目录:
- 事件广播源码
- 观察者模式
- Java事件机制
- Spring事件驱动机制
- 容器生命周期
事件广播源码
Spring初始化事件广播的源码很简单,和上一节初始化消息源的逻辑非常相似,我把代码贴在这。
1 protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { 2 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 3 // 检查配置中是否有applicationEventMulticaster的Bean定义 4 if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { 5 // 如果有则获取(实例化Bean) 6 this.applicationEventMulticaster = 7 beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); 8 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 9 logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); 10 } 11 } 12 else { 13 // 如果没有手动创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的实例 14 this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); 15 // 把创建的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster注册到BeanFactory 16 beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); 17 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 18 logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" + 19 APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + 20 "': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); 21 } 22 } 23 }
观察者模式
要想了解Spring和Java的事件机制你就得先了解下什么是观察者模式。我在这里简述下,观察者模式中主要分为三个元素,事件、观察者、被观察者,也可以叫做事件对象、事件源、监听器。
我你举个例方便你理解,就以最简单且常见的吃饭排号来说吧:
- 你一天中午去吃黄焖鸡,点完餐后服务员把你的排号给到了你,当你的黄焖鸡做好了后服务员便会大喊,多少号的黄焖鸡做好了,请到前台取餐之类的话术。
- 此时你听到叫到你的号了,便会去前台取餐。
- 在这个场景中:
- 取餐便是事件。
- 观察者是服务员,当黄焖鸡做好了后就会通知被观察者。
- 被观察者则是食客,也就是你,听到服务员(观察者)叫号后便去取餐(接收观察者的消息通知)。
具体代码实现如下:
https://www.cnblogs.com/bzfsdr/p/12685451.html
Java事件机制
说Java事件机制前首先让我们了解下什么是事件驱动机制:
- 事件驱动的常见形式便是发布-订阅模式。
- 在跨进程的通信间,我们通常采用引入MQ (消息队列) 来实现消息的发布和订阅。目前主流应用的架构中,均采用消息的发布-订阅模式来进行大型分布式系统的解耦。使得数据生产方和使用方分离,同时 MQ 还可起到削峰等作用。
- 同一进程内很多时候也需要这种事件驱动机制来进行逻辑解耦。
- 事件机制主要由三个部分组成:
- 事件对象:事件实体。封装事件源对象和事件,在事件源和监听器之间传递信息。
- 监听器:监听事件对象。事件发生时处理回调。
- 事件源:事件发生的起源。注册监听,对事件进行响应。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Java事件机制则是基于观察者模式,定义了如下接口:
- 事件对象:EventObject自定义事件对象需要继承该类。
- 监听器:EventListener事件监听器接口。
- 事件源:不需要实现任何接口,Java中也没给出相应的定义。
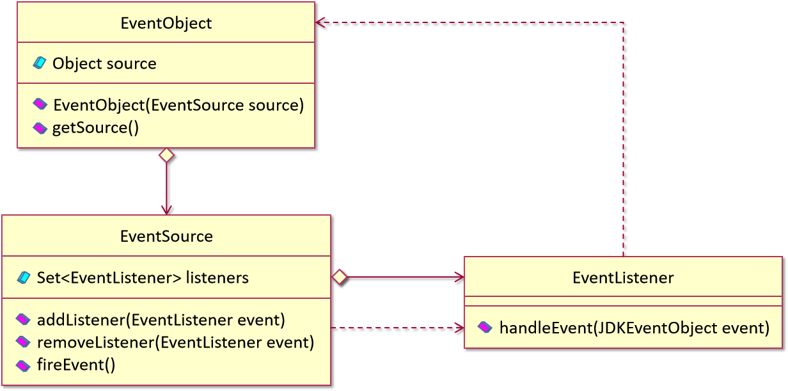
具体使用方式:与观察者模式大同小异。
1、事件对象:
1 public class JDKEventObject extends EventObject { 2 3 private Object source; 4 5 public JDKEventObject(JDKEventSource source) { 6 super(source); 7 this.source = source; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public Object getSource() { 12 return source; 13 } 14 }
2、监听器:
1 public interface JDKEventListener extends EventListener { 2 3 public void handleEvent(JDKEventObject event); 4 }
3、事件源:
1 public class JDKEventSource { 2 3 private Set<EventListener> listeners = new HashSet(); 4 5 private String message; 6 7 public void addListener(EventListener event) { 8 listeners.add(event); 9 } 10 11 public void removeListener(EventListener event) { 12 if (listeners.contains(event)) 13 listeners.remove(event); 14 } 15 16 public void fireEvent() { 17 Iterator<EventListener> iter = listeners.iterator(); 18 while (iter.hasNext()) { 19 JDKEventListener listener = (JDKEventListener) iter.next(); 20 listener.handleEvent(new JDKEventObject(this)); 21 } 22 } 23 }
Spring事件驱动机制
Spring事件驱动是基于Java的事件驱动实现的,并且内置了一些时间:
- ContextRefreshedEvent:ApplicationContext初始化或刷新时触发该事件。
- 通常在Spring加载或刷新应用上下文时,同时也想刷新预加载的资源,就可以通过监听ContextRefreshedEvent来做这样的事情。
- 这里的“初始化”是指所有Bean均已加载,检测到并激活了BeanPostProcessors,已预先实例化单例并且可以使用ApplicationContext对象。
- 只要上下文尚未关闭,选用的ApplicationContext支持这种“热”刷新(如:XmlWebApplicationContext支持热刷新,但GenericApplicationContext不支持),刷新可以被多次触发。
- ContextStartedEvent:ApplicationContext启动时触发该事件。
- "Started" 意味着所有Lifecycle Bean会获得启动事件。
- 通常,此事件用于在显式停止后重新启动Bean时,也可以用于启动尚未配置为自动启动的组件。
- ContextStoppedEvent:ApplicationContext被停止时触发该事件。
- "Stopped"是指所有Lifecycle Bean都收到一个明确的停止事件。
- 已停止的上下文可以通过start()调用重新启动。
- ContextClosedEvent:ApplicationContext被关闭时触发该事件。
- "Closed" 意味着容器管理的所有单例Bean都被销毁。
- 关闭的上下文表示容器生命周期结束,它不能刷新或重新启动。
- RequestHandledEvent:基于Web应用的事件,当一个HTTP请求完成后,触发该事件。该事件仅适用于使用DispatcherServlet的Web应用程序。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Spring事件机制中除了事件对象和监听者者两个角色之外,“事件广播器”则负责把事件转发给监听者:
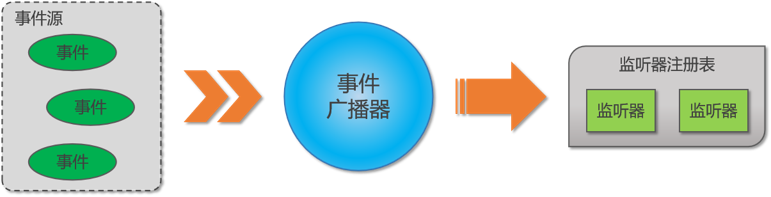
- ApplicationEvent:Spring提供的事件类,继承自EventObject类。
- ApplicationListener:事件监听者,该类接收一个泛型,供ApplicationEventPublisher在发布事件时选择EventListener。
- ApplicationEventPublisher:封装事件发布功能的接口,通知所有在Spring中注册的该事件的监听者进行处理。
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware:Spring提供的Aware接口之一,实现该接口的Bean可以获取ApplicationEventPublisher并进行发布事件。
- ApplicationEventMulticaster:管理多个ApplicationListener对象并向其发布事件的接口。
Spring 中,不需要我们手动进行监听器注册。ApplicationListener对象一旦在Spring容器中被注册,Spring会进行监听器的注册,实现事件的监听。
1、服务类:
1 // Spring容器检测到Service实现了ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口,会自动调用setApplicationEventPublisher 2 public class SpringService implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware { 3 4 private List<String> nameList; 5 private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; 6 7 @Override 8 public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) { 9 this.publisher = publisher; 10 } 11 12 public void setNameList(List<String> list) { 13 this.nameList = list; 14 } 15 16 // 要发布自定义ApplicationEvent,需要在ApplicationEventPublisher上调用publishEvent方法 17 public void sendMessage(String name) { 18 if (nameList.contains(name)) { 19 publisher.publishEvent(new SpringEvent(this, name)); 20 return; 21 } 22 } 23 }
2、监听器:
1 // 要接收自定义的ApplicationEvent,需要实现ApplicationListener监听器 2 public class SpringListener implements ApplicationListener<SpringEvent> { 3 4 String notifier; 5 6 public void setNotifier(String notifier) { 7 this.notifier = notifier; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void onApplicationEvent(SpringEvent event) { 12 System.out.println("onApplicationEvent: "+ notifier); 13 } 14 }
3、事件类:
1 public class SpringEvent extends ApplicationEvent { 2 3 String name; 4 5 /** 6 * Create a new ApplicationEvent. 7 * 8 * @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null}) 9 */ 10 public SpringEvent(Object source, String name) { 11 super(source); 12 this.name = name; 13 } 14 }
容器生命周期
之前我们所说的BeanPostProcessor及Bean的初始和销毁回调这些事件都是建立在容器已经成功启动的基础上,如果我们想在容器启动前后做一些处理就需要实现如下接口:
1 // 生命周期接口,任何Spring管理的对象都可以实现该接口 2 public interface Lifecycle { 3 void start(); 4 void stop(); 5 boolean isRunning(); 6 } 7 8 // 管理ApplicationContext生命周期 9 public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle { 10 void onRefresh(); 11 void onClose(); 12 } 13 14 public interface SmartLifecycle extends Lifecycle, Phased { 15 // Lifecycle Bean是否自动启动 16 boolean isAutoStartup(); 17 18 // 停止的时候执行回调,默认超时时间30秒 19 void stop(Runnable callback); 20 } 21 22 // Phased最小的对象首先启动,停止时,顺序和启动时相反 23 public interface Phased { 24 // SmartLifecycle的实现类默认Phase为0 25 int getPhase(); 26 }
示例:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 6 <bean class="com.jdr.spring.event.TestLifeCycle" name="testLifeCycle"/> 7 8 <bean class="com.jdr.spring.event.TestSmartLifeCycle" name="testSmartLifeCycle"/> 9 10 <bean class="com.jdr.spring.event.CustomContextEvent" name="customContextEvent"/> 11 12 </beans>
1 public class TestLifeCycle implements Lifecycle { 2 3 private boolean running = false; 4 5 public TestLifeCycle() { 6 System.out.println("TestLifeCycle...."); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public void start() { 11 System.out.println("TestLifeCycle start..."); 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public void stop() { 16 System.out.println("TestLifeCycle stop..."); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public boolean isRunning() { 21 return running; 22 } 23 }
1 public class TestSmartLifeCycle implements SmartLifecycle { 2 3 private boolean running = false; 4 5 public TestSmartLifeCycle() { 6 System.out.println("TestSmartLifeCycle...."); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public boolean isAutoStartup() { 11 // 若自动启动标识为false,则容器启动时不会调用start() 12 return true; 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public void stop(Runnable callback) { 17 System.out.println("TestSmartLifeCycle stop callback...."); 18 this.running = false; 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void start() { 23 System.out.println("TestSmartLifeCycle start...."); 24 this.running = true; 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void stop() { 29 System.out.println("TestSmartLifeCycle stop...."); 30 this.running = false; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public boolean isRunning() { 35 return running; 36 } 37 38 @Override 39 public int getPhase() { 40 return 100; 41 } 42 }
1 public class CustomContextEvent implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { 2 3 @Override 4 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { 5 if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) { 6 System.out.println("ContextRefreshedEvent..."); 7 } 8 if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent) { 9 System.out.println("ContextStartedEvent..."); 10 } 11 if (event instanceof ContextStoppedEvent) { 12 System.out.println("ContextStoppedEvent..."); 13 } 14 if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) { 15 System.out.println("ContextClosedEvent..."); 16 } 17 } 18 }
注意:
- 常规的Lifecycle接口只在容器上下文显式的调用start()/stop()方法时,才会去回调Lifecycle实现类的start/stop方法逻辑。
- 如果需要在容器启动时调用start()就需要实现SmartLifecycle接口,并且将isAutoStartup设置为true。
- 另外,LifeCycle Bean在销毁之前不能保证会收到停止通知。
- 正常关闭时,所有Lifecycle Bean在销毁回调之前首先会收到停止通知,但是在上下文的生命周期内进行热刷新或中止刷新尝试时,只会调用destroy方法。