序贯(Sequential)模型
序贯模型是多个网络层的线性堆叠,也就是“一条路走到黑”。
可以通过向Sequential模型传递一个layer的list来构造该模型:
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation model = Sequential([ Dense(32, units=784), Activation('relu'), Dense(10), Activation('softmax'), ])
也可以通过.add()方法一个个的将layer加入模型中:
model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_shape=(784,))) model.add(Activation('relu'))
指定输入数据的shape
模型需要知道输入数据的shape,因此,Sequential的第一层需要接受一个关于输入数据shape的参数,后面的各个层则可以自动的推导出中间数据的shape,因此不需要为每个层都指定这个参数。有几种方法来为第一层指定输入数据的shape
-
传递一个
input_shape的关键字参数给第一层,input_shape是一个tuple类型的数据,其中也可以填入None,如果填入None则表示此位置可能是任何正整数。数据的batch大小不应包含在其中。 -
有些2D层,如
Dense,支持通过指定其输入维度input_dim来隐含的指定输入数据shape,是一个Int类型的数据。一些3D的时域层支持通过参数input_dim和input_length来指定输入shape。 -
如果你需要为输入指定一个固定大小的batch_size(常用于stateful RNN网络),可以传递
batch_size参数到一个层中,例如你想指定输入张量的batch大小是32,数据shape是(6,8),则你需要传递batch_size=32和input_shape=(6,8)。
model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=784)) model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_shape=(784,)))
编译
在训练模型之前,我们需要通过compile来对学习过程进行配置。compile接收三个参数:
-
优化器optimizer:该参数可指定为已预定义的优化器名,如
rmsprop、adagrad,或一个Optimizer类的对象,详情见optimizers -
损失函数loss:该参数为模型试图最小化的目标函数,它可为预定义的损失函数名,如
categorical_crossentropy、mse,也可以为一个损失函数。详情见losses -
指标列表metrics:对分类问题,我们一般将该列表设置为
metrics=['accuracy']。指标可以是一个预定义指标的名字,也可以是一个用户定制的函数.指标函数应该返回单个张量,或一个完成metric_name - > metric_value映射的字典.请参考性能评估
# For a multi-class classification problem model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # For a binary classification problem model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # For a mean squared error regression problem model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='mse') # For custom metrics import keras.backend as K def mean_pred(y_true, y_pred): return K.mean(y_pred) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy', mean_pred])
训练
Keras以Numpy数组作为输入数据和标签的数据类型。训练模型一般使用fit函数,该函数的详情见这里。下面是一些例子。
# For a single-input model with 2 classes (binary classification): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu', input_dim=100)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy data import numpy as np data = np.random.random((1000, 100)) labels = np.random.randint(2, size=(1000, 1)) # Train the model, iterating on the data in batches of 32 samples model.fit(data, labels, epochs=10, batch_size=32) # For a single-input model with 10 classes (categorical classification): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu', input_dim=100)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy data import numpy as np data = np.random.random((1000, 100)) labels = np.random.randint(10, size=(1000, 1)) # Convert labels to categorical one-hot encoding one_hot_labels = keras.utils.to_categorical(labels, num_classes=10) # Train the model, iterating on the data in batches of 32 samples model.fit(data, one_hot_labels, epochs=10, batch_size=32)
例子
这里是一些帮助你开始的例子
在Keras代码包的examples文件夹中,你将找到使用真实数据的示例模型:
- CIFAR10 小图片分类:使用CNN和实时数据提升
- IMDB 电影评论观点分类:使用LSTM处理成序列的词语
- Reuters(路透社)新闻主题分类:使用多层感知器(MLP)
- MNIST手写数字识别:使用多层感知器和CNN
- 字符级文本生成:使用LSTM ...
基于多层感知器的softmax多分类:
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation from keras.optimizers import SGD # Generate dummy data import numpy as np x_train = np.random.random((1000, 20)) y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10, size=(1000, 1)), num_classes=10) x_test = np.random.random((100, 20)) y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10, size=(100, 1)), num_classes=10) model = Sequential() # Dense(64) is a fully-connected layer with 64 hidden units. # in the first layer, you must specify the expected input data shape: # here, 20-dimensional vectors. model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu', input_dim=20)) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) sgd = SGD(lr=0.01, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=128) score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=128)
MLP的二分类:
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout # Generate dummy data x_train = np.random.random((1000, 20)) y_train = np.random.randint(2, size=(1000, 1)) x_test = np.random.random((100, 20)) y_test = np.random.randint(2, size=(100, 1)) model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=20, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=128) score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=128)
类似VGG的卷积神经网络:
import numpy as np import keras from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D from keras.optimizers import SGD # Generate dummy data x_train = np.random.random((100, 100, 100, 3)) y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10, size=(100, 1)), num_classes=10) x_test = np.random.random((20, 100, 100, 3)) y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10, size=(20, 1)), num_classes=10) model = Sequential() # input: 100x100 images with 3 channels -> (100, 100, 3) tensors. # this applies 32 convolution filters of size 3x3 each. model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(100, 100, 3))) model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu')) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu')) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(256, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) sgd = SGD(lr=0.01, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=10) score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=32)
使用LSTM的序列分类
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout from keras.layers import Embedding from keras.layers import LSTM model = Sequential() model.add(Embedding(max_features, output_dim=256)) model.add(LSTM(128)) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=16, epochs=10) score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=16)
使用1D卷积的序列分类
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout from keras.layers import Embedding from keras.layers import Conv1D, GlobalAveragePooling1D, MaxPooling1D model = Sequential() model.add(Conv1D(64, 3, activation='relu', input_shape=(seq_length, 100))) model.add(Conv1D(64, 3, activation='relu')) model.add(MaxPooling1D(3)) model.add(Conv1D(128, 3, activation='relu')) model.add(Conv1D(128, 3, activation='relu')) model.add(GlobalAveragePooling1D()) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=16, epochs=10) score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=16)
用于序列分类的栈式LSTM
在该模型中,我们将三个LSTM堆叠在一起,是该模型能够学习更高层次的时域特征表示。
开始的两层LSTM返回其全部输出序列,而第三层LSTM只返回其输出序列的最后一步结果,从而其时域维度降低(即将输入序列转换为单个向量)
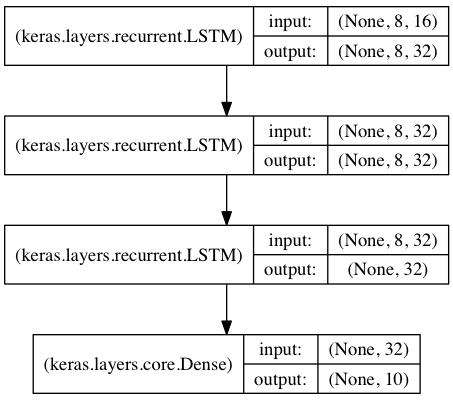
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense import numpy as np data_dim = 16 timesteps = 8 num_classes = 10 # expected input data shape: (batch_size, timesteps, data_dim) model = Sequential() model.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(timesteps, data_dim))) # returns a sequence of vectors of dimension 32 model.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=True)) # returns a sequence of vectors of dimension 32 model.add(LSTM(32)) # return a single vector of dimension 32 model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy training data x_train = np.random.random((1000, timesteps, data_dim)) y_train = np.random.random((1000, num_classes)) # Generate dummy validation data x_val = np.random.random((100, timesteps, data_dim)) y_val = np.random.random((100, num_classes)) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=5, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
采用stateful LSTM的相同模型
stateful LSTM的特点是,在处理过一个batch的训练数据后,其内部状态(记忆)会被作为下一个batch的训练数据的初始状态。状态LSTM使得我们可以在合理的计算复杂度内处理较长序列
请FAQ中关于stateful LSTM的部分获取更多信息
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense import numpy as np data_dim = 16 timesteps = 8 num_classes = 10 batch_size = 32 # Expected input batch shape: (batch_size, timesteps, data_dim) # Note that we have to provide the full batch_input_shape since the network is stateful. # the sample of index i in batch k is the follow-up for the sample i in batch k-1. model = Sequential() model.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=True, stateful=True, batch_input_shape=(batch_size, timesteps, data_dim))) model.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=True, stateful=True)) model.add(LSTM(32, stateful=True)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy training data x_train = np.random.random((batch_size * 10, timesteps, data_dim)) y_train = np.random.random((batch_size * 10, num_classes)) # Generate dummy validation data x_val = np.random.random((batch_size * 3, timesteps, data_dim)) y_val = np.random.random((batch_size * 3, num_classes)) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=5, shuffle=False, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))