ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class C8_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<Integer> nl = new ArrayList<Integer>();
nl.add((Integer) 1);
nl.add((Integer) 2);
nl.add((Integer) 3);
System.out.println("输出集合的所有元素" + nl);
System.out.println("输出下标为2的元素: " + nl.get(2));
nl.add(1, (Integer) 4);// 下标1的位置插入一个元素
System.out.println("元素下标1的位置插入4后,输出所有元素" + nl);
Integer b = (Integer) 1;
int n = nl.indexOf(b);// 查找指定元素的下标
nl.remove(n);// 删除指定下标的元素
System.out.println("n=" + n + " 删除n元素后输出集合中所有元素");
for(Integer i : nl){
System.out.print(i + " , ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}

LinkedList
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class C8_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
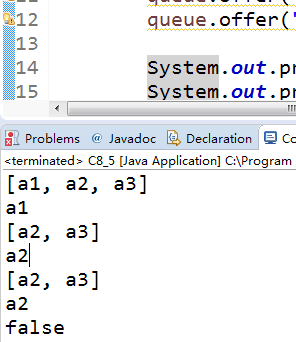
queue.offer("a1");// 入队列操作 queue.add()
queue.offer("a2");
queue.offer("a3");
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll());// 出队列操作 queue.pop()
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 取队列头元素操作,并没有把元素踢掉
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 出队列操作
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); // 判断队列空操作
}
}
TreeSet
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TestTreeSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
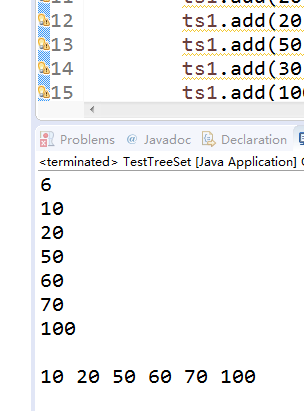
TreeSet ts1 = new TreeSet();
ts1.add(20);
ts1.add(20);
ts1.add(50);
ts1.add(30);
ts1.add(100);
ts1.add(10);
ts1.add(70);
ts1.add(60);
System.out.println("树里面的元素"+ts1);
System.out.println(ts1.isEmpty());
System.out.println(ts1.size()+" ");
System.out.println(ts1.contains(30));
ts1.remove(30);
System.out.println(ts1.contains(30));
System.out.println(ts1.size());
// 迭代器的使用方法
Iterator it = ts1.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next() + " ");
System.out.println();
Object[] data = ts1.toArray();
for(int i=0; i<data.length; i++)
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
HashSet
import java.util.*;
public class TestHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HashSet ts1 = new HashSet();
ts1.add(20);
ts1.add(50);
ts1.add(30);
ts1.add(100);
ts1.add(10);
ts1.add(70);
ts1.add(60);
ts1.add(30);
System.out.println(ts1);
System.out.println(ts1.isEmpty());
System.out.println(ts1.size());
System.out.println(ts1.contains(30));
ts1.remove(30);
System.out.println(ts1.contains(30));
System.out.println(ts1.size());
// 迭代器的使用方法
Iterator it = ts1.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
System.out.println();
// toArray方法的使用
Object[] data = ts1.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++)
System.out.print(data[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}

TreeMap
import java.util.*;
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
TreeMap register = new TreeMap();
register.put("zhangshan","jingsp");
register.put("lishi","1996-8");
register.put("wangwu","960515");
register.put("zhaoliu","overS");
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("entryset =");
Set s = register.entrySet();
Iterator it = s.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("key= value=");
Set s0 = register.entrySet();
Iterator it0 = s0.iterator();
while(it0.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry map = (Map.Entry)it0.next();
System.out.println("key:"+map.getKey()+" value:"+map.getValue());
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("keyset ====");
Set s1 = register.keySet();
Iterator it1 = s1.iterator();
while(it1.hasNext())
System.out.println(it1.next());
System.out.println("-------------------");
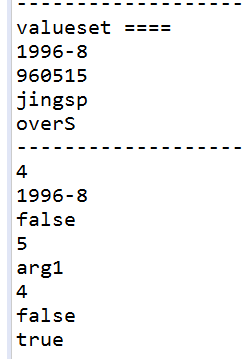
System.out.println("valueset ====");
Collection s2=register.values();
Iterator it2=s2.iterator();
while(it2.hasNext())
System.out.println(it2.next());
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println(register.size());
System.out.println(register.get("lishi"));
System.out.println(register.isEmpty());
register.put("chengjiu", "arg1");
System.out.println(register.size());
System.out.println(register.remove("chengjiu"));
System.out.println(register.size());
System.out.println(register.containsKey("chengjiu")); System.out.println(register.containsValue("960515"));
}
}

Map接口内部定义了一个接口Entry
interface Entry{
Object getKey();
Object getValue();
Object setValue();
boolean equals(Object value);
int hashCode();
}
HashMap
import java.util.*;
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HashMap register = new HashMap();
register.put("zhangshan", "jingsp");
register.put("lishi", "1996-8");
register.put("wangwu", "960515");
register.put("zhaoliu", "overS");
System.out.println(register);
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("entryset =");
Set s = register.entrySet();
System.out.println("hashCode " + s.hashCode());
Iterator it = s.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("key= value=");
Set s0 = register.entrySet();
Iterator it0 = s.iterator();
while (it0.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry map = (Map.Entry) it0.next();
System.out.println("key:" + map.getKey() + " value:"
+ map.getValue());
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("keyset ====");
Set s1 = register.keySet();
Iterator it1 = s1.iterator();
while (it1.hasNext())
System.out.println(it1.next());
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("valueset ====");
Collection s2 = register.values();
Iterator it2 = s2.iterator();
while (it2.hasNext())
System.out.println(it2.next());
}
}
{lishi=1996-8, zhangshan=jingsp, zhaoliu=overS, wangwu=960515}
-------------------
entryset =
hashCode 48127692
lishi=1996-8
zhangshan=jingsp
zhaoliu=overS
wangwu=960515
-------------------
key= value=
key:lishi value:1996-8
key:zhangshan value:jingsp
key:zhaoliu value:overS
key:wangwu value:960515
-------------------
keyset ====
lishi
zhangshan
zhaoliu
wangwu
-------------------
valueset ====
1996-8
jingsp
overS
960515