目录
- Spring启动流程概述
- 准备上下文刷新
- 获取BeanFactory
Spring启动流程概述
我们知道Spring容器的核心就是IOC和DI,所以Spring在实现控制反转和依赖注入的过程中可主要分为两个阶段:
- 容器启动阶段
- bean的实例化阶段
容器启动阶段:
- 加载配置
- 分析配置信息
- 将Bean信息装配到BeanDefinition
- 将Bean信息注册到相应的BeanDefinitionRegistry
- 其它后续处理
容器实例化阶段:
- 根据策略实例化对象
- 装配依赖
- Bean初始化前处理
- 对象初始化
- 对象其他处理
- 注册回调接口
Spring启动流程详解
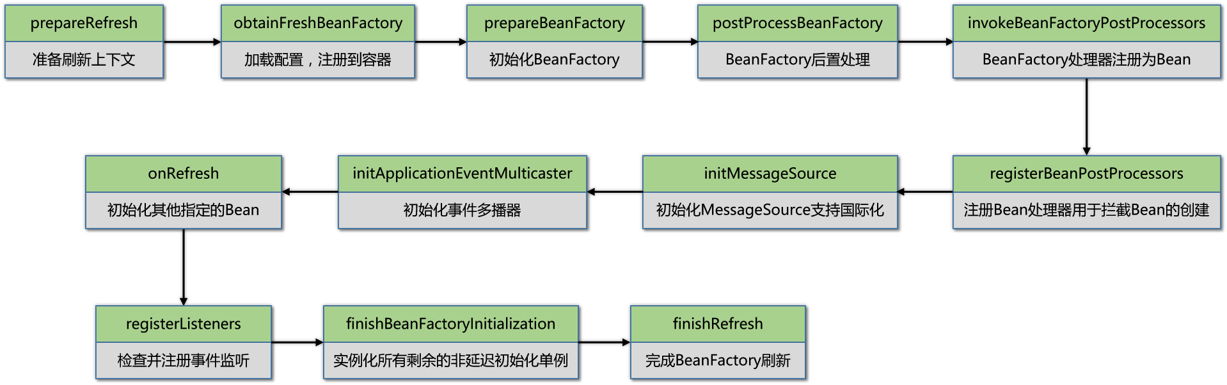
整体浏览:
1 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 super(parent); 5 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 6 if (refresh) { 7 refresh(); 8 } 9 }
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 // 方法加锁避免多线程同时刷新Spring上下文 4 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 5 // 准备上下文刷新 6 prepareRefresh(); 7 8 // 告诉子类刷新内部的beanFactory返回新的BeanFactory 9 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 10 11 // 在当前上下文中准备要beanFactory 12 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 13 14 try { 15 // 允许在上下文子类中对beanFactory进行后置处理 16 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 17 18 // 在上下文中将BeanFactory处理器注册为Bean 19 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 20 21 // 注册Bean处理器用于拦截Bean的创建 22 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 23 24 // 在上下文中初始化国际化信息 25 initMessageSource(); 26 27 // 在上下文中初始化event multicaster(事件多播器) 28 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 29 30 // 在指定的上下文子类中初始化其他指定的beans 31 onRefresh(); 32 33 // 检查并注册事件监听 34 registerListeners(); 35 36 // 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例 37 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 38 39 // 最后一步:发布相应的事件 40 finishRefresh(); 41 } 42 43 catch (BeansException ex) { 44 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 45 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 46 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 47 } 48 49 // 如果出现异常则销毁已创建的单例 50 destroyBeans(); 51 52 // 重置活动标志 53 cancelRefresh(ex); 54 55 // 将异常传递给调用者 56 throw ex; 57 } 58 59 finally { 60 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 61 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 62 resetCommonCaches(); 63 } 64 } 65 }
首先refresh会有一把锁,防止同时刷新Spring上下文;这把锁startupShutdownMonitor只有在refresh和close才会用到,用于同步Application的刷新和销毁。
从代码里可以看到销毁的时候有两个,registerShutdownHook、close;
区别:当close()被调用时会立即关闭或者停止ApplicationContext;而调用registerShutdownHook()将在稍后JVM关闭时关闭或停止ApplicationContext,该方法主要通过JVM ShutdownHook来实现。
ShutdownHook:Java 语言提供一种ShutdownHook(钩子)机制,当JVM接受到系统的关闭通知之后,调用ShutdownHook内的方法,用以完成清理操作,从而实现平滑退出应用。
准备上下文刷新
这一步很简单,主要做了一些属性的设置、验证、资源初始化等
1 protected void prepareRefresh() { 2 // 设置Spring容器启动时间 3 this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); 4 this.closed.set(false); 5 this.active.set(true); 6 7 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 8 logger.info("Refreshing " + this); 9 } 10 11 // 初始化属性资源 12 initPropertySources(); 13 14 // 验证所有属性是否都是可解析的(为null则不可解析) 15 getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 16 17 // ApplicationEvent初始化 18 this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>(); 19 }
获取BeanFactory
1 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { 2 refreshBeanFactory(); 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 4 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); 6 } 7 return beanFactory; 8 }
首先先刷新BeanFactory,然后就是获取BeanFactory了。
1 @Override 2 protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { 3 // 是否已经存在了BeanFactory 4 if (hasBeanFactory()) { 5 // 销毁beans 6 destroyBeans(); 7 // 关闭已存在的BeanFactory 8 closeBeanFactory(); 9 } 10 try { 11 // 创建新的BeanFactory对象 -> DefaultListableBeanFactory 12 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); 13 // 这很简单,就是给BeanFactory设置一个全局id 14 beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); 15 // 该方法主要对2个标志进行设置:allowBeanDefinitionOverriding和allowCircularReferences 16 // allowBeanDefinitionOverriding:是否允许使用相同名称重新注册不同的bean(Spring默认true,SpringBoot默认false) 17 // allowCircularReferences:是否允许循环依赖(默认为true) 18 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); 19 // 加载配置 20 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); 21 synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { 22 this.beanFactory = beanFactory; 23 } 24 } 25 catch (IOException ex) { 26 throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); 27 } 28 }
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
然后我们来看下销毁bean做了些什么处理:destroyBeans()
1 // 当前这个单例是否在销毁,true=已执行destory方法,或者出现异常时执行了destroySingleton方法 2 private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false; 3 // 缓存Bean与Bean的包含关系 4 private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(16); 5 // 缓存Bean与其它依赖Bean的关系 6 private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64); 7 // 缓存被依赖Bean与其它依赖Bean的关系 8 private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64); 9 10 public void destroySingletons() { 11 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 12 logger.debug("Destroying singletons in " + this); 13 } 14 synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { 15 // 设置清理标识 16 this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true; 17 } 18 19 // 销毁disposableBeans缓存中所有单例bean 20 String[] disposableBeanNames; 21 synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { 22 disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet()); 23 } 24 for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 25 destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]); 26 } 27 28 // 清空包含关系 29 this.containedBeanMap.clear(); 30 // 清空依赖和被依赖关系 31 this.dependentBeanMap.clear(); 32 this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear(); 33 34 // 清空缓存 35 clearSingletonCache(); 36 }
最主要的逻辑也就是清理了一些bean的依赖关系, 29 - 32行。上面的注释你可能有些模糊,没关系,我来举个例子。
1、containedBeanMap:缓存Bean与Bean的包含关系(见org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#registerContainedBean)。
1 public class A { 2 class B { 3 } 4 }
这就是包含关系,A包含B。
2、dependentBeanMap:缓存Bean与其它依赖Bean的关系(见org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#registerDependentBean)。
1 public class A { 2 private B b; 3 } 4 public class B { 5 }
上面这段代码就是A依赖于B
3、dependenciesForBeanMap:缓存被依赖Bean与其它依赖Bean的关系见org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#registerDependentBean)。
同dependentBeanMap,B被A依赖。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
最后我们来看下获取BeanFactory最复杂也是最重要的部分,loadBeanDefinitions,加载配置。
因为demo使用的是xml解析,所以我们调到AbstractXmlApplicationContext来看:
1 @Override 2 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { 3 // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. 4 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); 5 6 // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's 7 // resource loading environment. 8 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); 9 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); 10 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); 11 12 // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, 13 // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. 14 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); 15 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); 16 }
前面一段都比较简单,就是一些初始化的动作,我们直接看15行:
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); 3 if (configResources != null) { 4 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); 5 } 6 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); 7 if (configLocations != null) { 8 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); 9 } 10 }
解析的方式有两种,一种是Resource,一种是String;你可以通过查看代码或debug的方式得出代码会运行到第8行,而configLocations其实也就是我们刚开始定义了xml路径,如beans.xml。
但这两种解析方式实质是一样的,都会进入org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource)函数。
此函数主要用于,从执行的xml加载bean的定义,也就是从beans.xml读取配置。
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); 3 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 4 logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource); 5 } 6 7 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); 8 if (currentResources == null) { 9 currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); 10 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); 11 } 12 if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { 13 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 14 "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); 15 } 16 try { 17 // 将Resource资源转换为输出流InputSteam 18 InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); 19 try { 20 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); 21 if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { 22 inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); 23 } 24 // 执行加载bean的过程 25 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); 26 } 27 finally { 28 inputStream.close(); 29 } 30 } 31 catch (IOException ex) { 32 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 33 "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); 34 } 35 finally { 36 currentResources.remove(encodedResource); 37 if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { 38 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) 44 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 45 try { 46 // 加载XML文件,构造Document对象 47 Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); 48 // 注册Bean 49 return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); 50 } 51 // 抛出各种异常...... 52 }
构造Document对象就是解析XML,不是本次重点,有兴趣可以去瞅瞅,我们直接看Spring是怎样注册Bean的。
1 public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 // 使用代理类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 3 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); 4 int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); 5 // 读取bean的定义 6 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); 7 return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { 12 this.readerContext = readerContext; 13 logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); 14 Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); 15 // 注册bean实例 16 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); 17 }
好,重点来了,doRegisterBeanDefinitions:
1 // XML配置文件中beans元素 2 public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans"; 3 // XML配置文件中alias别名元素 4 public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias"; 5 // XML配置文件中name属性 6 public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name"; 7 // XML配置文件中alias属性 8 public static final String ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE = "alias"; 9 // XML配置文件中import元素 10 public static final String IMPORT_ELEMENT = "import"; 11 // XML配置文件中resource属性 12 public static final String RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = "resource"; 13 // XML配置文件中profile属性 14 public static final String PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE = "profile"; 15 16 protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { 17 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; 18 // 创建Bean解析代理工具类 19 this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); 20 21 if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 22 // 解析profile属性 23 String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); 24 if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { 25 String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( 26 profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); 27 if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { 28 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 29 logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + 30 "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); 31 } 32 return; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 preProcessXml(root); 38 // 解析XML并执行Bean注册 39 parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); 40 postProcessXml(root); 41 42 this.delegate = parent; 43 } 44 45 protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 46 // root根节点是默认标签 47 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 48 NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); 49 // 遍历XML Document的每个节点 50 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { 51 Node node = nl.item(i); 52 if (node instanceof Element) { 53 Element ele = (Element) node; 54 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { 55 // 解析默认标签 56 parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); 57 } 58 else { 59 // 解析自定义标签 60 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 // root根节点是自定义标签 66 else { 67 delegate.parseCustomElement(root); 68 } 69 } 70 71 // 解析XML配置文件的节点元素 72 private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 73 // 如果是Import元素 74 if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { 75 importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); 76 } 77 // 如果是Alias别名元素 78 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { 79 processAliasRegistration(ele); 80 } 81 // 如果是Bean元素 82 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { 83 processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); 84 } 85 // 如果是嵌套Bean元素(Beans) 86 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { 87 // recurse 88 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); 89 } 90 }
具体实现逻辑有兴趣的可以自行查阅源码。