在做大数据量的数据缓存,同时扩展性和可用性很重要的时候,一致性HASH算法是很有用的。
原文“
Thus, it is critical for our hash function to map items consistently: regardless of the existence of multiple, changing views of the system, each item should be mapped to only a small number of machines, and in such a way that all machines get roughly the same load of items.”
摘自论文 http://www8.org/w8-papers/2a-webserver/caching/paper2.html
一致性HASH算法的特点是它把目标的缓存服务器也做Hash。然后一致性Hash算法通过比较目标缓存机器的hash值与key的hash值, 来决定把对象缓存在哪一台缓存服务器。
注:这里的对象是指要被缓存的对象,不是指Java对象。
在了解一致性HASH算法的用处之前,我们有必要了解一下没有一致性Hash算法,我们如何在几台机器上做缓存。假如有两台缓存服务器,我们要把对象均匀地放到两台机器中,我们可能会用这样的算法
1. 确定 key/value;
2. 将Key做hash,得到一个无符号的long型值;
3. 将key的hash值 mod 2;
4. 如果结果是0, 放到第一台机器;如果结果是1,放到第二台机器;
问题来了,如果两台机器的性能不够了,我想增加一台机器,怎么办? 那么改算法,把对hash值对2取模,变成对3取模。于是算法变成这样,
1. 确定key/value;
2. 将key做hash,得到一个无符号的long型值;
3. 将key的hash值 mod 3;
4. 如果结果是0,放到第一台机器;如果结果是1,放到第二台机器;如果结果是2,放到第三台机器。
从上面的pseudocode我们可以看出,随着机器的增加,key的hash算法是需要变换的(机器数不同,对不同的数取模),是不一致的。
为了解决这个问题,一致性HASH算法被提了出来。
一致性HASH如何解决这个问题的。
首先,一致性hash把目标也做一个hash,比如根据目标机器的IP地址等(于是目标服务器也有了一个唯一的无符号long型的hash值)。
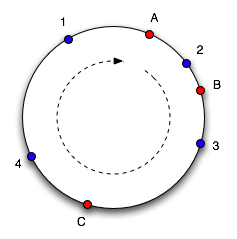
然后,把所有机器加入一个环,例如
图1
在图1中A,B,C是缓存服务器
最后,Key的hash值与环中服务器的hash值做个比较,如果key的hash值落到环中某两个服务器hash值的区间,把对象缓存到区间中的前一个服务去。比如,
key的hash值是123,环中机器A的hash值是100,机器B的hash值是200,那么对象存放在机器A中。
再来看看,环中服务器的增加或减少的情况,比如在环中添加一个服务器,key的hash算法可以不用变。所以说hash算法是一致的。
下面是对一致性HASH算法用于多缓存服务器的模拟。在模拟中,我采用端口号来区分不同的缓存服务器。
1. 一致性Hash
ConsistentHash
package art.programming.cache;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import art.programming.cache.CacheClient.ServerNotAliveException;
public class ConsistentHash {
private final int numberOfReplicas;
// Cache server cycle
private final SortedMap<Long, CacheClient> circle = new TreeMap<Long, CacheClient>();
private HashFunction hashFunction;
public ConsistentHash(HashFunction hashFunction, int numberOfReplicas,
Collection<CacheClient> nodes) {
this.hashFunction = hashFunction;
this.numberOfReplicas = numberOfReplicas;
for (CacheClient node : nodes) {
add(node);
}
}
public void add(CacheClient node) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfReplicas; i++) {
circle.put(hashFunction.hash(node.getCacheServerName() + i), node);
}
}
public void remove(String node) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfReplicas; i++) {
circle.remove(hashFunction.hash(node.toString() + i));
}
}
public void put(String key, String value) {
if (circle.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No cache server is available for now!");
}
long hash = hashFunction.hash(key);
System.out.println("The key has been hashed " + hash);
SortedMap<Long, CacheClient> tailMap = circle.tailMap(hash);
// The hash code of the cache server that store the key/value
long cacheServerHash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? circle.firstKey() : tailMap
.firstKey();
CacheClient cacheClient = circle.get(cacheServerHash);
if (!putValue(cacheClient, key, value)) {
// Recursively find the alive server
removeCacheServerFromCycle(cacheServerHash);
put(key, value);
}
}
private boolean putValue(CacheClient cacheClient, String key, String value) {
try {
cacheClient.put(key, value);
System.out.println(" and it is stored in " + cacheClient.getCacheServerName());
} catch (ServerNotAliveException e) {
return false;
}
return true;
/**
* java art.programming.cache.CacheServer
*
*/
}
private void removeCacheServerFromCycle(long cacheServerHash) {
circle.remove(cacheServerHash);
}
public String get(String key) {
if (circle.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
long hash = hashFunction.hash(key);
System.out.println("The key has been hashed " + hash);
SortedMap<Long, CacheClient> tailMap = circle.tailMap(hash);
// The hash code of the cache server that store the key/value
long cacheServerHash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? circle.firstKey() : tailMap
.firstKey();
CacheClient cacheClient = null;
try {
cacheClient = circle.get(cacheServerHash);
System.out.println("Going to server " + cacheClient.getCacheServerName() + " to fetch the value");
return get(cacheClient, key);
} catch (ServerNotAliveException e) {
System.out.println("The server is not available : " + cacheClient.getCacheServerName());
}
return get(key);
}
private String get(CacheClient cacheClient, String key)
throws ServerNotAliveException {
return cacheClient.get(key);
}
public static void main(String... args){
List<CacheClient> cacheClients = new ArrayList<CacheClient>();
for (int i =0; i < 10; i++){
int port = 7770 + i;
cacheClients.add(new CacheClient(String.valueOf(port)));
}
ConsistentHash consistentHash = new ConsistentHash(new HashFunctionImpl(), 1, cacheClients);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
String command = scanner.nextLine();
String[] commandArr = command.split(",");
if (commandArr[0].equals("put")){
consistentHash.put(commandArr[1], commandArr[2]);
}else{
String result = consistentHash.get(commandArr[1]);
System.out.println("The get ressult is " + result);
}
}
}
}
2. 缓存客户端
package art.programming.cache;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CacheClient {
private String cacheServerName;
private Socket socket;
public CacheClient(String cacheServerName){
this.cacheServerName = cacheServerName;
try {
this.socket = new Socket("localhost", Integer.valueOf(cacheServerName));
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String getCacheServerName(){
return cacheServerName;
}
public void put(String key, String value) throws ServerNotAliveException{
StringBuilder operationKeyValue = new StringBuilder("put,").append(key).append(",").append(value);
try {
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
output.writeUTF(operationKeyValue.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ServerNotAliveException();
}
}
public String get(String key) throws ServerNotAliveException{
StringBuilder operationKeyValue = new StringBuilder("get,").append(key);
String result = null;
try {
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
output.writeUTF(operationKeyValue.toString());
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream (socket.getInputStream());
result = in.readUTF();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ServerNotAliveException();
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String... args) throws ServerNotAliveException{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
CacheClient cacheClient = new CacheClient("7777");
while(true){
String command = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Command: " + command);
cacheClient.put("name", "alex");
}
}
public static class ServerNotAliveException extends Exception{
}
}
3. 缓存服务器
package art.programming.cache;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CacheServer {
private static Map<String, String> cache = new HashMap<String, String>();
public static void main(String... args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException{
String port = args[0];
System.out.println("Binding to the port: " + port);
ServerSocket socketServer = new ServerSocket();
socketServer.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", Integer.valueOf(port)) );
while(true){
Socket socket = socketServer.accept();
try{
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream (socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("Serves the request");
while(true){
String opAndKeyValue = in.readUTF();
System.out.println("Clent request " + opAndKeyValue);
String[] opAndKeyValueArr = opAndKeyValue.split(",");
String op = opAndKeyValueArr[0];
String key = opAndKeyValueArr[1];
System.out.println("The requested operation is " + op + " the key is " + key);
if (op.equals("get")){
out.writeUTF(cache.get(key));
System.out.println("return the value of key " + key +" to the client");
}else{
System.out.println("put the key" + key + " value " + opAndKeyValueArr[2]);
cache.put(key, opAndKeyValueArr[2]);
}
}
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}finally{
}
}
}
}
4. Hash函数
package art.programming.cache;
public interface HashFunction {
long hash(String node);
}
package art.programming.cache;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class HashFunctionImpl implements HashFunction {
public long hash(final String k) {
byte[] bKey = computeMd5(k);
long rv = ((long) (bKey[3] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (bKey[2] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (bKey[1] & 0xFF) << 8) | (bKey[0] & 0xFF);
return rv & 0xffffffffL; /* Truncate to 32-bits */
}
/**
* Get the md5 of the given key.
*/
public byte[] computeMd5(String k) {
MessageDigest md5 = null;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("md5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
md5.update(k.getBytes());
return md5.digest();
}
}
参考资料
http://java.dzone.com/articles/consistent-hashing
http://weblogs.java.net/blog/tomwhite/archive/2007/11/consistent_hash.html