数据来自UCI机器学习仓库中的垃圾信息数据集
数据可从http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/sms+spam+collection下载
转成csv载入数据
import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=[u'simHei'] matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,cross_val_score df = pd.read_csv('data/SMSSpamCollection.csv',header=None) print(df.head) print("垃圾邮件个数:%s" % df[df[0]=='spam'][0].count()) print("正常邮件个数:%s" % df[df[0]=='ham'][0].count())
垃圾邮件个数:747
正常邮件个数:4825
创建TfidfVectorizer实例,将训练文本和测试文本都进行转换
X = df[1].values y = df[0].values X_train_raw,X_test_raw,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y) vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer() X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw) X_test = vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw)
建立逻辑回归模型训练和预测
LR = LogisticRegression() LR.fit(X_train,y_train) predictions = LR.predict(X_test) for i,prediction in enumerate(predictions[:5]): print("预测为 %s ,信件为 %s" % (prediction,X_test_raw[i]))
预测为 ham ,信件为 Send to someone else :-) 预测为 ham ,信件为 Easy ah?sen got selected means its good.. 预测为 ham ,信件为 Sorry da. I gone mad so many pending works what to do. 预测为 ham ,信件为 What not under standing. 预测为 spam ,信件为 SIX chances to win CASH! From 100 to 20,000 pounds txt> CSH11 and send to 87575. Cost 150p/day, 6days, 16+ TsandCs apply Reply HL 4 info
二元分类性能指标:混淆矩阵
# In[2]二元分类分类指标 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # predictions 与 y_test confusion_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions) print(confusion_matrix) plt.matshow(confusion_matrix) plt.title("混淆矩阵") plt.colorbar() plt.ylabel("真实值") plt.xlabel("预测值") plt.show()
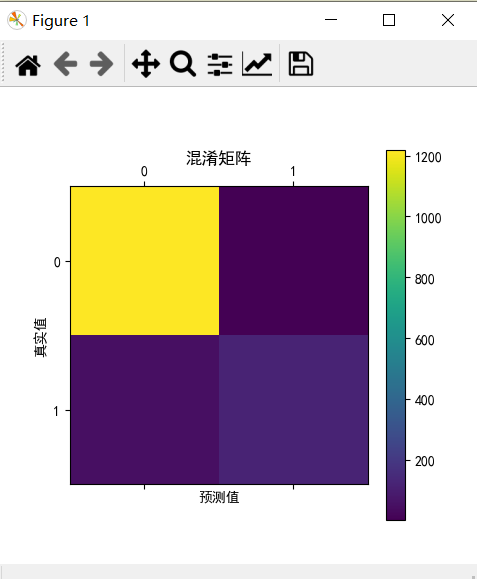
[[1217 1]
[ 52 123]]
准确率,召回率,精准率,F1值
# In[3] 给出 precision recall f1-score support from sklearn.metrics import classification_report print(classification_report(y_test,predictions)) from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,auc # 准确率 scores = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train,cv=5) print("准确率为: ",scores) print("平均准确率为: ",np.mean(scores)) # 有时必须要将标签转为数值 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder class_le = LabelEncoder() y_train_n = class_le.fit_transform(y_train) y_test_n = class_le.fit_transform(y_test) # 精准率 precision = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='precision') print("平均精准率为: ",np.mean(precision)) # 召回率 recall = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='recall') print("平均召回率为: ",np.mean(recall)) # F1值 f1 = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='f1') print("平均F1值为: ",np.mean(f1))
准确率为: [0.96654719 0.95459976 0.95449102 0.9508982 0.96047904] 平均准确率为: 0.9574030433756144 平均精准率为: 0.9906631114805584 平均召回率为: 0.6956979405034325 平均F1值为: 0.8162874707978786
画出ROC曲线,AUC为ROC曲线以下部分的面积
# In[4] ROC曲线 y_test_n为数值 predictions_pro = LR.predict_proba(X_test) false_positive_rate, recall, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test_n,predictions_pro[:,1]) roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, recall) plt.title("受试者操作特征曲线(ROC)") plt.plot(false_positive_rate, recall, 'b', label='AUC = % 0.2f' % roc_auc) plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.plot([0,1],[0,1],'r--') plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0]) plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0]) plt.xlabel('假阳性率') plt.ylabel('召回率') plt.show()

所有代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=[u'simHei'] matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,cross_val_score df = pd.read_csv('data/SMSSpamCollection.csv',header=None) print(df.head) print("垃圾邮件个数:%s" % df[df[0]=='spam'][0].count()) print("正常邮件个数:%s" % df[df[0]=='ham'][0].count()) # In[1] X = df[1].values y = df[0].values X_train_raw,X_test_raw,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y) vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer() X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train_raw) X_test = vectorizer.transform(X_test_raw) LR = LogisticRegression() LR.fit(X_train,y_train) predictions = LR.predict(X_test) for i,prediction in enumerate(predictions[:5]): print("预测为 %s ,信件为 %s" % (prediction,X_test_raw[i])) # In[2]二元分类分类指标 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # predictions 与 y_test confusion_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions) print(confusion_matrix) plt.matshow(confusion_matrix) plt.title("混淆矩阵") plt.colorbar() plt.ylabel("真实值") plt.xlabel("预测值") plt.show() # In[3] 给出 precision recall f1-score support from sklearn.metrics import classification_report print(classification_report(y_test,predictions)) from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,auc # 准确率 scores = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train,cv=5) print("准确率为: ",scores) print("平均准确率为: ",np.mean(scores)) # 必须要将标签转为数值 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder class_le = LabelEncoder() y_train_n = class_le.fit_transform(y_train) y_test_n = class_le.fit_transform(y_test) # 精准率 precision = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='precision') print("平均精准率为: ",np.mean(precision)) # 召回率 recall = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='recall') print("平均召回率为: ",np.mean(recall)) # F1值 f1 = cross_val_score(LR,X_train,y_train_n,cv=5,scoring='f1') print("平均F1值为: ",np.mean(f1)) # In[4] ROC曲线 y_test_n为数值 predictions_pro = LR.predict_proba(X_test) false_positive_rate, recall, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test_n,predictions_pro[:,1]) roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, recall) plt.title("受试者操作特征曲线(ROC)") plt.plot(false_positive_rate, recall, 'b', label='AUC = % 0.2f' % roc_auc) plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.plot([0,1],[0,1],'r--') plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0]) plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0]) plt.xlabel('假阳性率') plt.ylabel('召回率') plt.show()