count_ == maxSize_) {
std::cout << "bookshelf is full
";
return;
}
books_.push_back(book);
count_++;
}
~BookShelf() {
if (iterator_ != nullptr) {
delete iterator_;
iterator_ = nullptr;
}
if (backiter_ != nullptr) {
delete backiter_;
backiter_ = nullptr;
}
maxSize_ = 0;
count_ = 0;
books_.clear();
}
private:
int maxSize_;
int count_;
std::vector<Book> books_;
Iterator* iterator_;
Iterator* backiter_;
};
using namespace std;
// book class
int main()
{
BookShelf* myShelf = new BookShelf(5);
myShelf->Push(Book("《重构》"));
myShelf->Push(Book("《图解设计模式》"));
myShelf->Push(Book("《黎曼猜想》"));
Iterator* iter = myShelf->CreateForwardIterator();
cout << "前向遍历" << myShelf->Count() << "本书:
";
while (iter->HasNext()) {
cout << iter->Next().getName() << endl;
}
iter = nullptr;
iter = myShelf->CreateBackwardIterator();
cout << "后向遍历" << myShelf->Count() << "本书:
";
while (iter->HasNext()) {
cout << iter->Next().getName() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行效果如下
前向遍历3本书:
《重构》
《图解设计模式》
《黎曼猜想》
后向遍历3本书:
《黎曼猜想》
《图解设计模式》
《重构》
参考资料
- 图说设计模式 — Graphic Design Patterns
- 图灵程序设计丛书 图解设计模式,图解设计模式的pdf下载地址
- 设计模式目录:22种设计模式,乌克兰的某个程序员写的设计模式的网页,非常不错