1、持久化上下文
JPA中有持久化上下文存在,但是开发者不直接与之打交道,持久化上下文在应用程序中是透明的。
我们可以把持久化上下文理解成一个Map,该Map在事务开始的时候创建,在事务结束的时候销毁。在事务中,可以把对象关联到持久化上下文中,比如说findById方法,在查出来的时候,这个对象就跟持久化上下文关联起来了,可以理解成于放入Map中。
持久化上下文特性:
①、持久化上下文的生命周期与系统事务一致
②、持久化上下文提供自动脏检查
③、持久化上下文是一级缓存
第①个比较好理解,第②条解释如下:
在事务提交的时候,JPA会执行一个脏检查机制,会检查持久化上下文中的对象状态和数据库中的状态是否一致,如果不一致,就会根据持久化上下文中的状态去更新数据库中的状态。但是这个动作只有在数据库事务提交的时候在会做,如果事务回滚了,不会做这个动作。
可以调用JpaRepository提供的flush或saveAndFlush方法立刻同步状态到数据库,而不是等到事务提交的时候在同步。需要注意的是,这里的立刻同步到数据库是指将修改/删除操作所执行的SQL语句先执行,此时事务并没有提交,只有在事务提交后,这个更新/删除才会起作用。
可以通过下面的例子来理解:
组织实体:
/** * 组织 * @author caofanqi */ @Getter @Setter @Entity @Table(name = "jpa_organization") @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Organization extends AbstractID{ private String code; private String name; }
数据库中插入一条数据如下:
测试用例1:
/** * 观察update语句和success打印的顺序,没有调用flush方法时,success在update语句之前打印,因为此时事务还没有提交,没有将修改同步到数据库。 * 我们可以使用flush方法,将修改立即同步到数据库。 */ @Test void test1(){ TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition()); Optional<Organization> organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); Organization organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); organization.setName("xxxx"); // organizationRepository.flush(); System.out.println("success"); //提交事务 transactionManager.commit(status); //回滚事务 // transactionManager.rollback(status); }
没有调用flush方法时控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: select organizati0_.id as id1_14_0_, organizati0_.code as code2_14_0_, organizati0_.name as name3_14_0_ from cfq_jpa_organization organizati0_ where organizati0_.id=?
success
Hibernate: update cfq_jpa_organization set code=?, name=? where id=?
将数据库还原为初始状态,调用flush方法时控制台打印如下:
Hibernate: select organizati0_.id as id1_14_0_, organizati0_.code as code2_14_0_, organizati0_.name as name3_14_0_ from cfq_jpa_organization organizati0_ where organizati0_.id=? Hibernate: update cfq_jpa_organization set code=?, name=? where id=? success
第③条,可以理解为:在事务中查询时,首先会在持久化上下文中查找。只有在执行findById方法的时候,才会使用。
可以通过以下的例子来理解:
OrganizationRepository添加如下方法:
Optional<Organization> findOrganizationById(Long id); @Query(value = "select o from Organization o where o.id = :id ") Optional<Organization> selectById(Long id);
测试用例2及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 两次findById方法,只执行了一次SQL */ @Test @Transactional void test2(){ organizationRepository.findById(1L); organizationRepository.findById(1L); }

测试用例3及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 使用方法派生查询出数据,在使用findById方法查询,只执行一次SQL */ @Test @Transactional void test3(){ organizationRepository.findOrganizationById(1L); organizationRepository.findById(1L); }

测试用例4及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 使用@Query查询出数据,在使用findById方法查询,只执行一次SQL */ @Test @Transactional void test4(){ organizationRepository.selectById(1L); organizationRepository.findById(1L); }

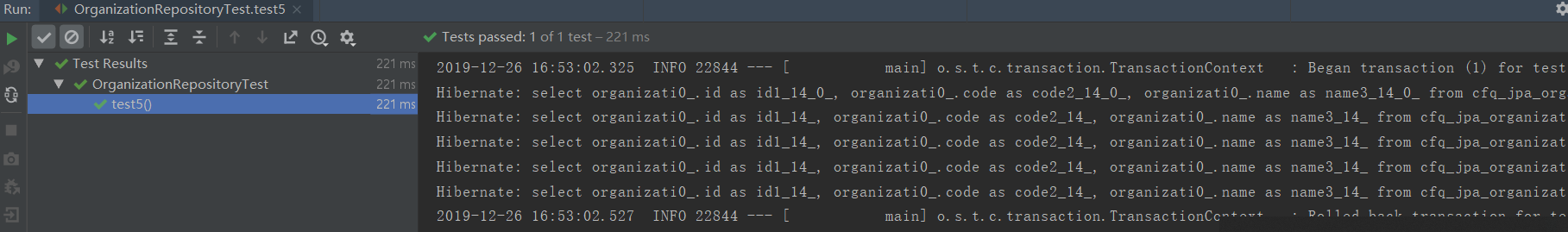
测试用例5及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 五句SQL */ @Test @Transactional void test5(){ organizationRepository.findById(1L); organizationRepository.selectById(1L); organizationRepository.selectById(1L); organizationRepository.findOrganizationById(1L); organizationRepository.findOrganizationById(1L); }
需要注意的点:
1、在事务中,对持久性上下文中的对象进行修改的话,再执行非findById查询时,不调用flush方法也会立刻同步,而不是事务提交时在同步。执行findById查询时,会先从持久化上下文中查找,找到了不再执行查询SQL。
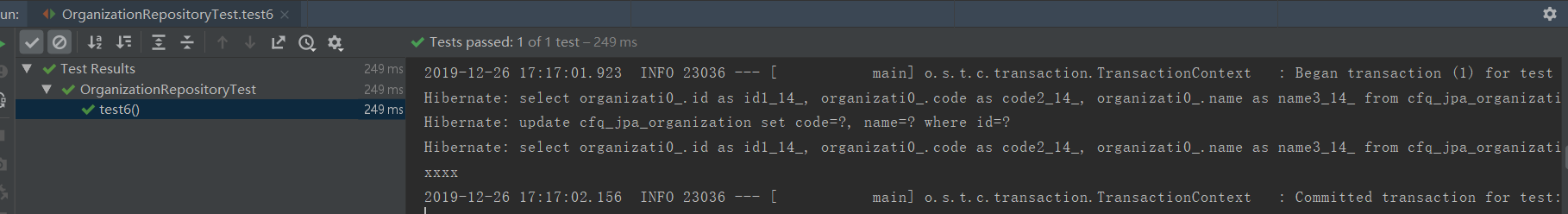
测试用例6及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 对持久性上下文中的对象进行修改的话,再执行非findById查询时,不调用flush方法也会立刻同步,而不是事务提交时在同步 * select,update,select,打印xxxx 3句SQL */ @Test @Rollback(false) @Transactional void test6(){ Optional<Organization> organizationOp = organizationRepository.findOrganizationById(1L); Organization organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); organization.setName("xxxx"); organizationOp = organizationRepository.findOrganizationById(1L); organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); System.out.println(organization.getName()); }
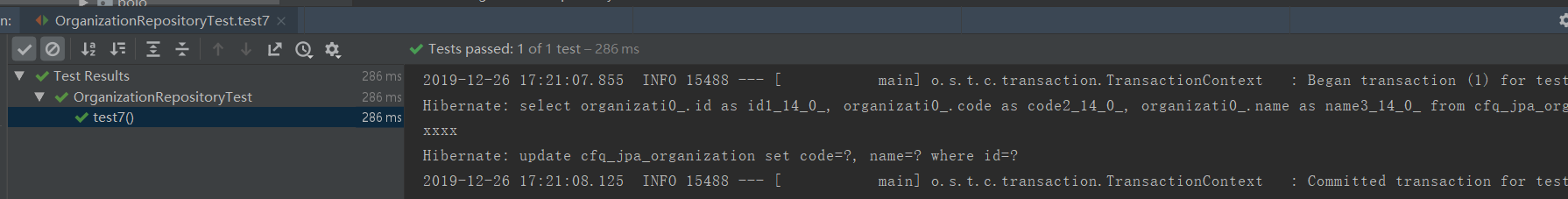
测试用例7及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 对持久性上下文中的对象进行修改的话,执行findById查询时,会先从持久化上下文中查找,找到了不再执行查询SQL * select,打印xxxx ,update 2句SQL */ @Test @Rollback(false) @Transactional void test7(){ Optional<Organization> organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); Organization organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); organization.setName("xxxx"); organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); System.out.println(organization.getName()); }
2、@Query+@Modifying对数据的修改不会同步到持久化上下文中。
如没有设置clearAutomatically属性,或clearAutomatically设置为false时,如果修改了持久化上下文中的对象,并再次使用findById方法查询到持久化上下文中的对象时,会导致查到未修改的对象。
OrganizationRepository新增方法:
@Modifying @Query("update Organization o set o.name = :name where o.id = :id") void updateNameById1(Long id,String name);
测试用例8及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 当@Modifying属性clearAutomatically为false时,修改后不清空持久化上下文, * 使用findById查询时,如果从持久化上下文中找到要查询的对象,那么该对象状态是未修改之前的。 */ @Test @Rollback(false) @Transactional void test8(){ //向持久化上下文中存放对象 Optional<Organization> organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); //如果使用@Query+@Modifying进行操作对象时,持久化上下文中的对象不会受到影响 organizationRepository.updateNameById1(1L,"xxxx"); //findById方法会取持久化上下文中的对象,(name没有修改为xxxx的),打印的是组织001 organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); Organization organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); System.out.println(organization.getName()); }
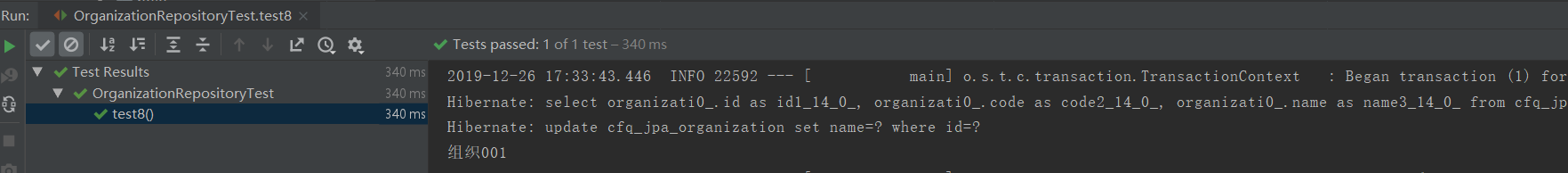
因对上面的问题,我们可以设置clearAutomatically为true,修改后直接清空持久化上下文,这样后面的findById方法,因为在持久化上下文中找不到数据,就会执行select进行查询。
OrganizationRepository新增方法:
@Modifying(clearAutomatically = true) @Query("update Organization o set o.name = :name where o.id = :id") void updateNameById2(Long id,String name);
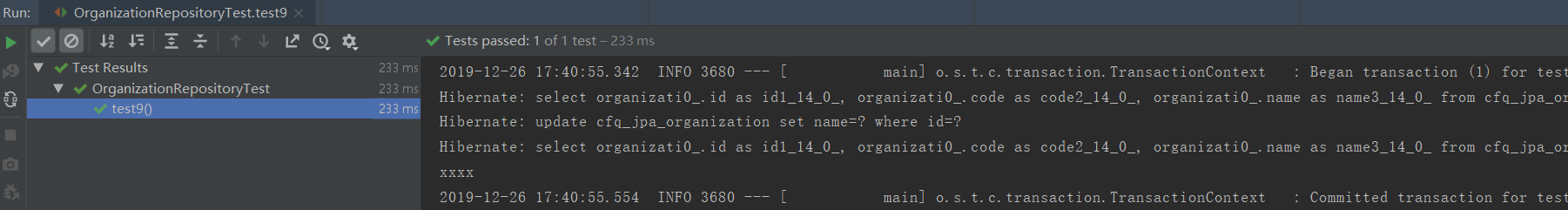
测试用例9及执行结果打印SQL:
/** * 当@Modifying属性clearAutomatically为true时,修改后清空持久化上下文 * 使用findById查询时,因为持久化上下文被清空了,所以会再次执行select语句。 */ @Test @Rollback(false) @Transactional void test9(){ //向持久化上下文中存放对象 Optional<Organization> organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); //如果使用@Query+@Modifying进行操作对象时,持久化上下文中的对象不会受到影响,但设置了清空持久化上下文 organizationRepository.updateNameById2(1L,"xxxx"); //因为持久化上下文中是空的,所以findById会执行select语句,打印的是xxxx organizationOp = organizationRepository.findById(1L); Organization organization = organizationOp.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("查询不到数据")); System.out.println(organization.getName()); }
源码地址:https://github.com/caofanqi/study-spring-data-jpa