ch7 视觉里程计1
本章目标:
1.理解图像特征点的意义,并掌握在单副图像中提取出特征点及多副图像中匹配特征点的方法
2.理解对极几何的原理,利用对极几何的约束,恢复出图像之间的摄像机的三维运动
3.理解PNP问题,以及利用已知三维结构与图像的对应关系求解摄像机的三维运动
4.理解ICP问题,以及利用点云的匹配关系求解摄像机的三维运动
5.理解如何通过三角化获得二维图像上对应点的三维结构
本章目的:基于特征点法的vo,将介绍什么是特征点,如何提取和匹配特征点,以及如何根据配对的特征点估计相机运动和场景结构,从而实现一个基本的两帧间视觉里程计。
特征点:角点、SIFT(尺度不变特征变换,Scale-Invariant Feature Transform)、SURF、、ORB(后三个是人工设计的特征点,具有更多的优点)
特征点的组成:
1.关键点:指特征点在图像里的位置
2.描述子:通常是一个向量,按照某种人为设计的方式,描述了该关键点周围像素的信息。相似的特征应该有相似的描述子(即当两个特征点的描述子在向量空间上的距离相近,认为这两个特征点是一样的)
以ORB特征为代表介绍提取特征的整个过程:
ORB特征:OrientedFAST关键点+BRIEF关键子
提取ORB特征的步骤:
1.提取FAST角点:找出图像中的“角点”,计算特征点的主方向,为后续BRIEF描述子增加了旋转不变特性
FAST角点:主要检测局部像素灰度变化明显的地方
特点:速度快
缺点:1).FAST特征点数量很大且不确定,但是我们希望对图像提取固定数量的特征
2).FAST角点不具有方向信息,并且存在尺度问题
解决方式:1).指定要提取的角点数量N,对原始FAST角点分别计算Harris响应值,然后选取前N个具有最大响应值的角点作为最终的角点集合
2).添加尺度和旋转的描述
尺度不变性的实现:构建图像金字塔,并在金字塔的每一层上检测角点(金字塔:指对图像进行不同层次的降采样,以获得不同分辨
率的图像)
特征旋转的实现:灰度质心法(质心:指以图像块灰度值作为权重的中心)
2.计算BRIEF描述子:对前一步提取出的特征点周围图像区域进行扫描
特点:使用随机选点的比较,速度非常快,由于使用了二进制表达,存储起来也十分方便,适用于实时的图像匹配
在不同图像之间进行特征匹配的方法:
1.暴力匹配:浮点类型的描述子,使用欧式距离度量
二进制类型的描述子(比如本例中的BRIEF描述子),使用汉明距离度量
缺点:当特征点数量很大时,暴力匹配法的运算量会变得很大
2.快速近似最近邻(FLANN):适合匹配特征点数量极多的情况
实践部分:
1.OpenCV的图像特征提取、计算和匹配的过程:演示如何提取ORB特征并进行匹配
代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 using namespace cv; 8 9 int main(int argc,char** argv) 10 { 11 if(argc!=3) 12 { 13 cout<<"usage:feature_extraction img1 img2"<<endl; 14 return 1; 15 } 16 17 //读取图像 18 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 19 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 20 21 //初始化 22 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2;//关键点,指特征点在图像里的位置 23 Mat descriptors_1,descriptors_2;//描述子,通常是向量 24 Ptr<ORB> orb=ORB::create(500,1.2f,8,31,0,2,ORB::HARRIS_SCORE,31,20); 25 26 //第一步:检测OrientFAST角点位置 27 orb->detect(img_1,keypoints_1); 28 orb->detect(img_2,keypoints_2); 29 30 //第2步:根据角点位置计算BRIEF描述子 31 orb->compute(img_1,keypoints_1,descriptors_1); 32 orb->compute(img_2,keypoints_2,descriptors_2); 33 34 Mat outimg1; 35 drawKeypoints(img_1,keypoints_1,outimg1,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT); 36 imshow("1.png的ORB特征点",outimg1); 37 Mat outimg2; 38 drawKeypoints(img_2,keypoints_2,outimg2,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT); 39 imshow("2.png的ORB特征点",outimg2); 40 41 //第3步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用Hamming距离 42 vector<DMatch> matches; 43 //特征匹配的方法:暴力匹配 44 BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING); 45 matcher.match(descriptors_1,descriptors_2,matches); 46 // for(auto it=matches.begin();it!=matches.end();++it) 47 // { 48 // cout<<*it<<" "; 49 // } 50 // cout<<endl; 51 52 //第4步:匹配点对筛选 53 distance是min_dist 54 55 double min_dist=10000,max_dist=0; 56 57 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离,即最相似的和最不相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 58 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 59 { 60 double dist=matches[i].distance; 61 // cout<<dist<<endl; 62 if(dist<min_dist) min_dist=dist; 63 if(dist>max_dist) max_dist=dist; 64 } 65 66 printf("--Max dist:%f ",max_dist); 67 printf("--Min dist:%f ",min_dist); 68 69 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误 70 //但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值作为下限 71 vector<DMatch> good_matches; 72 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 73 { 74 if(matches[i].distance<=max(2*min_dist,30.0)) 75 { 76 good_matches.push_back(matches[i]); 77 } 78 } 79 80 //第5步:绘制匹配结果 81 Mat img_match; 82 Mat img_goodmatch; 83 drawMatches(img_1,keypoints_1,img_2,keypoints_2,matches,img_match); 84 drawMatches(img_1,keypoints_1,img_2,keypoints_2,good_matches,img_goodmatch); 85 imshow("所有匹配点对",img_match); 86 imshow("优化后匹配点对",img_goodmatch); 87 waitKey(0); 88 89 return 0; 90 }
实验结果:1.png中提取到的特征点
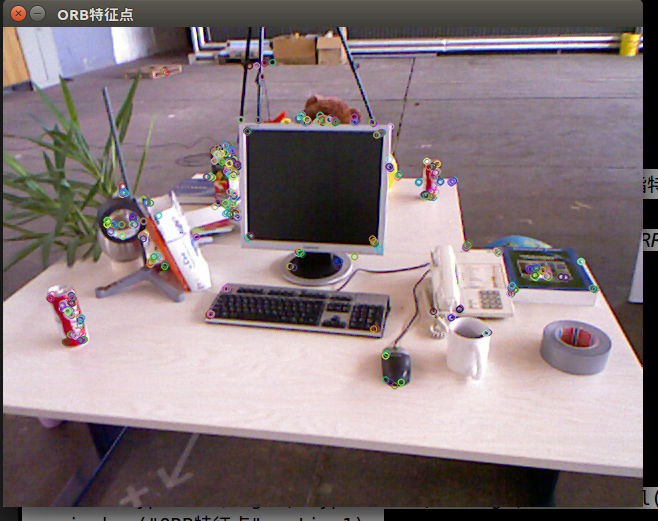

2.png中提取到的特征点
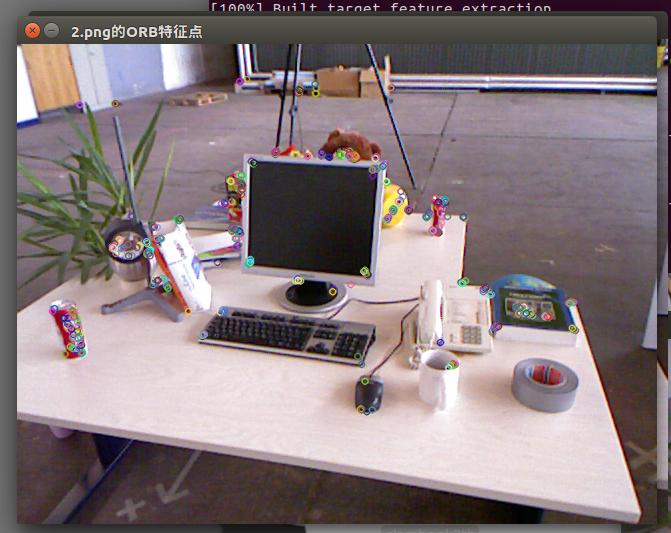
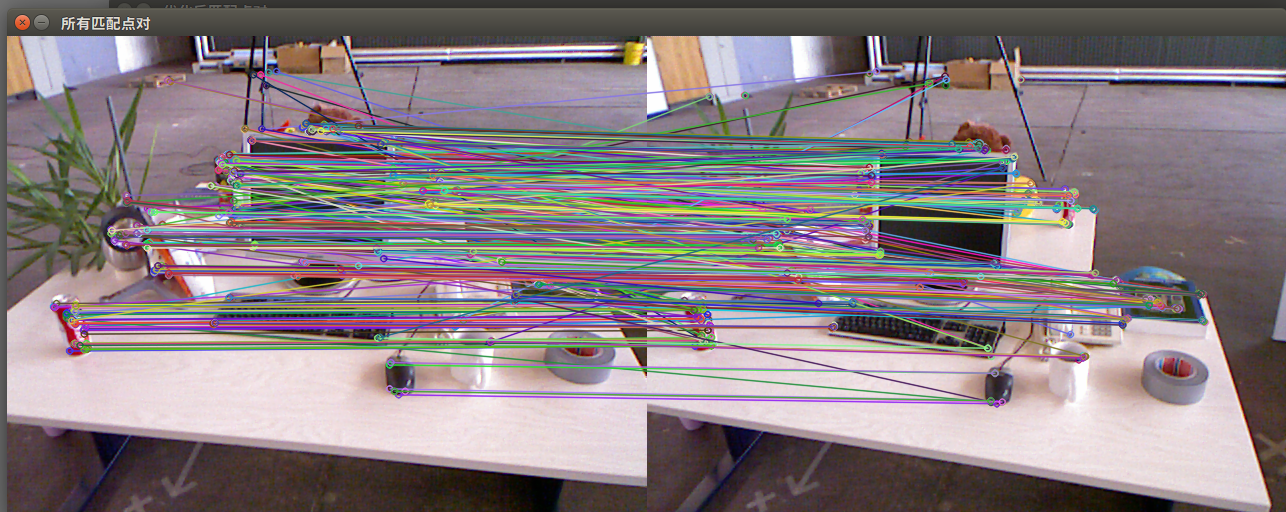
匹配结果:
所有点对匹配结果

优化后的匹配点对结果(筛选依据是Hamming距离小于最小距离的两倍)
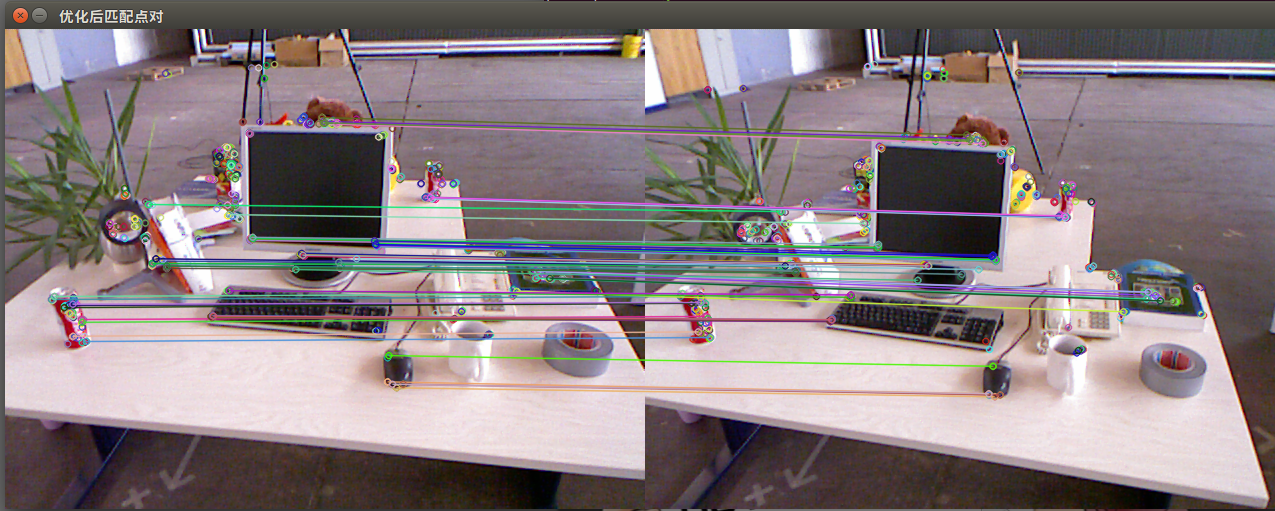
结果分析:尽管在这个例子中利用工程经验优化筛选出正确的匹配,但并不能保证在所有其他图像中得到的匹配都是正确的,所以,在后面的运动估计中,还要使用去除误匹配的算法。
2.演示如何利用匹配点对估计相机运动及利用相机运动估计特征点的空间位置
估计相机运动
2.1.如果是单目相机:只能得到2D的像素坐标->根据两组2D点估计运动,方法:对极几何
步骤如下:
1).根据配对点的像素位置求出本质矩阵E或基础矩阵F
2).根据E或F求出R,t。
公式见P143
对E的介绍:
1).E在不同尺度下是等价的
2).本质矩阵的内在性质:E的奇异值一定是[σ,σ,0]T的形式
3).由于尺度等价性,E实际上有5个自由度。
求解方法:八点法(Eight-point -algorithm)。求出E后,对其分解->R,t
单应矩阵(Homograohy)H:
描述了两个平面之间的映射关系。如果场景中的特征点都落在同一个平面上(墙、地面等),可通过单应性来估计运动
求解方法:直接线性变换法(Direct Linear Transform)。求出H后,对其分解(分解方法:数值法、解析法)->R,t
重要意义:P148
实践:利用对极约束求解相机运动
1).将利用匹配好的特征点来计算E、F、H
2).分解E得到R,t
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 6 7 using namespace cv; 8 using namespace std; 9 10 void find_feature_matches(const Mat& img_1,const Mat& img_2,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_1,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_2,vector<DMatch>& matches) 11 { 12 //初始化 13 Mat descriptors_1,descriptors_2; 14 //查看opencv版本号:pkg-config --modversion opencv 15 //used in OpenCV3 16 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector=ORB::create(); 17 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor=ORB::create(); 18 //if used in OpenCV2 19 //Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector=ORB::create("ORB"); 20 //Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor=ORB::create("ORB"); 21 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher=DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming"); 22 23 //第1步:检测Oriented FAST角点位置 24 detector->detect(img_1,keypoint_1); 25 detector->detect(img_2,keypoint_2); 26 27 //第2步:根据角点位置计算BRIEF描述子 28 descriptor->compute(img_1,keypoint_1,descriptors_1); 29 descriptor->compute(img_2,keypoint_2,descriptors_2); 30 31 //第3步:对两幅图像中的BRIED描述子进行匹配,使用Hamming距离 32 vector<DMatch> match; 33 matcher->match(descriptors_1,descriptors_2,match); 34 35 //第4步:匹配点对筛选 36 double min_dist=10000,max_dist=0; 37 38 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离,即是最相似和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 39 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 40 { 41 double dist=match[i].distance; 42 if(dist<min_dist) min_dist=dist; 43 if(dist>max_dist) max_dist=dist; 44 } 45 46 cout<<"Max dist: "<<max_dist<<endl; 47 cout<<"Min dist: "<<min_dist<<endl; 48 49 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误。 50 //但有时候最小距离非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限 51 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 52 { 53 if(match[i].distance<=max(2*min_dist,30.0)) 54 { 55 matches.push_back(match[i]); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 61 void pose_estimation_2d2d(vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_2,vector<DMatch> matches,Mat& R,Mat& t) 62 { 63 //相机内参,TUM Freiburg2 64 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1,0,521.0,249.7,0,0,1); 65 66 //把匹配点转换成vector<Point2f>的形式 67 vector<Point2f> points1; 68 vector<Point2f> points2; 69 70 for(int i=0;i<(int)matches.size();++i) 71 { 72 points1.push_back(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);//用法? 73 points2.push_back(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);//用法? 74 } 75 76 //计算基础矩阵F 77 Mat fundamental_matrix; 78 //使用8点法计算F 79 fundamental_matrix=findFundamentalMat(points1,points2,CV_FM_8POINT); 80 cout<<"fundamental_matrix ="<<endl<<fundamental_matrix<<endl; 81 82 //计算本质矩阵E 83 Point2d principal_point(325.1,249.7);//相机光心,TUM dataset标定值 84 double focal_length=521;//相机焦距,TUM dataset标定值 85 Mat essential_matrix; 86 essential_matrix=findEssentialMat(points1,points2,focal_length,principal_point); 87 cout<<"essential_matrix = "<<endl<<essential_matrix<<endl; 88 89 //计算单应矩阵 90 Mat homography_matrix; 91 homography_matrix=findHomography(points1,points2,RANSAC,3); 92 cout<<"homography_matrix = "<<endl<<homography_matrix<<endl; 93 94 //从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息 95 recoverPose(essential_matrix,points1,points2,R,t,focal_length,principal_point); 96 cout<<"R ="<<endl<<R<<endl; 97 cout<<"t ="<<endl<<t<<endl; 98 } 99 100 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d& p,const Mat& K) 101 { 102 return Point2d 103 ( 104 (p.x-K.at<double>(0,2))/K.at<double>(0,0), 105 (p.y-K.at<double>(1,2))/K.at<double>(1,1) 106 ); 107 } 108 109 int main(int argc,char** argv) 110 { 111 if(argc!=3) 112 { 113 cout<<"usage:pose_estimation_2d2d img1 img2"<<endl; 114 return 1; 115 } 116 117 //读取图像 118 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 119 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 120 121 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2; 122 vector<DMatch> matches; 123 find_feature_matches(img_1,img_2,keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches); 124 125 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size()<<"组匹配点对"<<endl; 126 127 //估计两张图像间运动 128 Mat R,t; 129 pose_estimation_2d2d(keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches,R,t); 130 131 //验证E=t^R 132 Mat t_x=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<< 133 0, -t.at<double>(2,0), t.at<double>(1,0), 134 t.at<double>(2,0), 0, -t.at<double>(0,0), 135 -t.at<double>(1,0), t.at<double>(0,0), 0 ); 136 // cout<<"t^ = "<<endl<<t_x<<endl; 137 cout<<"t^R ="<<endl<<t_x*R<<endl;//!=E??? 138 139 //验证对极约束 140 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1,0,521.0,249.7,0,0,1); 141 for(DMatch m:matches) 142 { 143 Point2d pt1=pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt,K); 144 Mat y1=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<pt1.x,pt1.y,1); 145 Point2d pt2=pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt,K); 146 Mat y2=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<pt2.x,pt2.y,1); 147 Mat d=y2.t()*t_x*R*y1; 148 cout<<"epipolar constraint = "<<d<<endl; 149 } 150 return 0; 151 }
实验结果:
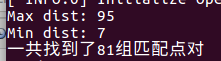
计算得到的F、F、H分别为:
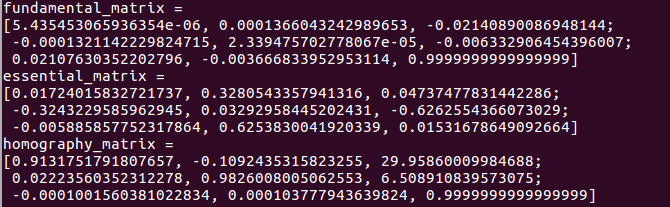
恢复的R和t:
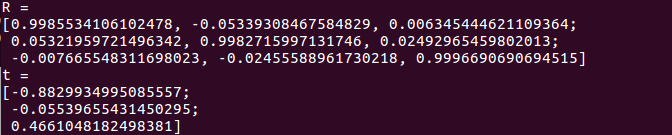
验证E=t^R:
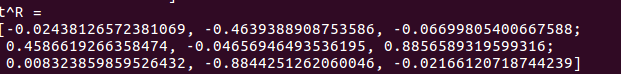
这里有个疑问:t^R计算后得到的矩阵和E相差有点大(不知道能不能这样说),所以,是怎么回事呢?
验证堆积约束:x2Tt^Rx1=0
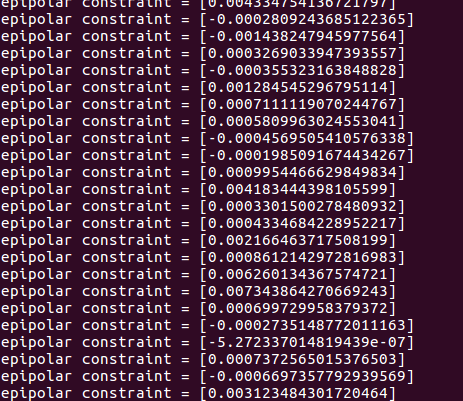
……
单目视觉slam:尺度不确定性。即对轨迹和地图缩放任意倍数,得到的图像依然是一样的
固定尺度的做法:1.对两张图像的t归一化
2.令所有的特征点平均深度为1(相比较而言,特征点深度归一化可控制场景的规模大小,使得计算在数值上更稳定)
单目初始化不能只有纯旋转,必须要有一定程度的平移,才可进行单目的初始化.
估计特征点的空间位置
在获估计了相机运动之后,需要借助相机的运动估计特征点的空间位置。方法:三角测量(Triangulation)(或三角化)来估计地图点的深度
三角测量:通过在两处观察同一个点的夹角,从而确定该点的距离
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 using namespace cv; 9 10 void find_feature_matches(const Mat& img_1,const Mat& img_2, 11 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 12 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 13 vector<DMatch>& matches) 14 { 15 //初始化 16 Mat descriptors_1,descriptors_2; 17 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector=ORB::create(); 18 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor=ORB::create(); 19 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher=DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming"); 20 21 //第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 22 detector->detect(img_1,keypoints_1); 23 detector->detect(img_2,keypoints_2); 24 25 //第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 26 descriptor->compute(img_1,keypoints_1,descriptors_1); 27 descriptor->compute(img_2,keypoints_2,descriptors_2); 28 29 //第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 30 vector<DMatch> match; 31 matcher->match(descriptors_1,descriptors_2,match); 32 33 //第四步:匹配点对筛选 34 double min_dist=1000,max_dist=0; 35 36 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 37 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 38 { 39 double dist=match[i].distance; 40 if(dist<min_dist) min_dist=dist; 41 if(dist>max_dist) max_dist=dist; 42 } 43 44 printf("Max dist :%f ",max_dist); 45 printf("Min dist :%f ",min_dist); 46 47 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 48 for(int i=0;i<descriptors_1.rows;++i) 49 { 50 if(match[i].distance<=max(2*min_dist,30.0)) 51 { 52 matches.push_back(match[i]); 53 } 54 } 55 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; 56 } 57 58 //估计两张图像间运动 59 void pose_estimation_2d2d(const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 60 const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 61 const vector<DMatch>& matches, 62 Mat& R,Mat& t) 63 { 64 //相机内参,TUM Freiburg2 65 Mat K=(Mat_<double> (3,3)<<520.9,325.1,0,521.0,249.7,0,0,1); 66 67 //把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式 68 vector<Point2f> points1; 69 vector<Point2f> points2; 70 71 for(int i=0;i<(int)matches.size();++i) 72 { 73 points1.push_back(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);//? 74 points2.push_back(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);//? 75 } 76 77 //计算基础矩阵 78 Mat fundamental_matrix; 79 fundamental_matrix=findFundamentalMat(points1,points2,CV_FM_8POINT); 80 cout<<"fundamental_matrix ="<<endl<<fundamental_matrix<<endl; 81 82 //计算本质矩阵 83 Point2d principal_point(325.1,249.7);//相机光心,TUM dataset标定值 84 int focal_length=521;////相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值 85 Mat essential_matrix; 86 essential_matrix=findEssentialMat(points1,points2,focal_length,principal_point); 87 cout<<"essential_matrix = "<<endl<<essential_matrix<<endl; 88 89 //计算单应矩阵 90 Mat homography_matrix; 91 homography_matrix=findHomography(points1,points2,RANSAC,3); 92 cout<<"homography_matrix = "<<homography_matrix<<endl; 93 94 //从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息 95 recoverPose(essential_matrix,points1,points2,R,t,focal_length,principal_point); 96 cout<<"R = "<<endl<<R<<endl; 97 cout<<"t = "<<endl<<t<<endl; 98 } 99 100 Point2f pixel2cam(const Point2d& p,const Mat& K) 101 { 102 return Point2f( 103 (p.x-K.at<double>(0,2))/K.at<double>(0,0), 104 (p.y-K.at<double>(1,2))/K.at<double>(1,1) 105 ); 106 } 107 108 void triangulation(const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_1, 109 const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_2, 110 const vector<DMatch>& matches, 111 const Mat& R,const Mat& t, 112 vector<Point3d>& points) 113 { 114 Mat T1=(Mat_<float> (3,4)<< 115 1,0,0,0, 116 0,1,0,0, 117 0,0,1,0); 118 Mat T2=(Mat_<float>(3,4)<< 119 R.at<double>(0,0),R.at<double>(0,1),R.at<double>(0,2),t.at<double>(0,0), 120 R.at<double>(1,0),R.at<double>(1,1),R.at<double>(1,2),t.at<double>(1,0), 121 R.at<double>(2,0),R.at<double>(2,1),R.at<double>(2,2),t.at<double>(2,0) 122 ); 123 124 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1,0,521.0,249.7,0,0,1); 125 vector<Point2f> pts_1,pts_2; 126 for(DMatch m:matches) 127 { 128 //将像素坐标转换至相机坐标 129 pts_1.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt,K)); 130 pts_2.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt,K)); 131 } 132 133 Mat pts_4d; 134 triangulatePoints(T1,T2,pts_1,pts_2,pts_4d); 135 cout<<pts_4d.cols<<endl; 136 //转换成非齐次坐标 137 for(int i=0;i<pts_4d.cols;++i) 138 { 139 Mat x=pts_4d.col(i); 140 x/=x.at<float>(3,0);//归一化 141 Point3d p( 142 x.at<float>(0,0), 143 x.at<float>(1,0), 144 x.at<float>(2,0) 145 ); 146 cout<<"p = "<<endl<<p<<endl; 147 points.push_back(p); 148 } 149 } 150 151 152 153 int main(int argc,char** argv) 154 { 155 if(argc!=3) 156 { 157 cout<<"usage:triangulation img1 img2"<<endl; 158 return 1; 159 } 160 161 //读取图像 162 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 163 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 164 165 //寻找匹配点对 166 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2; 167 vector<DMatch> matches; 168 find_feature_matches(img_1,img_2,keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches); 169 170 //估计两张图像间运动 171 Mat R,t; 172 pose_estimation_2d2d(keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches,R,t); 173 174 //三角化 175 vector<Point3d> points; 176 triangulation(keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches,R,t,points); 177 178 //验证三角化点与特征点的重投影关系 179 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1,0,521.0,249.7,0,0,1); 180 for(int i=0;i<matches.size();++i) 181 { 182 Point2d pt1_cam=pixel2cam(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt,K); 183 Point2d pt1_cam_3d( 184 points[i].x/points[i].z, 185 points[i].y/points[i].z 186 ); 187 cout<<"point in the first camera frame: "<<pt1_cam<<endl; 188 cout<<"point projected from 3D"<<pt1_cam_3d<<",d="<<points[i].z<<endl; 189 190 //第二个图 191 Point2f pt2_cam=pixel2cam(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt,K); 192 Mat pt2_trans=R*(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<points[i].x,points[i].y,points[i].z)+t; 193 pt2_trans/=pt2_trans.at<double>(2,0); 194 cout<<"point in the second camera a frame: "<<pt2_cam<<endl; 195 cout<<"point projected from second frame: "<<pt2_trans.t()<<endl; 196 cout<<endl; 197 198 } 199 200 201 return 0; 202 }
纯旋转无法使用三角测量,因为对极约束会永远满足。
提高三角化精度的方法:1.提高特征点的提取精度,即提高图像分辨率。缺点:会导致图像变大,增加计算成本。
2.使平移量增大(平移较大时,在同样的相机分辨率下,三角化测量会更精确)。缺点:导致图像的外观会发生明显变化,使得特征提取和匹配变得困难。
三角测量的矛盾:增大平移量->匹配失效;平移太小->三角化精度不够。
2.2.已有3D点及其在相机的投影位置(3D-2D),来估计相机的运动,方法:PnP
PnP:求解3D到2D点对运动的方法。描述了当知道n个3D空间点及其投影位置时,如何估计相机的位姿
优点:无需使用对极约束,又可在很少的匹配点中获得较好的运动估计,是最重要的一种姿态估计方法。
求解方法:P3P-用3对点估计位姿
DLT-直接线性变换
EPnP(Efficient PnP)
UPnP
Bundle Adjustment-非线性优化的方式,构建最小二乘问题并迭代求解
1).DLT(Direct Linear Transform)
2).P3P
输入数据:3对3D-2D匹配点。记3D点为A,B,C。2D点为a,b,c。小写字母对应的点为对应大写字母代表的点在相应的成像平面上的 投影
注意:A,B,C表示的是在世界坐标系中的坐标,而不是在相机坐标系中的坐标。如果一旦能算出3D点在相机坐标系下的坐标,就能得到3D-3D的对应点,从而把PnP问题转化为ICP问题。
缺点:1.P3P只利用3个点的信息,当给定的配对点多于3组时,难以利用更多的信息。
2.如果2D点或3D点受噪声的影响,或存在误匹配,则算法失效
3).EPnP、UPnP等
相较于P3P来说,优点:1.利用更过的信息
2.用迭代的方式对相机的位姿进行优化,尽可能消除噪声的影响
缺点:原理更复杂
通常的做法:先使用P3P/EPnP等方法估计相机位姿,然后构建最小二乘优化问题对估计值进行调整(Bundle Adjustment)
线性方法:先求相机位姿,再求空间位置
非线性优化:把相机位姿和空间位置均看作优化变量,放在一起优化
4).Bundle Adjustment
两个重要的公式见P164(公式7.45)和P165(公式7.47)-分别描述了观测相机方程关于相机位姿与特征点的两个导数矩阵。能够在优化过程中(优化位姿和优化特征点的空间位置)提供重要的梯度方向,指导优化的迭代。
实验代码如下:首先用OpenCV提供的EPnP求解PnP问题,然后通过g2o对结果进行优化
第一步:使用EPnP求解位姿
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 6 #include <Eigen/Core> 7 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 8 #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> 9 #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> 10 #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> 11 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h> 12 #include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h> 13 #include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h> 14 #include <chrono> 15 16 using namespace std; 17 using namespace cv; 18 19 void find_feature_matches ( 20 const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 21 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 22 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 23 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ); 24 25 // 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 26 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ); 27 28 int main ( int argc, char** argv ) 29 { 30 if ( argc != 4 ) 31 { 32 cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1"<<endl; 33 return 1; 34 } 35 //-- 读取图像 36 Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 37 Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 38 39 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2; 40 vector<DMatch> matches; 41 find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches ); 42 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; 43 44 // 建立3D点 45 Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 46 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); 47 vector<Point3f> pts_3d; 48 vector<Point2f> pts_2d; 49 for ( DMatch m:matches ) 50 { 51 ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ]; 52 if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth 53 continue; 54 float dd = d/5000.0; 55 Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K ); 56 pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) ); 57 pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt ); 58 } 59 60 cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl; 61 62 Mat r, t; 63 solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false ); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法 64 Mat R; 65 cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 66 67 cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl; 68 cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl; 69 } 70 71 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 72 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 73 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 74 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 75 { 76 //-- 初始化 77 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 78 // used in OpenCV3 79 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 80 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 81 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 82 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 83 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 84 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 85 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 86 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 87 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 88 89 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 90 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 91 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 92 93 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 94 vector<DMatch> match; 95 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 96 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 97 98 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 99 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 100 101 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 102 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 103 { 104 double dist = match[i].distance; 105 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 106 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 107 } 108 109 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 110 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 111 112 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 113 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 114 { 115 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 116 { 117 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 118 } 119 } 120 } 121 122 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ) 123 { 124 return Point2d 125 ( 126 ( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), 127 ( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 ) 128 ); 129 }
运行结果为:
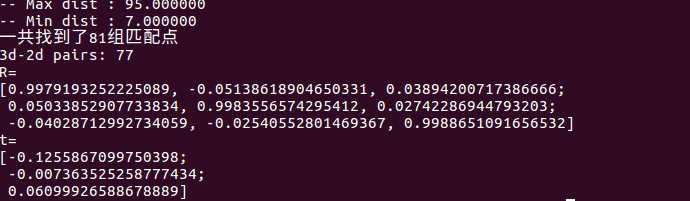
分析:在有3D信息时,由于引入了新的深度信息,估计的R与之前2D-2D情况下求解的R几乎是相同的,但是t相差较大。不过由于Kinect采集的深度地图本身会有一些误差,导致这里的3D点也不是准确的。所以,下一步要把位姿和所有三维特征点同时优化。
第二步:使用前一步的估计值作为初始值,对结果进行优化:
2.2.1 利用g2o优化库提供的Bundle Adjustment对结果进行优化。g2o优化的步骤如下:
1)先将优化问题表示成图:顶点——优化变量
边——误差项
(1)定义顶点和边的类型:如果顶点和边的类型在g2o中有提供,就不用自己实现,否则,要自己实现。
(2)构建图
(这一步是利用g2o优化求解的关键)
2) 选择优化算法:GN、LM、DogLeg……
3)调用g2o进行优化,返回结果
我们来分析下这个问题的优化思路:
首先构建最小二乘问题,见P162公式(7.53)。该问题的误差项表示的是,将像素坐标(观测到的投影位置)与3D点按照当前估计的位姿进行投影得到的位置相比较得到的误差(重投影误差)。
所以该问题中,优化问题是pose(我们选第2个相机的位姿节点,因为第1个相机位姿固定为0,故不用写到优化变量中。思考:如果把第1个相机的位姿与观测也考虑进来呢?)
问题转化为:根据一组3D点和第二个图像中得2D投影估计第二个相机的位姿。
因为这个优化问题中的边(即误差项,EdgeProjectXTZ2UV(投影方程边))和顶点(即优化变量,VertexSE3Expmap(李代数位姿)、VertexSBAPointXYZ(空间点位置))提供了,所以不用自己实现。
明确了g2o优化的思路和步骤,下面我们就利用g2o优化库来进行优化,代码如下:
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 6 #include <Eigen/Core> 7 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 8 #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> 9 #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> 10 #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> 11 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h> 12 #include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h> 13 #include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h> 14 #include <chrono> 15 16 using namespace std; 17 using namespace cv; 18 19 void find_feature_matches ( 20 const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 21 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 22 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 23 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ); 24 25 // 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 26 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ); 27 28 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> points_3d, 29 const vector<Point2f> points_2d, 30 const Mat& K, 31 Mat& R,Mat& t 32 ); 33 34 int main ( int argc, char** argv ) 35 { 36 if ( argc != 4 ) 37 { 38 cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1"<<endl; 39 return 1; 40 } 41 //-- 读取图像 42 Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 43 Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 44 45 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2; 46 vector<DMatch> matches; 47 find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches ); 48 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; 49 50 // 建立3D点 51 Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 52 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); 53 vector<Point3f> pts_3d; 54 vector<Point2f> pts_2d; 55 for ( DMatch m:matches ) 56 { 57 ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ]; 58 if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth 59 continue; 60 float dd = d/5000.0; 61 Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K ); 62 pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) ); 63 pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt ); 64 } 65 66 cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl; 67 68 Mat r, t; 69 solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false ); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法 70 Mat R; 71 cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 72 73 cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl; 74 cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl; 75 76 cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl; 77 78 bundleAdjustment(pts_3d,pts_2d,K,R,t); 79 } 80 81 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 82 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 83 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 84 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 85 { 86 //-- 初始化 87 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 88 // used in OpenCV3 89 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 90 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 91 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 92 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 93 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 94 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 95 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 96 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 97 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 98 99 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 100 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 101 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 102 103 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 104 vector<DMatch> match; 105 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 106 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 107 108 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 109 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 110 111 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 112 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 113 { 114 double dist = match[i].distance; 115 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 116 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 117 } 118 119 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 120 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 121 122 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 123 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 124 { 125 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 126 { 127 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 128 } 129 } 130 } 131 132 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ) 133 { 134 return Point2d 135 ( 136 ( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), 137 ( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 ) 138 ); 139 } 140 141 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> points_3d, 142 const vector<Point2f> points_2d, 143 const Mat &K, Mat &R, Mat &t) 144 { 145 // 初始化g2o 146 typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3>> Block;//pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3 147 Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver=new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<Block::PoseMatrixType>();//线性方程求解器 148 Block* solver_ptr=new Block(unique_ptr<Block::LinearSolverType>(linearSolver));//矩阵块求解器 149 g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver=new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(unique_ptr<Block>(solver_ptr)); 150 g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; 151 optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); 152 153 //vertex 154 g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose=new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap();//camera pose 155 Eigen::Matrix3d R_mat; 156 R_mat<< 157 R.at<double>(0,0),R.at<double>(0,1),R.at<double>(0,2), 158 R.at<double>(1,0),R.at<double>(1,1),R.at<double>(1,2), 159 R.at<double>(2,0),R.at<double>(2,1),R.at<double>(2,2); 160 pose->setId(0); 161 pose->setEstimate(g2o::SE3Quat( 162 R_mat, 163 Eigen::Vector3d(t.at<double>(0,0),t.at<double>(1,0),t.at<double>(2,0)) 164 )); 165 optimizer.addVertex(pose); 166 167 int index=1; 168 for(const Point3f p:points_3d)//landmarks 169 { 170 g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* point=new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ(); 171 point->setId(index++); 172 point->setEstimate(Eigen::Vector3d(p.x,p.y,p.z)); 173 point->setMarginalized(true);//g2o 中必须设置 marg 参见第十讲内容 174 optimizer.addVertex(point); 175 } 176 177 //parameter:camera intrinsics 178 g2o::CameraParameters* camera=new g2o::CameraParameters( 179 K.at<double>(0,0),Eigen::Vector2d(K.at<double>(0,2),K.at<double>(1,2)),0); 180 camera->setId(0); 181 optimizer.addParameter(camera); 182 183 //edges 184 index=1; 185 for(const Point2f p:points_2d) 186 { 187 g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge=new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV(); 188 edge->setId(index); 189 edge->setVertex(0,dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> (optimizer.vertex(index))); 190 edge->setVertex(1,pose); 191 edge->setMeasurement(Eigen::Vector2d(p.x,p.y)); 192 edge->setParameterId(0,0); 193 edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity()); 194 optimizer.addEdge(edge); 195 index++; 196 } 197 198 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 199 optimizer.setVerbose(true); 200 optimizer.initializeOptimization(); 201 optimizer.optimize(100); 202 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 203 chrono::duration<double> time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2-t1); 204 cout<<"optimization costs time: "<<time_used.count()<<endl; 205 206 cout<<endl<<"after optimization:"<<endl; 207 cout<<"T = "<<endl<<Eigen::Isometry3d(pose->estimate()).matrix()<<endl; 208 }
实验结果:
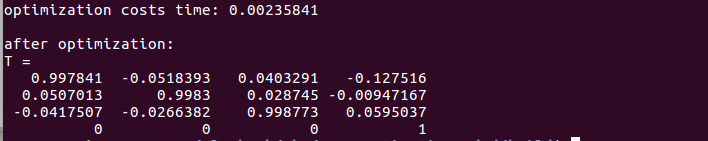
可以看出,由于同时优化了特征点和相机位姿,最后输出的位姿变换矩阵T,对比之前直接做PnP的结果,大约在小数点后第3位发生了一 些变化。
2.2.2 利用Ceres优化库,见《视觉SLAM十四讲》课后习题—ch7(更新中……)习题10。
2.3.如果是双目或RGB-D相机时,或者能获得距离信息->根据两组3D点估计运动,方法:ICP(迭代最近点,Iterative Closest Point)
假设有一组配对好的3D点:P={p1,…,pn}, P'={p1',…,pn'},我们要找一个欧式变换R,t,使得:对于所有i,pi=Rpi'+t.这个问题就用ICP方法 求解。
注意:仅考虑两组3D点之间得变换时,和相机并没有关系。
ICP的求解方式:1)利用线性代数的求解(主要是SVD)。2)利用非线性优化的求解方方式(类似与BA)
2.3.1 SVD方法
简化后的目标优化函数为:
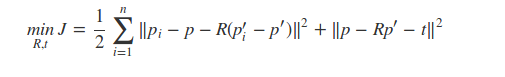
分3个步骤求解:
(1)计算两组点的质心位置p,p',然后计算每个点的去质心坐标:令qi=pi-p,qi'=pi'-p
(2)根据以下优化问题计算旋转矩阵:
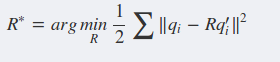
(3)根据第2步的R求t:t*=p-Rp'
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 6 #include <Eigen/Core> 7 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 8 #include <Eigen/SVD> 9 //#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> 10 //#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> 11 //#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> 12 //#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h> 13 //#include <g2o/solvers/eigen/linear_solver_eigen.h> 14 //#include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h> 15 #include <chrono> 16 17 using namespace std; 18 using namespace cv; 19 20 void find_feature_matches(const Mat& img_1,const Mat& img_2, 21 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 22 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 23 vector<DMatch>& matches); 24 25 //像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 26 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d& p,const Mat& K); 27 28 void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f>& pts1, 29 const vector<Point3f>& pts2, 30 Mat& R,Mat& t); 31 32 33 int main(int argc,char** argv) 34 { 35 if(argc!=5) 36 { 37 cout<<"usage:pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"<<endl; 38 return 1; 39 } 40 41 //读取图像 42 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);//test 43 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 44 45 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2; 46 vector<DMatch> matches; 47 find_feature_matches(img_1,img_2,keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches); 48 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size()<<"组匹配点"<<endl; 49 50 //建立3D点 51 Mat depth_1=imread(argv[3],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 52 Mat depth_2=imread(argv[4],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 53 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1, 54 0,521.0,249.7, 55 0,0,1); 56 vector<Point3f> pts1,pts2; 57 for(DMatch m:matches) 58 { 59 ushort d1=depth_1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)]; 60 ushort d2=depth_2.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x)]; 61 if(d1==0 || d2==0)//bad depth 62 continue; 63 Point2d p1=pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt,K); 64 Point2d p2=pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt,K); 65 float dd1=float(d1)/5000.0; 66 float dd2=float(d2)/5000.0; 67 pts1.push_back(Point3f(p1.x*dd1,p1.y*dd1,dd1)); 68 pts2.push_back(Point3f(p2.x*dd2,p2.y*dd2,dd2)); 69 } 70 71 cout<<"3d-3d pairs: "<<pts1.size()<<endl; 72 Mat R,t; 73 pose_estimation_3d3d(pts1,pts2,R,t); 74 cout<<"ICP via SVD results: "<<endl; 75 cout<<"R ="<<endl<<R<<endl; 76 cout<<"t ="<<endl<<t<<endl; 77 cout<<"R_inv ="<<endl<<R.t()<<endl; 78 cout<<"t_inv ="<<endl<<-R.t()*t<<endl; 79 return 0; 80 } 81 82 //匹配特征点对 83 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 84 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 85 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 86 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 87 { 88 //-- 初始化 89 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 90 // used in OpenCV3 91 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 92 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 93 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 94 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 95 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 96 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 97 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 98 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 99 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 100 101 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 102 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 103 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 104 105 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 106 vector<DMatch> match; 107 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 108 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 109 110 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 111 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 112 113 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 114 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 115 { 116 double dist = match[i].distance; 117 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 118 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 119 } 120 121 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 122 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 123 124 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 125 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 126 { 127 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 128 { 129 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 130 } 131 } 132 } 133 134 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) 135 { 136 return Point2d( 137 (p.x-K.at<double>(0,2))/K.at<double>(0,0), 138 (p.y-K.at<double>(1,2))/K.at<double>(1,1) 139 ); 140 } 141 142 void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1, const vector<Point3f> &pts2, Mat &R, Mat &t) 143 { 144 Point3f p1,p2;//center of mass 145 int N=pts1.size(); 146 //计算两组点的质心位置p1,p2 147 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 148 { 149 p1+=pts1[i]; 150 p2+=pts2[i]; 151 } 152 p1=Point3f(Vec3f(p1)/N);//test 153 p2=Point3f(Vec3f(p2)/N);//test 154 155 //计算每个点的去质心坐标q1,q2 156 vector<Point3f> q1(N),q2(N); 157 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 158 { 159 q1[i]=pts1[i]-p1; 160 q2[i]=pts2[i]-p2; 161 } 162 163 //compute q1*q2^T,即书中P174的矩阵W 164 Eigen::Matrix3d W=Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero(); 165 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 166 { 167 W+=Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x,q1[i].y,q1[i].z)*Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x,q2[i].y,q2[i].z).transpose(); 168 } 169 cout<<"W ="<<endl<<W<<endl<<endl; 170 171 //SVD on W 172 Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W,Eigen::ComputeFullU|Eigen::ComputeFullV); 173 Eigen::Matrix3d U=svd.matrixU(); 174 Eigen::Matrix3d V=svd.matrixV(); 175 176 if(U.determinant()*V.determinant()<0) 177 { 178 for(int x=0;x<3;++x) 179 { 180 U(x,2)*=-1; 181 } 182 } 183 184 cout<<"U="<<U<<endl; 185 cout<<"V="<<V<<endl; 186 187 Eigen::Matrix3d R_=U*(V.transpose()); 188 Eigen::Vector3d t_=Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x,p1.y,p1.z)-R_*Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x,p2.y,p2.z); 189 190 191 192 //convert to cv::Mat 193 R=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<< 194 R_(0,0),R_(0,1),R_(0,2), 195 R_(1,0),R_(1,1),R_(1,2), 196 R_(2,0),R_(2,1),R_(2,2)); 197 t=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<t_(0,0),t_(1,0),t_(2,0)); 198 }
运行结果:
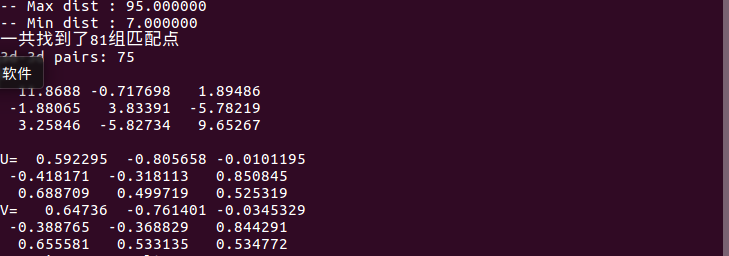
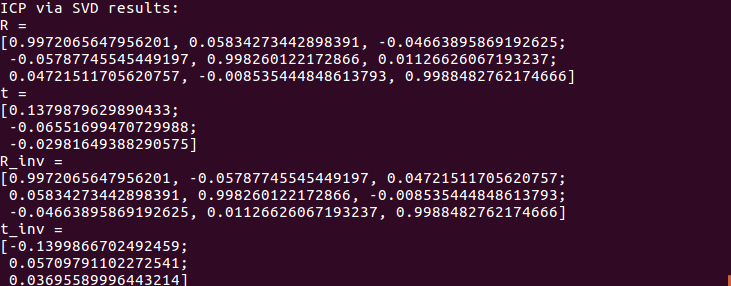
与Section2.2 PnP得到的结果对比,可以看出这里的R,t是第二帧到第一帧的变换,与前面的PnP是相反的。
由对极几何->PnP->ICP,我们使用了越来越多的信息:没有深度->有一个图的深度->有两个图的深度。在深度准确的情况下,得到的估计也会越来越准确。
ICP方法也存在一些缺点:由于Kinect的深度图存在噪声,并且数据可能会丢失,使得一些深度数据的特征点不得不丢弃。这可能会导致ICP的估计不够准确。并且,如果特征点丢失的太多,可能会因为特征点太少而无法进行运动估计。
2.3.2 非线性优化方法:以迭代的方式寻找最优值
目标函数:minξ=½∑ni=1||pi-exp(ξ^)pi'||22
ICP问题存在唯一解或无穷多解的情况,在唯一解的情况下,只要能找到极小值解,这个极小值解就是我们要求的全局最小值=>已知匹配点时求解ICP的好处:ICP求解可以选定任意的初始值。
与SVD方法的不同之:在优化中不仅考虑相机的位姿,同时会优化3D点的空间位置。
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 6 #include <Eigen/Core> 7 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 8 #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> 9 #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> 10 #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> 11 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h> 12 #include <g2o/solvers/eigen/linear_solver_eigen.h> 13 #include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h> 14 #include <chrono> 15 16 using namespace std; 17 using namespace cv; 18 19 void find_feature_matches(const Mat& img_1,const Mat& img_2, 20 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 21 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 22 vector<DMatch>& matches); 23 24 //像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 25 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d& p,const Mat& K); 26 30 31 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f>& pts1, 32 const vector<Point3f>& pts2, 33 Mat& R,Mat& t); 34 35 //g2o edge 36 class EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly:public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<3,Eigen::Vector3d,g2o::VertexSE3Expmap> 37 { 38 public: 39 EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; 40 EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly(const Eigen::Vector3d& point):_point(point){} 41 42 virtual void computeError() 43 { 44 const g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose=static_cast<const g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*>(_vertices[0]); 45 //measurement is p,point is p' 46 _error=_measurement-pose->estimate().map(_point); 47 } 48 49 virtual void linearizeOplus() 50 { 51 g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose=static_cast<g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*>(_vertices[0]); 52 g2o::SE3Quat T(pose->estimate()); 53 Eigen::Vector3d xyz_trans=T.map(_point); 54 double x=xyz_trans[0]; 55 double y=xyz_trans[1]; 56 double z=xyz_trans[2]; 57 58 // 误差项对待优化变量的Jacobin 59 _jacobianOplusXi(0,0)=0; 60 _jacobianOplusXi(0,1)=-z; 61 _jacobianOplusXi(0,2)=y; 62 _jacobianOplusXi(0,3)=-1; 63 _jacobianOplusXi(0,4)=0; 64 _jacobianOplusXi(0,5)=0; 65 66 _jacobianOplusXi(1,0)=z; 67 _jacobianOplusXi(1,1)=0; 68 _jacobianOplusXi(1,2)=-x; 69 _jacobianOplusXi(1,3)=0; 70 _jacobianOplusXi(1,4)=-1; 71 _jacobianOplusXi(1,5)=0; 72 73 _jacobianOplusXi(2,0)=-y; 74 _jacobianOplusXi(2,1)=x; 75 _jacobianOplusXi(2,2)=0; 76 _jacobianOplusXi(2,3)=0; 77 _jacobianOplusXi(2,4)=0; 78 _jacobianOplusXi(2,5)=-1; 79 } 80 81 bool read(istream& in) {} 82 bool write(ostream& out) const{} 83 protected: 84 Eigen::Vector3d _point; 85 }; 86 87 88 int main(int argc,char** argv) 89 { 90 if(argc!=5) 91 { 92 cout<<"usage:pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"<<endl; 93 return 1; 94 } 95 96 //读取图像 97 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);//test 98 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 99 100 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2; 101 vector<DMatch> matches; 102 find_feature_matches(img_1,img_2,keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches); 103 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size()<<"组匹配点"<<endl; 104 105 //建立3D点 106 Mat depth_1=imread(argv[3],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 107 Mat depth_2=imread(argv[4],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 108 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1, 109 0,521.0,249.7, 110 0,0,1); 111 vector<Point3f> pts1,pts2; 112 for(DMatch m:matches) 113 { 114 ushort d1=depth_1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)]; 115 ushort d2=depth_2.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x)]; 116 if(d1==0 || d2==0)//bad depth 117 continue; 118 Point2d p1=pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt,K); 119 Point2d p2=pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt,K); 120 float dd1=float(d1)/5000.0; 121 float dd2=float(d2)/5000.0; 122 pts1.push_back(Point3f(p1.x*dd1,p1.y*dd1,dd1)); 123 pts2.push_back(Point3f(p2.x*dd2,p2.y*dd2,dd2)); 124 } 125 126 cout<<"3d-3d pairs: "<<pts1.size()<<endl; 127 Mat R,t; 128 129 cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl; 130 bundleAdjustment(pts1,pts2,R,t); 131 return 0; 132 } 133 134 //匹配特征点对 135 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 136 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 137 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 138 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 139 { 140 //-- 初始化 141 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 142 // used in OpenCV3 143 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 144 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 145 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 146 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 147 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 148 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 149 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 150 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 151 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 152 153 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 154 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 155 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 156 157 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 158 vector<DMatch> match; 159 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 160 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 161 162 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 163 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 164 165 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 166 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 167 { 168 double dist = match[i].distance; 169 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 170 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 171 } 172 173 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 174 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 175 176 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 177 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 178 { 179 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 180 { 181 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 182 } 183 } 184 } 185 186 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) 187 { 188 return Point2d( 189 (p.x-K.at<double>(0,2))/K.at<double>(0,0), 190 (p.y-K.at<double>(1,2))/K.at<double>(1,1) 191 ); 192 } 193 194 195 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> &pts1, const vector<Point3f> &pts2, Mat &R, Mat &t) 196 { 197 //初始化g2o 198 typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3>>Block;////pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3 199 Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver=new g2o::LinearSolverEigen<Block::PoseMatrixType>();//线性方程求解器 200 Block* solver_ptr=new Block(unique_ptr<Block::LinearSolverType>(linearSolver));//矩阵块求解器 201 g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver=new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(unique_ptr<Block>(solver_ptr)); 202 g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; 203 optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); 204 205 //vertex 206 g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose=new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap();//camera pose 207 pose->setId(0); 208 pose->setEstimate(g2o::SE3Quat( 209 Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(), 210 Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,0) 211 )); 212 optimizer.addVertex(pose); 213 214 //edges 215 int index=1; 216 vector<EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly*> edges; 217 for(size_t i=0;i<pts1.size();++i) 218 { 219 EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly* edge=new EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly( 220 Eigen::Vector3d(pts2[i].x,pts2[i].y,pts2[i].z)); 221 edge->setId(index); 222 edge->setVertex(0,dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*>(pose)); 223 edge->setMeasurement(Eigen::Vector3d( 224 pts1[i].x,pts1[i].y,pts1[i].z)); 225 edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity()*1e4); 226 optimizer.addEdge(edge); 227 ++index; 228 edges.push_back(edge); 229 } 230 231 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 232 optimizer.setVerbose(true); 233 optimizer.initializeOptimization(); 234 optimizer.optimize(10); 235 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 236 chrono::duration<double> time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2-t1); 237 cout<<"optimization consts time: "<<time_used.count()<<" seconds."<<endl; 238 239 cout<<"after optimization: "<<endl; 240 cout<<"T= "<<endl<<Eigen::Isometry3d(pose->estimate()).matrix()<<endl; 241 }
运行结果:
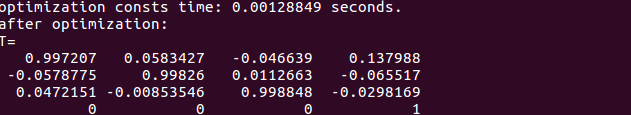
本例得到的结果与我们前面SVD方法得到的位姿结果几乎相同,说明SVD方法已经给出了最优化的解析解
不过,这里有一点疑问,在section 2.3.1的SVD中,先是利用PnP方法求出R,t,作为BA的初始值。而在本例中,SVD和BA是分开的两个方法,那BA是如何设定初始值的呢?:Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(),初始值设为单位矩阵