前言
Django中的视图的概念是一类具有相同功能和模板的网页的集合。通俗一点来说,就是你平常打开浏览器,看到浏览器窗口展示出来的页面内容,那就是视图。
前面一章通过浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8000能在页面上展示出hello world的纯文本内容,通常我们打开浏览器页面,展示的是一个html页面,本篇讲下如何打开html页面。
新建应用
上一篇通过"django-admin startproject helloworld"是创建项目,一个项目下可以有多个应用(app)。打开cmd,cd到manage.py所在目录使用如下指令创建一个应用
python manage.py startapp xjyn
新建成功后,生成的目录结果如下
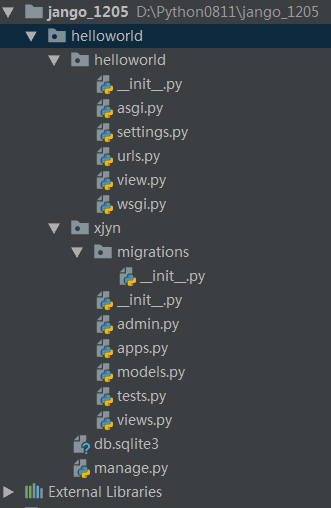
setting配置
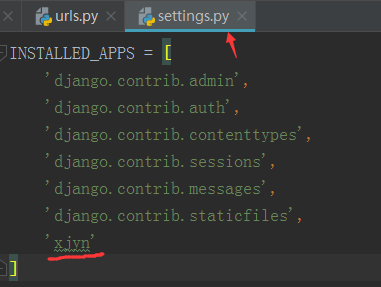
新建应用后,一定要在setting.py脚本里面,把刚才新建的引用名称添加到INSTALLED_APPS里,要不然无法识别到新增的这个引用,如下最后一行。
templates模板
在xjyn目录下新建一个templates包(包名必须是templates),再新建一个a.html文件(名称可随意命名),写入以下内容;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>我就是最漂亮的烟火</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
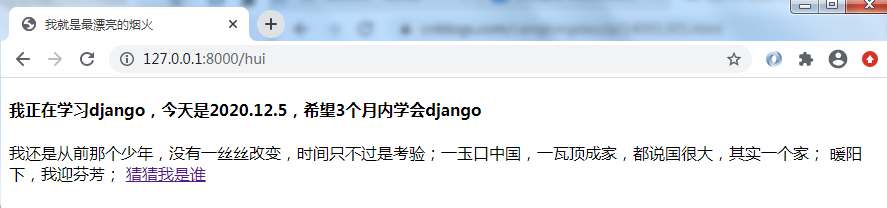
<h4>我正在学习django,今天是2020.12.5,希望3个月内学会django</h4>
<p>我还是从前那个少年,没有一丝丝改变,时间只不过是考验;一玉口中国,一瓦顶成家,都说国很大,其实一个家;
暖阳下,我迎芬芳;
<a href="https://www.baidu.com" target="_blank">猜猜我是谁</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
视图与url
html的内容页面有了,接下来就是如何能让他在指定的url地址上展示出来了,在xjyn/views.py里写视图函数
在hello/views.py里写视图函数,把上一篇新建的view.py里面全部内容统一放到hello/views.py下管理
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("hello world! come on")
def hui(request):
return render(request,'a.html')
在helloworld/urls.py里添加url访问路径
#helloworld/helloworld/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from xjyn import views
urlpatterns=[
url('^$',views.index),
url('^hui$',views.hui),
]
接下来在浏览器输入地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/hui 就能访问到a.html页面啦