我们常用的一些接口Callable、Runnable、Comparator等在JDK8中都添加了@FunctionalInterface注解。
通过JDK8源码javadoc,可以知道这个注解有以下特点:
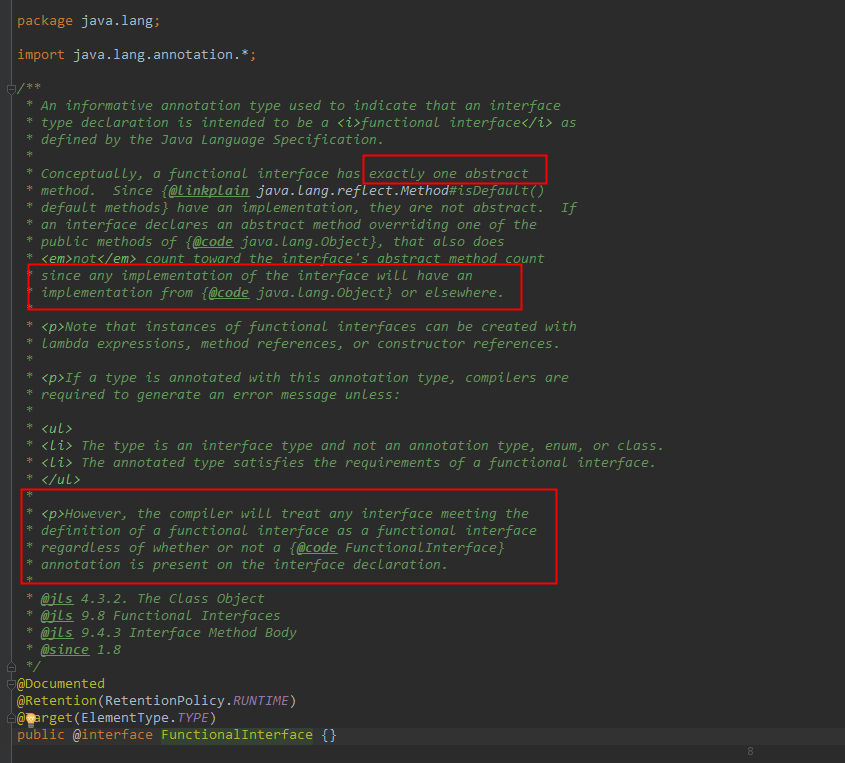
1、该注解只能标记在”有且仅有一个抽象方法”的接口上。
2、JDK8接口中的静态方法和默认方法,都不算是抽象方法。
3、接口默认继承Java.lang.Object,所以如果接口显示声明覆盖了Object中方法,那么也不算抽象方法。
4、该注解不是必须的,如果一个接口符合”函数式接口”定义,那么加不加该注解都没有影响。加上该注解能够更好地让编译器进行检查。如果编写的不是函数式接口,但是加上了@FunctionInterface,那么编译器会报错。
@FunctionalInterface标记在接口上,“函数式接口”是指仅仅只包含一个抽象方法的接口。
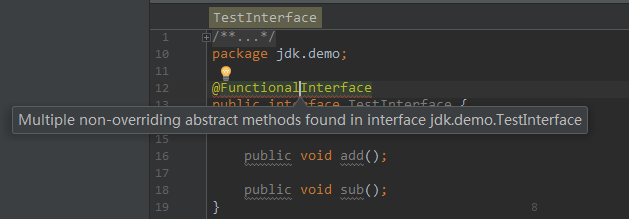
如果一个接口中包含不止一个抽象方法,那么不能使用@FunctionalInterface,编译会报错。
比如下面这个接口就是一个正确的函数式接口:
// 正确的函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TestInterface {
// 抽象方法
public void sub();
// java.lang.Object中的方法不是抽象方法
public boolean equals(Object var1);
// default不是抽象方法
public default void defaultMethod(){
}
// static不是抽象方法
public static void staticMethod(){
}
}
java8中常用的函数式接口:
常用的函数式接口主要有四种类型,是通过其输入和输出的参数来进行区分的。定义了编码过程中主要的使用场景。

public class FunctionalInterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 先看看如何创建它们
*/
Function<String,String> function1 = item -> item +"返回值";
Consumer<String> function2 = iterm -> {System.out.println(iterm);};//lambda语句,使用大括号,没有return关键字,表示没有返回值
Predicate<String> function3 = iterm -> "".equals(iterm);
Supplier<String> function4 = () -> new String("");
/**
* 再看看怎么使用
* demo释义:
* 1、创建一个String类型的集合
* 2、将集合中的所有元素的末尾追加字符串'1'
* 3、选出长度大于2的字符串
* 4、遍历输出所有元素
*/
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("zhangsan","lisi","wangwu","xiaoming","zhaoliu");
list.stream()
.map(value -> value + "1") //传入的是一个Function函数式接口
.filter(value -> value.length() > 2) //传入的是一个Predicate函数式接口
.forEach(value -> System.out.println(value)); //传入的是一个Consumer函数式接口
}
}
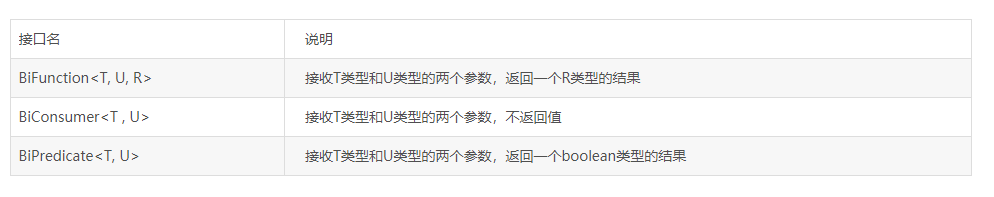
因此对于多个参数的操作也是如此。Java8中对于接收两个参数的场景提供了相关的函数式接口。如下:
public class FunctionalInterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Bi类型的接口创建
*/
BiFunction<String, String, Integer> biFunction = (str1,str2) -> str1.length()+str2.length();
BiConsumer<String, String> biConsumer = (str1,str2) -> System.out.println(str1+str2);
BiPredicate<String, String> biPredicate = (str1,str2) -> str1.length() > str2.length();
/**
* Bi类型的接口使用
*/
int length = getLength("hello", "world", (str1,str2) -> str1.length() + str2.length()); //输出10
boolean boolean1 = getBoolean("hello", "world", (str1,str2) -> str1.length() > str2.length()); //输出false
System.out.println(length);
System.out.println(boolean1);
noResult("hello", "world", (str1,str2) -> System.out.println(str1+" "+str2)); //没有输出
}
public static int getLength(String str1,String str2,BiFunction<String, String, Integer> function){
return function.apply(str1, str2);
}
public static void noResult(String str1,String str2,BiConsumer<String, String> biConcumer){
biConcumer.accept(str1, str2);
}
public static boolean getBoolean(String str1,String str2,BiPredicate<String, String> biPredicate){
return biPredicate.test(str1, str2);
}
}
关于多个参数值的使用,无论实在Function接口中,还是在BI类型的接口都提供了类似的操作。(注:java8中,接口的方法是可以有实现的,但需要default关键字修饰,这是其他版本的jdk没有的特性)
Function接口的andThen方法和compose方法
源码:
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
说明:
Compose方法:方法接收一个Function类型的参数,返回一个值。这也是一个标准的Function类型的定义。在compose方法内部也有一个apply方法。在执行compose方法中的apply方法之前,它先执行了before接口的apply方法,也是compose方法的输入参数。然后将before方法执行的返回值作为compose中apply方法的输入参数。实际上是形成了一种链式组合。
andThen方法:该方法与compose方法很类似。不同之处在于,andThen是先执行自身的apply方法,将apply的返回值作为after接口的输入值。相对于compose方法,只是方向的不同
public class FunctionalInterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = getLength1("hello", value -> "hello的长度:"+value, value -> value.length()); //输出:hello的长度:5
System.out.println(str1);
Integer result = getLength2("hello", value -> value, value -> value.length()); //输出:5
System.out.println(result);
}
public static String getLength1(String str1,Function<Integer, String> function1,Function<String,Integer> function2){
/**
* 这里一定要注意,function1和function2的参数类型。
* function2的输出类型与function1的输入类型一定要一致,
* 否则编译不会通过
*/
return function1.compose(function2).apply(str1);
}
public static Integer getLength2(String str1,Function<String, String> function1,Function<String,Integer> function2){
/**
* 这里一定要注意,function1和function2的参数类型。
* function1的输出类型与function2的输入类型一定要一致,(方向相反)
* 否则编译不会通过
*/
return function1.andThen(function2).apply(str1);
}
}
什么是函数式接口(Functional Interface)
其实之前在讲Lambda表达式的时候提到过,所谓的函数式接口,当然首先是一个接口,然后就是在这个接口里面只能有一个抽象方法。
这种类型的接口也称为SAM接口,即Single Abstract Method interfaces。
函数式接口用途
它们主要用在Lambda表达式和方法引用(实际上也可认为是Lambda表达式)上。
如定义了一个函数式接口如下:
@FunctionalInterface
interface GreetingService
{
void sayMessage(String message);
}
那么就可以使用Lambda表达式来表示该接口的一个实现(注:JAVA 8 之前一般是用匿名类实现的):
GreetingService greetService1 = message -> System.out.println("Hello " + message);
关于@FunctionalInterface注解
Java 8为函数式接口引入了一个新注解@FunctionalInterface,主要用于编译级错误检查,加上该注解,当你写的接口不符合函数式接口定义的时候,编译器会报错。
正确例子,没有报错:
@FunctionalInterface
interface GreetingService
{
void sayMessage(String message);
}
错误例子,接口中包含了两个抽象方法,违反了函数式接口的定义,Eclipse报错提示其不是函数式接口。

提醒:加不加@FunctionalInterface对于接口是不是函数式接口没有影响,该注解知识提醒编译器去检查该接口是否仅包含一个抽象方法
函数式接口里允许定义默认方法
函数式接口里是可以包含默认方法,因为默认方法不是抽象方法,其有一个默认实现,所以是符合函数式接口的定义的;
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
interface GreetingService
{
void sayMessage(String message);
default void doSomeMoreWork1()
{
// Method body
}
default void doSomeMoreWork2()
{
// Method body
}
}函数式接口里允许定义静态方法
函数式接口里是可以包含静态方法,因为静态方法不能是抽象方法,是一个已经实现了的方法,所以是符合函数式接口的定义的;
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
interface GreetingService
{
void sayMessage(String message);
static void printHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}函数式接口里允许定义java.lang.Object里的public方法
函数式接口里是可以包含Object里的public方法,这些方法对于函数式接口来说,不被当成是抽象方法(虽然它们是抽象方法);因为任何一个函数式接口的实现,默认都继承了Object类,包含了来自java.lang.Object里对这些抽象方法的实现;
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
interface GreetingService
{
void sayMessage(String message);
@Override
boolean equals(Object obj);
}JDK中的函数式接口举例
java.lang.Runnable,
java.awt.event.ActionListener,
java.util.Comparator,
java.util.concurrent.Callable
java.util.function包下的接口,如Consumer、Predicate、Supplier等