ContentType组件介绍
ContentType是Django的内置的一个组件,可以追踪项目中所有的APP和model的对应关系,并记录在ContentType表中。跟其他建表外键如(ForeignKey、OneToOneField等)一样,实现表与表之间的联系。但ContentType与其他外键不同的是,ContentType组件更强大,比如对表与表之间混搭、适用于一张表同时和多张表关联。
ContentType组件的使用
1.引入django.contrib.contenttypes到settings.py的INSTALLED_APPS中
2.配置model (这里我们定义普通课程、学位课程加上价格策略)
使用contenttype时先导入模块
from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey,GenericRelation #GenericRelation:反向查询 from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
然后是model中的内容
from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey,GenericRelation #GenericRelation:反向查询 from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType # Create your models here. class Course(models.Model): """ 普通课程 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 用于反向查询到ReportRecord表, 不会生成表字段 #reports = GenericRelation(to='PricePolicy') class DegreeCourse(models.Model): """ 学位课程 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 用于反向查询到ReportRecord表, 不会生成表字段 # reports = GenericRelation(to='PricePolicy') class PricePolicy(models.Model): """ 价格策略 """ price = models.IntegerField() period = models.IntegerField() content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, max_length=32,on_delete=models.CASCADE) # ContentTpye组件:把所有表名存放到ContentType组件的表中 object_id = models.IntegerField(verbose_name='关联的表中的数据行的ID') content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type','object_id')
3.迁移数据表
makemigrations migrate
之间已经迁移好了。这里就没有在生成了。
4.配置url(API)
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('test/',views.TestView), ]
5.配置View
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from .models import PricePolicy,DegreeCourse,ContentType,Course # Create your views here. def TestView(request): #1.为学位课“c”添加一个价格策略 #方式一: 麻烦 # GR = DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='c') #获得该课程的对象 # price = PricePolicy.objects.get() # CT = ContentType.objects.get(model='degreecourse').first() #获得该表名的对象 # PricePolicy.objects.create(price='9.9',period='30',content_type=CT.id,object_id=GR) #方式二: 推荐 CT = ContentType.objects.get(model='degreecourse') #获得该表名的对象 GR = DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='c').first() #获得该课程的对象 PricePolicy.objects.create(price=9.9,period=30,content_type=CT,object_id=GR.id) CT1 = ContentType.objects.get(model='degreecourse') # 获得该表名的对象 GR = DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='java') .first() #获得该课程的对象 PricePolicy.objects.create(price=19.9, period=30, content_type=CT1,object_id=GR.id) CT2 = ContentType.objects.get(model='course') # 获得该表名的对象 GR = Course.objects.filter(title='c1').first() # 获得该课程的对象 PricePolicy.objects.create(price=19.9, period=30, content_type=CT2, object_id=GR.id) return HttpResponse('添加成功')
model各表分析:(注意 到这里这个步骤只是数据迁移加上生成了model中的表,没有执行程序)
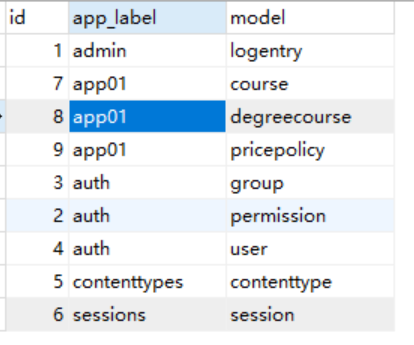
1.django_content_type表
是ContentType组件自动生成的表,记录当前的Django项目中所有model所属的app(即app_label属性)以及model的名字(即model属性)
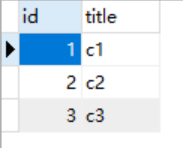
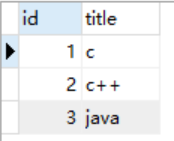
2.Course表(记录普通课程信息)
3.DegreeCourse学位表(记录全套课程信息)
结果分析:(运行程序后)
在app01_pricepolicy表中添加了一下数据
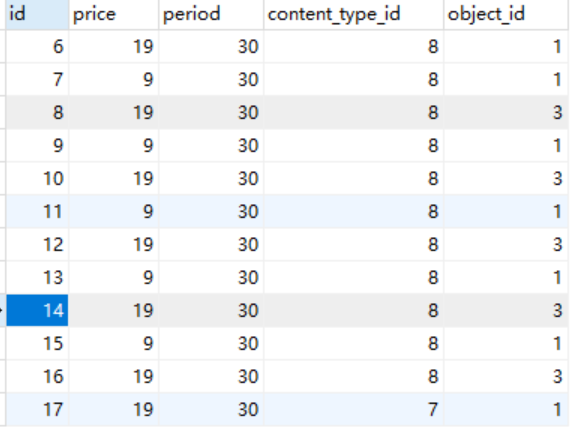
content_type_id是通过django_content_type的model属性获得对应表名的ID(代表表的id)
object_id通过表中的课程名获得课程的id(课程id)
综上所述,我个人觉得ContentTypet挺强大的,比喻是一座桥梁(交通枢纽),使人或车能跨越河流顺利同行