Tomcat
Tomcat是什么,Tomcat是目前市场上主流Web服务器之一,是用Java语言开发的项目。Tomcat支持Servlet和JSP的规范,它由一组嵌套的层次和组件组成。结构如下图
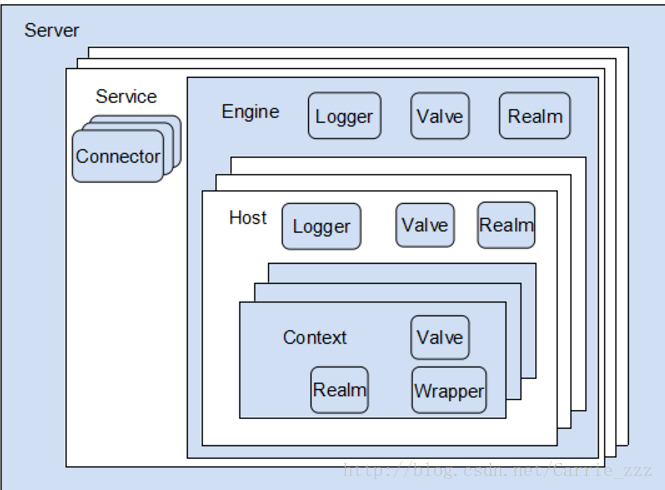
所有组件都实现lifecycle生命周期方法,里面包含了init,start,stop,destroy等方法,用来控制生命周期
Server是Tomcat最顶层的容器,代表着整个服务器,即一个Tomcat只有一个Server,Server中包含至少一个Service组件,用于提供具体服务。
Service组件包含了Connector组件和Engine组件,相当于Connector和Engine组件的包装器。一个Server可以包含多个Service(它们相互独立,只是公用一个JVM及类库),一个Service负责维护多个Connector和一个Container。
Connector用于接受请求并将请求封装成Request和Response,然后交给Container进行处理,Container处理完之后在交给Connector返回给客户端。
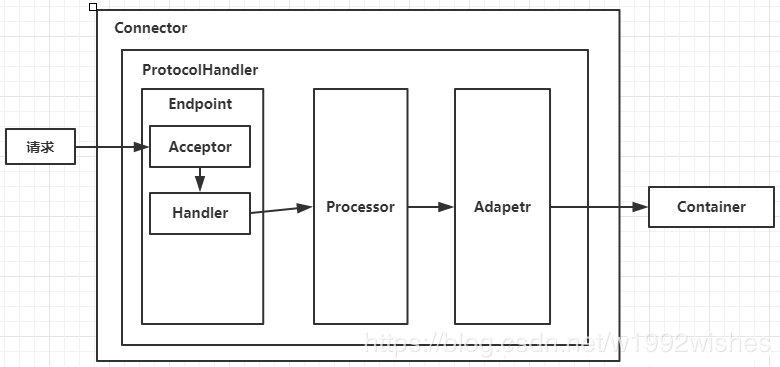
Engine引擎通是指处理请求的Servlet引擎组件,即Catalina Servlet引擎,它检查每一个请求的HTTP首部信息以辨别此请求应该发往哪个host或context,并将请求处理后的结果返回的相应的客户端。严格意义上来说,容器不必非得通过引擎来实现,它也可以是只是一个容器。如果Tomcat被配置成为独立服务器,默认引擎就是已经定义好的引擎。而如果Tomcat被配置为Apache Web服务器的提供Servlet功能的后端,默认引擎将被忽略,因为Web服务器自身就能确定将用户请求发往何处。一个引擎可以包含多个host组件。
Host,代表一个站点,也可以叫虚拟主机,一个Host可以配置多个Context,在server.xml文件中的默认配置为<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">, 其中appBase=webapps, 也就是<CATALINA_HOME>webapps目录,unpackingWARS=true 属性指定在appBase指定的目录中的war包都自动的解压,autoDeploy=true 属性指定对加入到appBase目录的war包进行自动的部署。
一个Engine包含多个Host的设计,使得一个服务器实例可以承担多个域名的服务,是很灵活的设计。
Context,代表一个应用程序,就是日常开发中的web程序,或者一个WEB-INF目录以及下面的web.xml文件,换句话说每一个运行的webapp最终都是以Context的形式存在,每个Context都有一个应用路径docBase和请求路径path;
<Context path="/urlpath" docBase="/test/xxx" reloadable=true />
Wrapper是最底层的容器,负责管理一个Servlet,包括加载,初始化,执行和资源回收。创建filter链,调用service方法等。
下面是Tomcat中容器init和start的执行流程

Servlet
Java的Web应用是基于Servlet规范运转的,而Servlet规范的核心接口即是Servlet接口,它是所有Servlet类必须实现的接口,描述了Servlet 生命周期为从创建直到销毁的整个过程,如下
public interface Servlet { void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException; ServletConfig getServletConfig(); void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; String getServletInfo(); void destroy(); }
init方法
init 方法被设计成只调用一次。它在第一次创建 Servlet 时被调用,在后续每次用户请求时不再调用。可以在方法简单地创建或加载一些数据,这些数据将被用于 Servlet 的整个生命周期。
service方法
service() 方法是执行我们业务逻辑的主要方法。每次有请求到达Servlet时,执行该方法 。
destroy方法
destroy() 方法只会被调用一次,在Servlet 容器关闭时执行 ,此时Servlet 生命周期结束。
在Java Servelt API中已经提供了两个抽象类方便开发者实现Servlet类,分别是GenericServlet 和 HttpServlet,GenericServlet定义了一个通用的、协议无关的Servlet,而HttpServlet则定义了Http协议的Servlet,这两个抽象类可以使Servlet类复用很多共性功能。
我们一般使用的是HttpServlet,重写doGet、doPost方法,实际上是在HttpServlet的service方法里面根据request的method执行对应的doGet、doPost等方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); long lastModified; if (method.equals("GET")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1L) { this.doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) { this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(304); } } } else if (method.equals("HEAD")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("POST")) { this.doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("PUT")) { this.doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("DELETE")) { this.doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) { this.doOptions(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("TRACE")) { this.doTrace(req, resp); } else { String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method}; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(501, errMsg); } }
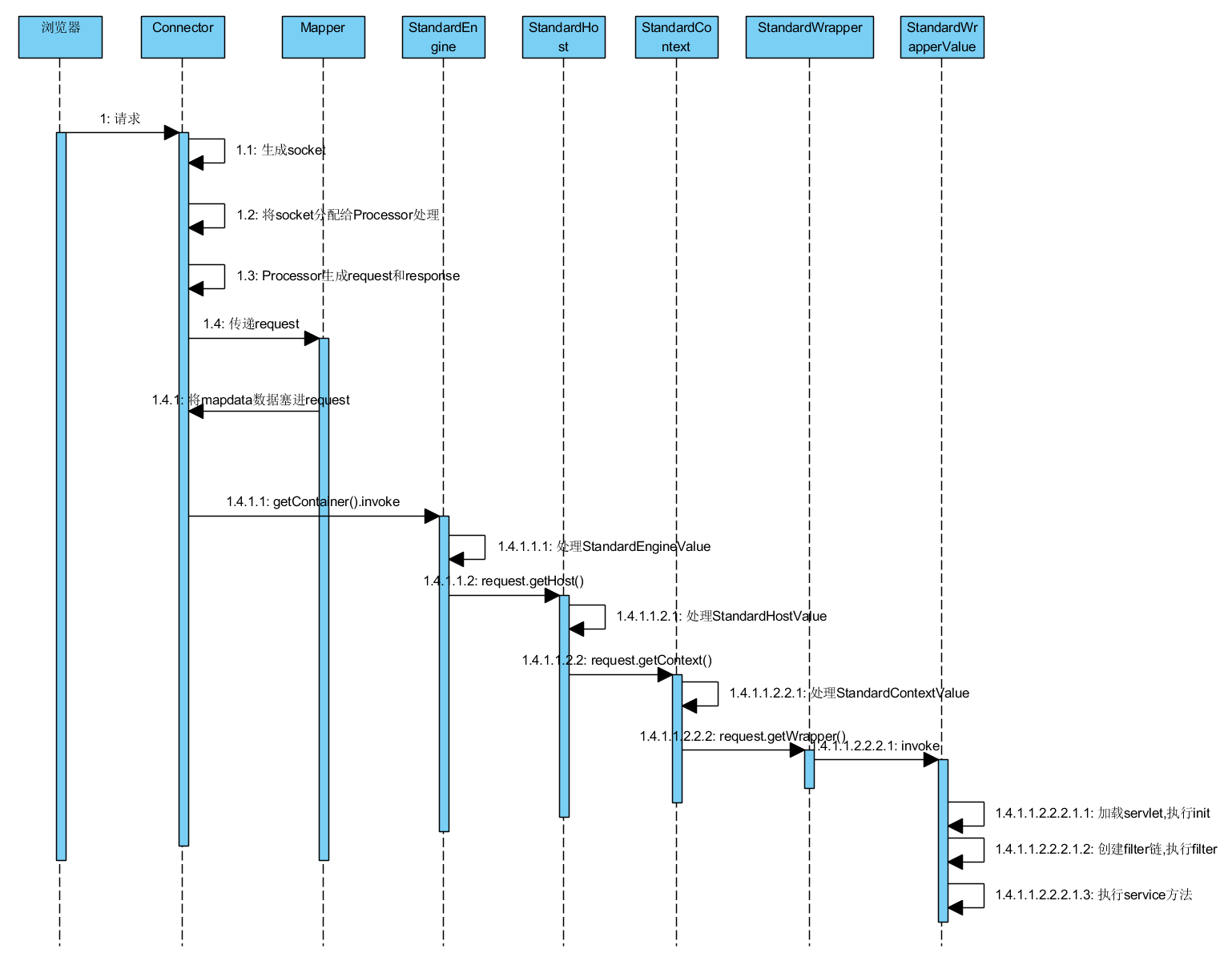
下面是一次请求到达Servlet的过程
参考
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201708/664458.html
https://blog.csdn.net/w1992wishes/article/details/79242797
<深入分析Java Web技术内幕>