目录
一、索引测试
1.准备测试数据
#1. 准备表
create table t1(
id int,
name varchar(20),
gender char(6),
email varchar(50)
);
#2. 创建存储过程,实现批量插入记录
delimiter $$ #声明存储过程的结束符号为$$
create procedure auto_insert1()
BEGIN
declare i int default 1;
while(i<3000000)do #300w数据
insert into t1 values(i,'mm','male',concat('mm',i,'@boy'));
set i=i+1;
end while;
END$$ #$$结束
delimiter ; #重新声明分号为结束符号
#3. 查看存储过程
show create procedure auto_insert1G
#4. 调用存储过程
call auto_insert1(); # 过程会很慢,一分钟后可强制结束,也已将创建了一些
2.未创建索引前的查询速度缓慢
#无索引:从头到尾扫描一遍,所以查询速度很慢
mysql> select * from s1 where id=333;
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| id | name | gender | email |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| 333 | mm| male | cm333@oldboy |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
1 row in set (1.33 sec)
mysql> explain select * from s1 where id=333;
mysql> select * from s1 where email='cm333@oldboy';
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| id | name | gender | email |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| 333 | cm333 | male | cm333@oldboy |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
1 row in set (1.50 sec)
3.加上索引后查询速度极快
1. 一定是为搜索条件的字段创建索引,比如select * from s1 where id > 5;就需要为id加上索引
2. 在表中已经有大量数据的情况下,建索引会很慢,且占用硬盘空间,插入删除更新都很慢,只有查询快
比如create index idx on s1(id);会扫描表中所有的数据,然后以id为数据项,创建索引结构,存放于硬盘的表中。
建完以后,再查询就会很快了
mysql> create index idx on s1(id);
3. 需要注意的是:innodb表的索引会存放于s1.ibd文件中,而myisam表的索引则会有单独的索引文件table1.MYI
mysql> select * from s1 where id=333;
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| id | name | gender | email |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
| 333 | cm333 | male | cm333@oldboy |
+------+---------+--------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
# 建立完索引,那个数据的ibd文件是变大了,但是如果删除完索引,但是那个ibd文件却不会变小,这是一个bug
# 因为ibd里面的数据和索引里面的内容都放在ibd文件里了
二、正确使用索引
1、索引命中也未必会加速
并不是说我们创建了索引就一定会加快查询速度,若想利用索引达到预想的提高查询速度的效果,我们在添加索引时,必须遵循以下问题
# 1、如何正确使用索引
1、以什么字段的值为基础构建索引
2、最好是不为空、唯一、占用空间小的字段
# 2、针对全表查询语句如何优化?
应用场景:用户想要浏览所有的商品信息
select count(id) from s1;
如何优化:
开发层面分页查找,用户每次看现从数据中拿
# 3、针对等值查询
以重复度低字段为基础创建索引加速效果明显
create index xxx on s1(id);
select count(id) from s1 where id = 33;
以重复度高字段为基础创建索引加速效果明显
create index yyy on s1(name);
select count(id) from s1 where name="egon"; -- 速度极慢
select count(id) from s1 where name!="egon"; -- 速度快
select count(id) from s1 where name="yy"; -- 速度快
以占用空间大字段为基础创建索引加速效果不明显
# 总结:给重复低、且占用空间小的字段值为基础构建索引
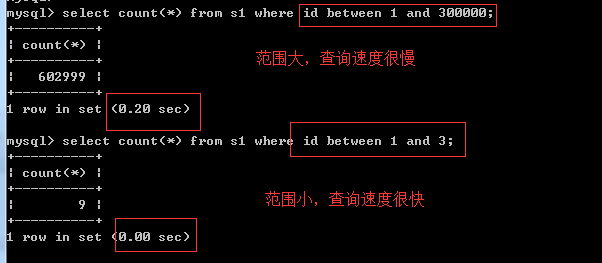
# 4、关于范围查询
select count(id) from s1 where id=33;
select count(id) from s1 where id>33;
select count(id) from s1 where id>33 and id < 36;
select count(id) from s1 where id>33 and id < 1000000;
# 总结:innodb存储能加速范围查询,但是查询范围不能特别大
5、关于条件字段参与运算
select count(id) from s1 where id*12 = 10000;
select count(id) from s1 where id = 10000/12;
select count(id) from s1 where func(id) = 10000/12;
# 总结:不要让条件字段参与运算,或者说传递给函数
范围问题,或者说条件不明确,条件中出现这些符号或关键字:>、>=、<、<=、!= 、between...and...、like
2、大于号、小于号
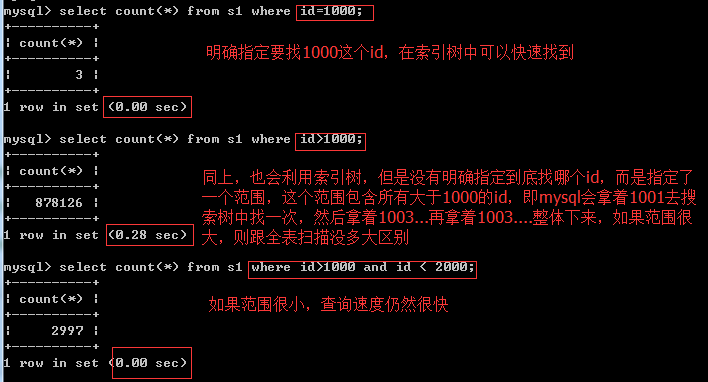
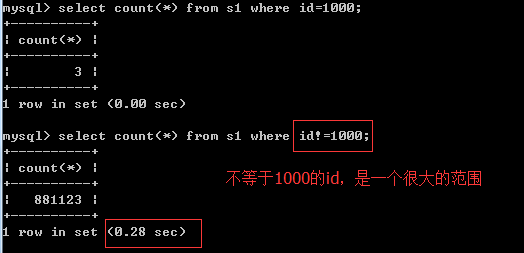
3、不等于!=
4、 between …and…
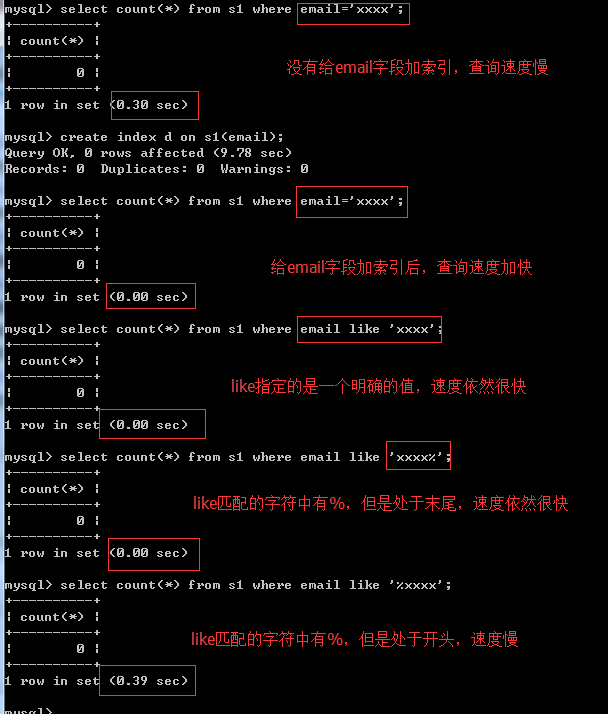
5、like
like:%或者_应该放在右边,并且左边的字符应该尽可能地精确一些,这样锁定的范围才会小一些,例如like "egon3%"而不是like "%egon3"、like "eg%"
6、索引下推技术
索引下推技术默认是开启的
# 删除索引xxx
mysql> drop index xxx on t1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> desc t1;
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| gender | char(6) | YES | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
+--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# and查询
# 对于连续多个and: mysql会按照联合索引,从左到右的顺序找一个区分度高的索引字段(这样便可以快速锁定很小的范围),加速查询。
# 区分度最高的是email(命中普通索引),所以制作联合索引为(email,name,gender)
mysql> explain select count(id) from t1 where name="nana" and email="nana666@haha" and gender="male";
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | ref | zzz | zzz | 203 | const | 1 | Using index condition; Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+------------------------------------+
# or查询
# 对于连续多个or: mysql会按照条件的顺序,从左到右依次判断,即联合索引为(name,email,gender),并不会加速查询
mysql> explain select count(id) from t1 where name="nana" or email="nana666@haha" or gender="male";
and与or的逻辑:
条件1 and 条件2:所有条件都成立才算成立,但凡要有一个条件不成立则最终结果不成立
条件1 or 条件2:只要有一个条件成立则最终结果就成立
and连接的多个条件属于小范围,or连接的多个条件属于大范围。
对于连续多个and:
mysql会按照联合索引,从左到右的顺序找一个区分度高的索引字段(这样可以快速锁定很小的范围),加速查询。
对于连续多个or:
mysql会按照条件的顺序,从左到右依次判断,并不会加速查询。
7、其他情况:不走索引
# 1)没有查询条件,或者查询条件没有用到索引列
没有查询条件
mysql> explain select * from world.city;
没有用索引列做条件
mysql> explain select * from world.city where 1=1;
mysql> explain select * from world.city where name='shanghai';
# 2)查询结果集是原表中的大部分数据,应该是25%以上
如果生产中,必须有这种全表扫描的需求不走索引
mysql> explain select * from world.city where population > 50;
如果业务允许,可以使用limit控制,可以走索引
mysql> explain select * from world.city where population>50 limit 10;
如果业务不允许,可以使用缓存
前面加上缓存,memcached,redis
# 3)索引本身失效,统计数据不真实
反复修改,插入数据,索引被修改坏了,每次都会进行排序
# 4)查询条件使用函数在索引列上或者对索引列进行运算,运算包括(+,-,*等)
mysql> explain select * from world.city where id=9;
mysql> select * from tb1 where reverse(email) = 'egon';
查询ID等于9的数据,会导致不走索引
mysql> explain select * from world.city where id-1=8;
查询ID等于9的数据,可以在后面作加减
mysql> explain select * from world.city where id=8+1;
# 5)隐式转换,会导致索引失效
如果列是字符串类型,传入条件是必须用引号引起来,不然...
select * from tb1 where email = 999;
创建一个表
create table test(id int, name varchar(20), phonenum varchar(10));
插入几条数据
insert into test values(1,'jc','110'),(2,'xf',119),(3,'jh',120);
建立索引,没有相同值可以给唯一索引
alter table test unique key idx_num(phonenum);
查看索引
show index from test;
查询语句级别
不走索引
explain select * from test where phonenum=110;
走索引
explain select * from test where phonenum='110'; -- 引号可能导致大事故
因为这一列是varchar类型,必须以字符来查询
# 6)<> 和 not in , or 也不走索引
mysql> explain select * from test where phonenum <> '120';
mysql> explain select * from test where phonenum not in (120);
mysql> explain select * from test where telnum='110' or telnum='119';
使用union all可以走索引
mysql> explain select * from test where telnum='110' union all select * from test where telnum='119';
# 7)like模糊查询%在最前面,不走索引
%在前面不走索引
mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode like '%HN';
%在后面,走索引
mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode like 'CH%';
放在后面也不是一定了,因为涉及到第二点结果的占总数据的比例
%在最前面的搜索需求,建议使用elasticsearch ES ELK(E) 搜索引擎式的 数据库
# 8)单独引用联合索引里非第一位置的索引列
组合索引最左前缀
如果组合索引为:(name,email)
name and email -- 命中索引
name -- 命中索引
email -- 未命中索引
# 9)排序条件为索引,则select字段必须也是索引字段,否则无法命中
- order by
select name from s1 order by email desc;
当根据索引排序时候,select查询的字段如果不是索引,则速度仍然很慢
select email from s1 order by email desc;
特别的:如果对主键排序,则还是速度很快:
select * from tb1 order by nid desc;
8、总结索引使用原则
- 1、在创建索引的时候,会把该列所有的数据按照btree的方式进行排序
- 2、为常作为查询条件的字段建立索引
- 3、限制索引的数目,不要每列都创建索引
每个索引都需要占用磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。
修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦。越多的索引,会使更新表变得很浪费时间。
- 4、在同一列上,尽量避免创建多个索引,可以创建多个但是它们是有优先级的,先走一个就不会再走另一个索引了;
alter table student add index idx_name(name);
alter table country add unique key uni_name(name);
- 5、避免对大列建索引,在数据很长的列上创建前缀索引
- 6、如果可以创建唯一索引,就创建唯一索引(该列的数据不重复),查询速度快
- 7、不要对重复度高的字段创建索引
- 8、索引不要参与计算
- 9、为经常要排序,分组,联合操作的列,创建联合索引
经常需要ORDER BY、GROUP BY、DISTINCT和UNION等操作的字段,排序操作会浪费很多时间。
如果为其建立索引,可以有效地避免排序操作
- 10、尽量使用前缀来索引
创建索引的时候,可以给该列所有数据进行排序
create index xxxx on tb(title(19)) # text类型,必须制定长度
- 11、删除不再使用或者很少使用的索引
表中的数据被大量更新,或者数据的使用方式被改变后,原有的一些索引可能不再需要。数据库管理员应当定期找出这些索引,将它们删除,从而减少索引对更新操作的影响。
- 12、避免使用select *
- 13、count(1)或count(列) 代替 count(*),ps:mysql中没有差别了
- 14、创建表时尽量时 varchar 代替 char
- 15、表的字段顺序固定长度的字段优先
- 16、使用连接(JOIN)来代替子查询(Sub-Queries)
- 17、连表时注意条件类型需一致
9、联合索引与最左前缀匹配原则
条件中需要用到多个字段,并且多次查询中的多个字段都包含某一个字段,即可创建联合索引
什么时候创建联合索引?
条件中需要用到多个字段,并且多次查询中的多个字段都包含某一个字段。
创建联合索引需要注意的问题:
重复度低且占用空间较小的字段应该尽量往左放,让其称为最左前缀。
使用联合索引,满足加速条件的规则:
使用select查询数据的时候,where条件中必须包含最左前缀的字段,命中索引才可以实现加速
三、慢查询优化的基本步骤
# 0.先运行看看是否真的很慢,注意设置SQL_NO_CACHE
# 1.where条件单表查,锁定最小返回记录表。这句话的意思是把查询语句的where都应用到表中返回的记录数最小的表开始查起,单表每个字段分别查询,看哪个字段的区分度最高
# 2.explain查看执行计划,是否与1预期一致(从锁定记录较少的表开始查询)
# 3.order by limit 形式的sql语句让排序的表优先查
# 4.了解业务方使用场景
# 5.加索引时参照建索引的几大原则
# 6.观察结果,不符合预期继续从0分析
四、explain使用
之前总说到查询速度、查询效率,那使用什么去查看查询的快慢呢,就用explain
1.explain用法
我们之前查询过SQL、
#1.查询中国和美国的城市 or 和 in
mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA';
mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
#2.union all (联合查询) 讲索引的时候再说
mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode=‘USA’ union all select * from world.city where countrycode=‘CHN’;
#3.explain用法
explain select * from city where countrycode='USA' or countrycode='CHN';
explain select * from city where countrycode in ('USA','CHN');
explain select * from world.city where countrycode='USA' union all select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN';
2.explain结果注解
mysql> explain select id from student where id=2;
#ID:
id相同,执行顺序由上至下
id不同,如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id值越大优先级越高,越先被执行
#type:
查询使用了哪种类型
#possible_keys:
可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个
#key:
实际使用的索引,如果为NULL,则没有使用索引
#key_len (可以使用前缀索引控制)
表示索引中使用的字节数,可通过该列计算查询中使用的索引的长度,在不损失精确性的情况下,长度越短越好。
#ref
级别是否在ref之上
#rows
根据表统计信息及索引选用情况,大致估算出找到所需的记录所需要读取的行数,也就是说,用的越少越好
#Extra
Using filesort:使用order by时
Using temporary:使用排序order by和分组查询group by时
3.查询数据种类
1)全表扫描
#1.什么是全表扫描
在explain语句结果中type为ALL,MySQL将遍历全表以找到匹配的行
#2.什么时候出现全表扫描?
1.业务确实要获取所有数据
mysql> explain select * from city;
2.不走索引导致的全表扫描
2.1 没索引
mysql> explain select * from city where District=‘shanghai’;
#创建索引后速度会提升,变成索引扫描了
mysql> alter table city add index idx_District(District);
mysql> explain select * from city where District=‘shanghai’;
2.2 索引创建有问题
2.3 语句有问题
2)索引扫描
#常见的索引扫描类型:
1)index 全索引扫描,index与ALL区别为index类型只遍历索引树(性能也不高)
mysql> explain select population from city;
2)range 范围查询,只检索给定范围的行,使用一个索引来选择行,一般来说,SQL语句只要达到range级别,就可以了
mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode in (‘USA’,‘CHN’);
3)ref 精确查找,匹配条件有普通索引
#先给population列一个索引
mysql> alter table city add index idx_population(population);
#然后查询
mysql> explain select * from city where population=300000000;
4)eq_ref 类似ref,区别就在使用的索引是唯一索引
explain select city.name,city.countrycode,country.name from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.population<100;
5)const 使用的索引是主键索引
mysql> explain select * from country where code=‘CHN’;
6)system system是const类型的特例,当查询的表只有一行的情况下
mysql> delete from country where code != ‘CHN’;
#有外键删除不了
7)null 执行过程不用访问表或索引,直接选取索引列的最小值
mysql> explain select min(population) from city;