先来一个Demo,然后再来进行源码分析:
一、示例
1.创建一个Bean,并实现一些XxxAware 接口
public class Book implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private String bookName; public Book() { System.out.println("bean实例化 "); } public void setBookName(String bookName) { this.bookName = bookName; System.out.println("设置属性值"); } public String getBookName() { return bookName; } // 实现 BeanNameAware 的方法 @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法"); } // 实现 BeanFactoryAware 的方法 @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法"); } // 实现 ApplicationContextAware 的方法 @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法"); } // 自定义初始化方法 @PostConstruct public void springPostConstruct() { System.out.println("@PostConstruct"); } // 实现 InitializingBean 的方法 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法"); } // init-method public void myPostConstruct() { System.out.println("调用 init-method 属性配置的初始化方法"); } // 自定义销毁方法 @PreDestroy public void springPreDestory() { System.out.println("@PreDestory"); } // 实现 DisposableBean @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法"); } // destroy-method public void myPreDestory() { System.out.println("调用 destroy-method 属性配置的销毁方法"); System.out.println("---------------destroy-----------------"); } @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("------inside finalize-----"); } }
2.自定义一个 BeanPostProcessor
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof Book) { System.out.println("调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法"); } return bean; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof Book) { System.out.println("调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法"); } return bean; } }
3.bean-lifecycle.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 扫描bean --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.lifecycle" /> <!-- 实现了用户自定义初始化和销毁方法 --> <bean id="book" class="com.lifecycle.Book" init-method="myPostConstruct" destroy-method="myPreDestory"> <!-- 注入bean 属性名称 --> <property name="bookName" value="《thingking in java》" /> </bean> <!--引入自定义的BeanPostProcessor --> <bean class="com.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor" /> </beans>
4.测试
public class SpringBeanLifecycleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-lifecycle.xml"); Book book = (Book) context.getBean("book"); System.out.println("开始使用bean:book.bookName = " + book.getBookName()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy(); } }
打印结果:
bean实例化 设置属性值 调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法 调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法 调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法 @PostConstruct 调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 调用 init-method 属性配置的初始化方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法 开始使用bean:book.bookName = 《thingking in java》 @PreDestory 调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法 调用 destroy-method 属性配置的销毁方法 ---------------destroy-----------------
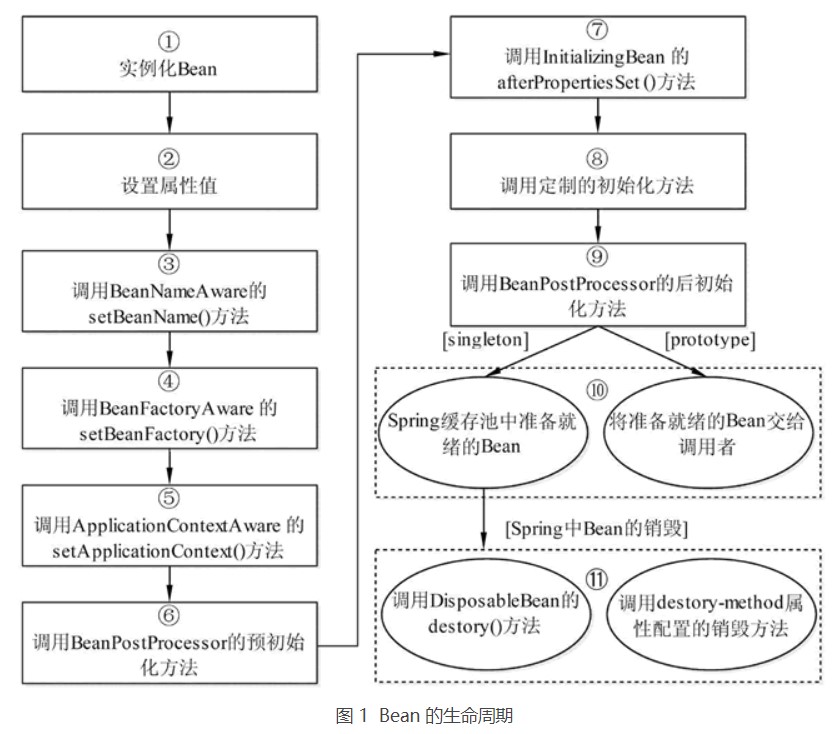
Bean的生命周期总结如图
二、完成的示例
接下来我们再来看一个完成版的Bean生命周期
1.创建一个子类,继承Book类,并实现一些XxxAware类
public class SubBookClass extends Book implements BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware, EmbeddedValueResolverAware, ResourceLoaderAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware { private String bookSystem; public SubBookClass() { super(); System.out.println("子类:bean实例化 "); } public String getBookSystem() { return bookSystem; } public void setBookSystem(String bookSystem) { System.out.println("子类:设置属性值"); this.bookSystem = bookSystem; } // 实现 BeanClassLoaderAware 的方法 public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) { System.out.println("子类:调用 BeanClassLoaderAware 的 setBeanClassLoader 方法"); } // 实现 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的方法 public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { System.out.println("子类:调用 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的 setApplicationEventPublisher 方法"); } // 实现 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 的方法 public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) { System.out.println("子类:调用 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 的 setEmbeddedValueResolver 方法"); } // 实现 EnvironmentAware 的方法 public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { System.out.println("子类:调用 EnvironmentAware 的 setEnvironment 方法"); } // 实现 MessageSourceAware 的方法 public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) { System.out.println("子类:调用 MessageSourceAware 的 setMessageSource 方法"); } // 实现 ResourceLoaderAware 的方法 public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { System.out.println("子类:调用 ResourceLoaderAware 的 setResourceLoader 方法"); } }
2.sub-bean-lifecycle.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="bookClass" class="com.lifecycle.SubBookClass" init-method="myPostConstruct" destroy-method="myPreDestory"> <property name="bookSystem" value="Java System" /> </bean> <bean class="com.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor" /> </beans>
3.测试
public class SpringBeanLifecycleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 为面试而准备的Bean生命周期加载过程 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-lifecycle.xml"); Book book = (Book) context.getBean("book"); System.out.println("开始使用bean:book.bookName = " + book.getBookName()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy(); System.out.println(" "); // 完整的加载过程,当然了解的越多越好 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sub-bean-lifecycle.xml"); SubBookClass subBookClass = (SubBookClass) applicationContext.getBean("bookClass"); System.out.println("BookSystemName = " + subBookClass.getBookSystem()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook(); } }
打印结果:
bean实例化 :com.lifecycle2.Book@22eeefeb 设置属性值:bookName《thingking in java》 调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法 book 调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法 调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法 @PostConstruct 调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 调用 init-method 属性配置的初始化方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法 开始使用bean:book.bookName = 《thingking in java》 @PreDestory 调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法 调用 destroy-method 属性配置的销毁方法 ---------------destroy----------------- bean实例化 :com.lifecycle2.SubBookClass@27fe3806 子类:bean实例化 子类:设置属性值 调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法 bookClass 子类:调用 BeanClassLoaderAware 的 setBeanClassLoader 方法 调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法 子类:调用 EnvironmentAware 的 setEnvironment 方法 子类:调用 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 的 setEmbeddedValueResolver 方法 子类:调用 ResourceLoaderAware 的 setResourceLoader 方法 子类:调用 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的 setApplicationEventPublisher 方法 子类:调用 MessageSourceAware 的 setMessageSource 方法 调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法 调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 调用 init-method 属性配置的初始化方法 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法 BookSystemName = Java System 调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法 调用 destroy-method 属性配置的销毁方法 ---------------destroy-----------------
- 创建Bean:加载配置的时候
- 使用Bean
- 销毁Bean:调用 destroy 方法的时候
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { // 1.实例化bean instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; // 省略部分代码 ... // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { // 2.属性赋值 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { // 3.初始化bean exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } // 省略部分代码 ... return exposedObject; }
通过doCreateBean 方法,我们知道创建Bean大概有3大步骤:
实例化 bean
属性注入
初始化 bean
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { // 3.1 调用实现XxxAware类的方法 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { // 3.1 调用Aware的方法 // 3.1 调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法 // 3.1 调用 BeanClassLoaderAware 的 setBeanClassLoader // 3.1 调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 3.2 执行 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法 // 3.2 调用 EnvironmentAware 的 setEnvironment 方法 // 3.2 调用 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 的 setEmbeddedValueResolver 方法 // 3.2 调用 ResourceLoaderAware 的 setResourceLoader 方法 // 3.2 调用 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的 setApplicationEventPublisher 方法 // 3.2 调用 MessageSourceAware 的 setMessageSource 方法 // 3.2 调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法 // 3.2 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { // 3.3 调用初始化方法 // (1)调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 // (2)调用 用户定义的初始化方法,即init-method 属性配置的方法 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 3.4 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
通过initializeBean 方法,我们把初始化Bean大概有4大步骤:
调用实现XxxAware类的方法
执行 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法
调用初始化方法
调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { // 如果实现 BeanNameAware 接口,则会调用 setBeanName 方法 if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } // 如果实现 BeanClassLoaderAware 接口,则会调用 setBeanClassLoader 方法 if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader()); } // 如果实现 BeanFactoryAware 接口,则会调用 setBeanFactory 方法 if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } }
3.2 执行 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法
@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { // 这里首先会调用 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 // 这里最后会调用 MyBeanPostProcessor 中的postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法 result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
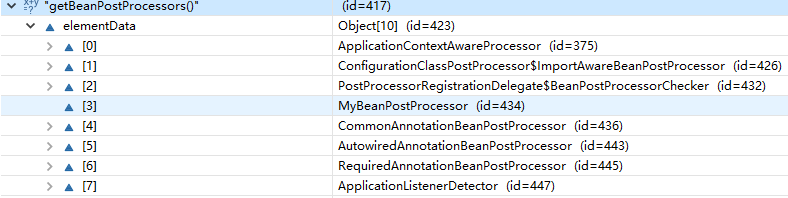
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法如下:
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { AccessControlContext acc = null; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware || bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware || bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) { acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext(); } if (acc != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); return null; } }, acc); } else { // 核心代码: invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); } return bean; }
下面这段代码就是判断是否实现了XxxAware 接口,并调用相应的setXxx 方法
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { // 如果实现了 EnvironmentAware 接口,则会调用 setEnvironment方法 if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) { ((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment()); } // 如果实现了 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口,则会调用 setEmbeddedValueResolver方法 if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) { ((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver); } // 如果实现了 ResourceLoaderAware 接口,则会调用 setResourceLoader方法 if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) { ((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); } // 如果实现了 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 接口,则会调用 setApplicationEventPublisher方法 if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) { ((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext); } // 如果实现了 MessageSourceAware 接口,则会调用 setMessageSource方法 if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) { ((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext); } // 如果实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,则会调用 setApplicationContext方法 if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext); } } }
3.3 调用初始化方法
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() throws Exception { // 调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { // 调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { // 调用 用户定义的初始化方法,即init-method 属性配置的方法 invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
3.4 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化方法
@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { // 这里就会调用 MyBeanPostProcessor 中的 postProcessAfterInitialization result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
根据源码,总结spring bean的生命周期:
创建Bean:
1.实例化 bean
2.属性注入
3.初始化 bean
3.1调用实现XxxAware类的方法
调用 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法
调用 BeanClassLoaderAware 的 setBeanClassLoader
调用 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法
3.2执行 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化方法
调用 EnvironmentAware 的 setEnvironment 方法
调用 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 的 setEmbeddedValueResolver 方法
调用 ResourceLoaderAware 的 setResourceLoader 方法
调用 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的 setApplicationEventPublisher 方法
调用 MessageSourceAware 的 setMessageSource 方法
调用 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法
调用 BeanPostProcessor 的预初始化 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
3.3调用初始化方法
调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法
调用 用户定义的初始化方法,即init-method 属性配置的方法
3.4调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后初始化 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
销毁Bean:
调用 @PreDestroy 注解的方法
调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法
调用 destroy-method 属性配置的销毁方法
我们再看一下BeanFactory 源码给出的解释:
/* * * <p>Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces * as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is: * 初始化方法执行的标准顺序: * <ol> * <li>BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName} * <li>BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader} * <li>BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory} * <li>EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment} * <li>EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver} * <li>ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader} (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher} (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource} (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext} (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext} (only applicable when running in a web application context) * <li>{@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors * <li>InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * <li>a custom init-method definition * <li>{@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors * </ol> * * <p>On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply: * 销毁时: * <ol> * <li>{@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors * <li>DisposableBean's {@code destroy} * <li>a custom destroy-method definition * </ol> */ public interface BeanFactory { }