原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/abcwt112/p/7777258.html
原文作者:abcwt112
主题
在工作中遇到1个问题....我们定义了一个Controller基类,所有Springmvc自定义的controller都继承它....在它内部定义一个@Autowired HttpServletRequest request;可不可以? 能不能从这个对象里取requestParamters和attributes? 多线程之间会不会影响?
思考
初次思考,我想这应该是不行的.为什么呢?
注入bean是在spring容器启动的时候...request的实现类是在tomcat里(我使用的servlet容器是tomcat)....我又没在spring的容器里配置这个bean.注入应该是失败的...
退一步说,就算是成功了....那注入的也就是1个对象而已.每次servlet接受到请求都会重新生成1个request...这明显和之前启动的那个对象不同吧....怎么想都不可能成功...
如果确实是这样的....那就没有这篇文章了....后来实践了一下..发现这个注入是可以的.使用起来取数据也没任何问题....
其实我那个时候debug看了一下,基本就知道为什么可以取到数据了..但是我并不知道原理和Spring(Springmvc)的处理流程...所以现在研究了一下并记录下来...
原理
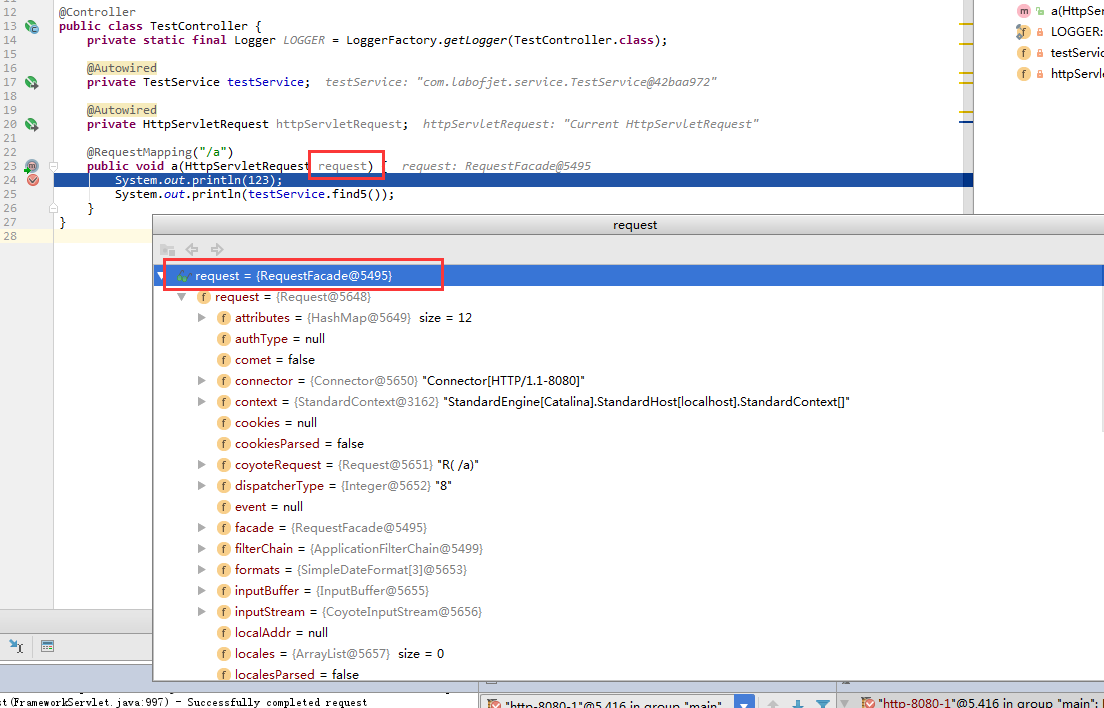
首先给大家看一下在方法中注入request作为参数和在成员域中注入request的 注入的request对象之间的区别....
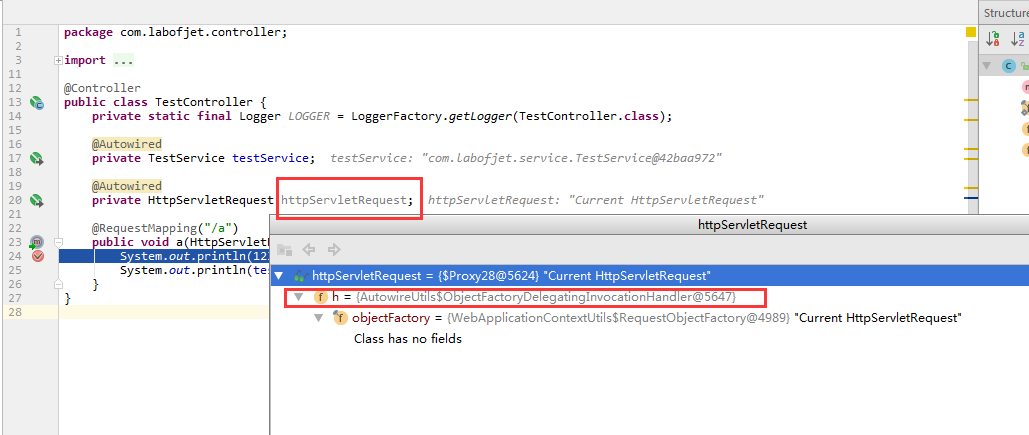
成员域注入的时候注入的是1个代理对象.是 AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler的实例.
方法注入的就是一般tomcat原生的requestFacade对象.
所以这是不同的...
/** * Reflective InvocationHandler for lazy access to the current target object. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory; public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) { this.objectFactory = objectFactory; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); if (methodName.equals("equals")) { // Only consider equal when proxies are identical. return (proxy == args[0]); } else if (methodName.equals("hashCode")) { // Use hashCode of proxy. return System.identityHashCode(proxy); } else if (methodName.equals("toString")) { return this.objectFactory.toString(); } try { return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw ex.getTargetException(); } } }
当代理对象(就是成员域request)的大部分方法被调用的时候,ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler会使用objectFactory获取对象(原生request),再调用对象上的方法.
然后我们来看下XmlWebApplicationContext初始化到请求到进入controller里几个对注入request成员域有影响的步骤.
refresh方法和postProcessBeanFactory方法
ApplicationContext的抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext(基本是所有ac的父类)里定义了ac的refresh方法(包含了使用BeanFactory注入bean)的流程..
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. // 记录开始wac开始初始化的时间,设置激活标记,servlet的相关param设置到env(之前做过1次),校验env中必须的props prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. // 将旧的BF里的bean删掉,新建1个BF,设置部分属性,加载XML配置文件 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 1.设置BF解析bean配置需要用到的一些对象比如env. 2.注册一些BeanPostProcessor比如ApplicationContextAwareProcessor去设置Aware需要的对象 // 3.忽略一些特定class注入的对象,设置一些特定class注入的对象为指定值 // 4.将一些env中的properties map当做bean注册到BF中 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. // 1.设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象 // 2.在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope // 3.把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. // 初始化并调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // 注册BeanPostProcessors并注册到BF中去 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex); // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } } }
其中有1个模板方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这个方法允许AbstractApplicationContext的子类覆盖它并实现对BF的定制(这个时候bean的defination路径已经指定了,但是bean还没加载).
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext覆盖了这个方法
/** * Register request/session scopes, a {@link ServletContextAwareProcessor}, etc. * 1.设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象 * 2.在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope * 3.把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中 * */ @Override protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // 设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig)); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); // 在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext); // 把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中 WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); }
其中有一步
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
这里设置了一些特殊的bean的scope,比如request,session,globalSession,application.(当然这个不是我这篇文章的主题.)
同时设置了一些特殊的autowired bean
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
ServletRequest的实现类(比如HttpServletRequest)被指定使用RequestObjectFactory注入.
RequestObjectFactory
RequestObjectFactory就是1个ObjectFactory就是前面ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler里的ObjectFactory.所以在成员域request对象上调用方法其实就是通过RequestObjectFactory获取对象再调用方法.
/** * Factory that exposes the current request object on demand. */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable { @Override public ServletRequest getObject() { return currentRequestAttributes().getRequest(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Current HttpServletRequest"; } }
/** * Return the current RequestAttributes instance as ServletRequestAttributes. * @see RequestContextHolder#currentRequestAttributes() */ private static ServletRequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() { RequestAttributes requestAttr = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes(); if (!(requestAttr instanceof ServletRequestAttributes)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Current request is not a servlet request"); } return (ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttr; }
RequestObjectFactory的getObject方法很简单,就是调用静态方法
RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getRequest()
RequestContextHolder
public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException { RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes(); if (attributes == null) { if (jsfPresent) { attributes = FacesRequestAttributesFactory.getFacesRequestAttributes(); } if (attributes == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No thread-bound request found: " + "Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, " + "or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? " + "If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, " + "your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet/DispatcherPortlet: " + "In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request."); } } return attributes; }
/** * Return the RequestAttributes currently bound to the thread. * @return the RequestAttributes currently bound to the thread, * or {@code null} if none bound */ public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() { RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get(); if (attributes == null) { attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get(); } return attributes; }
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new NamedThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request attributes"); private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request context");
上面是一些关键方法
所以最终其实request是从threadlocal中取...
FrameworkServlet
那么request是什么时候设置到threadlocal中去的呢?
是在Springmvc的dispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet里操作的.
@Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
不管你是doGet还是doPost还是doXXX方法都是委托processRequest方法去做的.
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } }
其中调用了
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
private void initContextHolders( HttpServletRequest request, LocaleContext localeContext, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { if (localeContext != null) { LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable); } if (requestAttributes != null) { RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable); } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Bound request context to thread: " + request); } }
就是在这里设置到RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去的...
小结
1.在controller中注入的request是jdk动态代理对象,ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler的实例.当我们调用成员域request的方法的时候其实是调用了objectFactory的getObject()对象的相关方法.这里的objectFactory是RequestObjectFactory.
2.RequestObjectFactory的getObject其实是从RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去取值的.
3.请求刚进入springmvc的dispatcherServlet的时候会把request相关对象设置到RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去.
对于原文的补充
原文没有详细描述成员域request注入的具体过程,补充如下:
ApplicationContext的初始化调用过程如下:
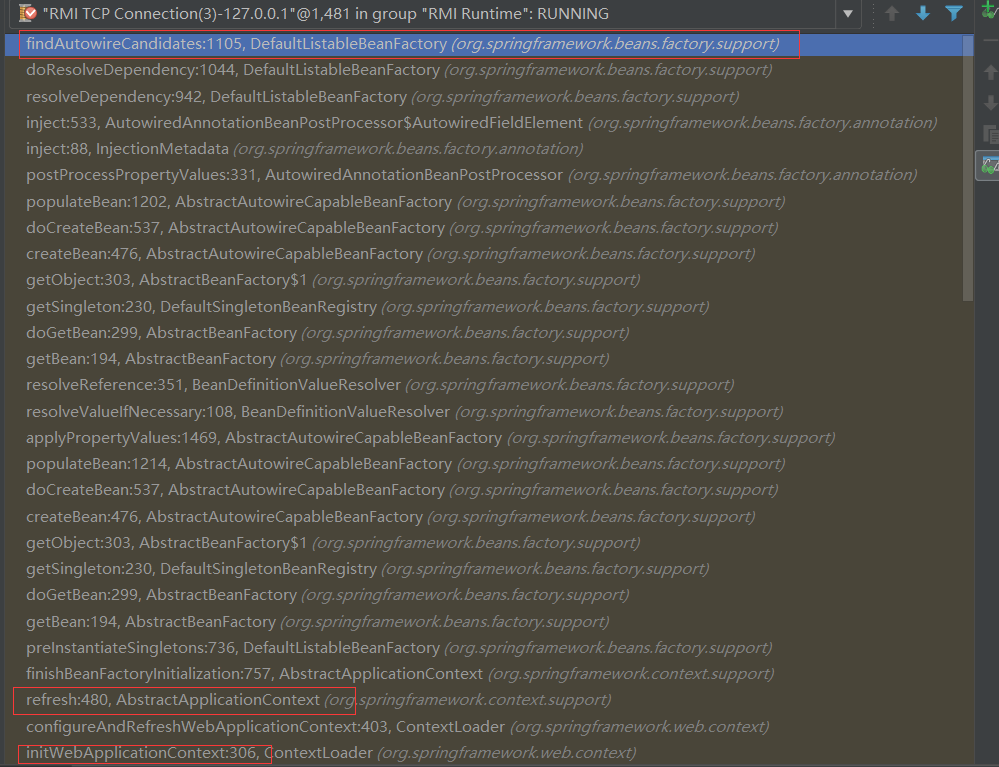
在refresh方法被调用后,会调用org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#findAutowireCandidates
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates( String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) { String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager()); Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(candidateNames.length); for (Class<?> autowiringType : this.resolvableDependencies.keySet()) { if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) { Object autowiringValue = this.resolvableDependencies.get(autowiringType); autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType); if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) { result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue); break; } } } for (String candidateName : candidateNames) { if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidateName) && isAutowireCandidate(candidateName, descriptor)) { result.put(candidateName, getBean(candidateName)); } } if (result.isEmpty()) { DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch(); for (String candidateName : candidateNames) { if (!candidateName.equals(beanName) && isAutowireCandidate(candidateName, fallbackDescriptor)) { result.put(candidateName, getBean(candidateName)); } } } return result; }
该方法内部会调用:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils#resolveAutowiringValue
public static Object resolveAutowiringValue(Object autowiringValue, Class<?> requiredType) { if (autowiringValue instanceof ObjectFactory && !requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) { ObjectFactory<?> factory = (ObjectFactory<?>) autowiringValue; if (autowiringValue instanceof Serializable && requiredType.isInterface()) { autowiringValue = Proxy.newProxyInstance(requiredType.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] {requiredType}, new ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(factory)); } else { return factory.getObject(); } } return autowiringValue; }
可以看到,如果需要注入的对象是接口类型的话,则为其创建代理对象。