参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zilanpotou182/article/details/66478915(SIFT、SURF、ORB三种特征点的区别)
1.除了本书介绍的ORB特征点外,你还能找到哪些特征点?请说说SIFT或SURF的原理,并对比它们与ORB之间的优劣
特征点:图像里一些特别的地方
特征点的种类:SIFT、SURF、ORB、FAST
SIFT算法充分考虑了在图像变换过程中出现的光照、尺度、旋转等变化,但是这会带来极大的计算量。
SURF算法的速度远快于SIFT,SURF的鲁棒性很好,特征点识别率较SIFT高,在视角、光照、尺度变化等情形下,大体上都优于SIFT。
ORB算法运算速度与前两者相比速度最快,但是这种算法尺度方面效果较差,因为ORB不具备尺度变换。
定量比较:计算速度:ORB>>SURF>>SIFT(各差一个量级)
旋转鲁棒性:SURF>ORB~SIFT(表示差不多)
模糊鲁棒性: SURF>ORB~SIFT
尺度变换鲁棒性: SURF>SIFT>ORB(ORB并不具备尺度变换性)
综上,我们在选择特征点时的依据是如果对计算实时性要求非常高,可选用ORB算法,但基本要保证正对拍摄;如果对实行性要求稍高,可以选择SURF;基本不用SIFT
2.设计程序调用OpenCV中的其他种类特征点。统计在提取1000个特征点时在你的机器上的运行时间。
首先我们要知道如果要调用opencv中的SIFT和SURF特征点,SIFT和SURF都在nonfree模块中,所以我们就需要nonfree模块。
但是在opencv3中,SURF/SIFT 以及其它的一些东西被移动到了独立的库(opencv_contrib)中。
所以首先我们需要安装opencv_contrib:(如果你用的是opencv2可以省略安装opencv_contrib这一步骤)
安装步骤见:安装opencv_contrib(ubuntu16.0)
ORB、SIFT、SURF三种特征点提取方法的代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 //#include <opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp> 5 //#include <opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp>//SIFT 6 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 7 #include <opencv2/xfeatures2d/nonfree.hpp>//SIFT 8 #include <chrono> 9 10 //using namespace xfeatures2d; 11 using namespace std; 12 using namespace cv; 13 14 int main(int argc,char** argv) 15 { 16 if(argc!=2) 17 { 18 cout<<"usage:feature_extraction img1"<<endl; 19 return 1; 20 } 21 22 //读取图像 23 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 24 25 //初始化 26 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1;//关键点,指特征点在图像里的位置 27 28 //orb 29 chrono::steady_clock::time_point ORB_t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 30 Ptr<ORB> orb=ORB::create(500,1.2f,8,31,0,2,ORB::HARRIS_SCORE,31,20); 31 chrono::steady_clock::time_point ORB_t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 32 chrono::duration<double> ORB_time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(ORB_t2-ORB_t1); 33 cout<<"extract keypoints of ORB costs: "<<ORB_time_used.count()<<" seconds."<<endl; 34 orb->detect(img_1,keypoints_1); 35 36 cout<<"KP1 = "<<keypoints_1.size()<<endl;//特征点的数量 37 Mat outimg1; 38 drawKeypoints(img_1,keypoints_1,outimg1,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT); 39 imshow("1.png的ORB特征点",outimg1); 40 41 42 // //SIFT 43 // chrono::steady_clock::time_point SIFT_t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 44 // Ptr<xfeatures2d::SiftFeatureDetector> siftDetector_1=xfeatures2d::SiftFeatureDetector::create(); 45 // siftDetector_1->detect(img_1,keypoints_1); 46 // chrono::steady_clock::time_point SIFT_t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 47 // chrono::duration<double> SIFT_time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(SIFT_t2-SIFT_t1); 48 // cout<<"extract keypoints of SIFT costs: "<<SIFT_time_used.count()<<" seconds."<<endl; 49 // Mat outImg; 50 // drawKeypoints(img_1,keypoints_1,outImg,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT); 51 52 // cout<<"KP1 = "<<keypoints_1.size()<<endl; 53 // imshow("1.png的SIFT特征点",outImg); 54 55 // //SURF 56 // chrono::steady_clock::time_point SURF_t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 57 // Ptr<xfeatures2d::SurfFeatureDetector> surfDetector_1=xfeatures2d::SurfFeatureDetector::create(); 58 // surfDetector_1->detect(img_1,keypoints_1); 59 // chrono::steady_clock::time_point SURF_t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 60 // chrono::duration<double> SURF_time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(SURF_t2-SURF_t1); 61 // cout<<"extract keypoints of SURF costs: "<<SURF_time_used.count()<<" seconds."<<endl; 62 // Mat outImg; 63 // drawKeypoints(img_1,keypoints_1,outImg,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT); 64 // cout<<"KP1 = "<<keypoints_1.size()<<endl; 65 // imshow("1.png的SURF特征点",outImg); 66 waitKey(0); 67 68 return 0; 69 }
实验结果:原始图像为:

1) ORB

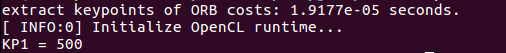
2) SIFT

![]()
3) SURF
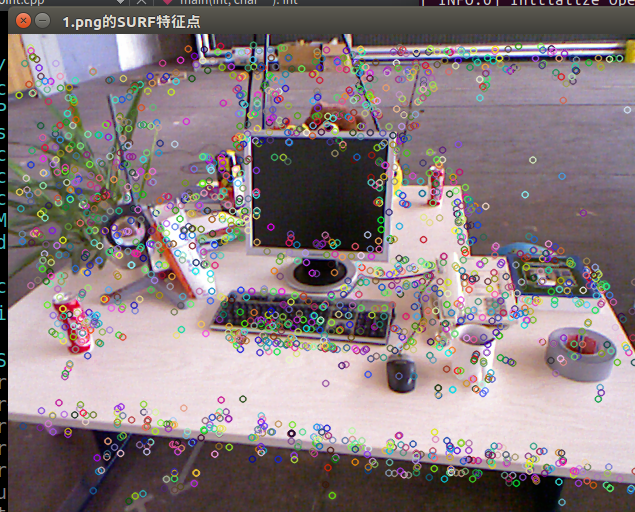
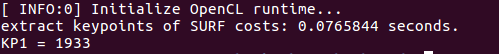
分析:可见,计算速度是ORB最快,SURF次之,SIFT最慢。
但是为什么基于同一张图片提取特征点,三种方法提取出的特征点数目不一样而且相差还很多呢?应该是因为三种方法的原理决定的吧,是因为三种方法提取特征点时选择什么是特征点的依据不同?
SURF选取特征点的依据:SURF算法先利用Hessian矩阵确定候选点,然后进行非极大抑制。
3.我们发现,OpenCV提供的ORB特征点在图像当中分布不够均匀,你是否能找到或提出让特征点分布更加均匀的方法?
我的想法是对于一张待提取特征点的图像,我们把它分成一个个小块,设定一个阈值,对于对个小块,提取特征点,若特征点的数目超过了阈值就不再提取(这种方式可能速度快一些,但是缺点也很明显……),或者在所有提取到的特征点中选择等于阈值的更好的特征点?
利用非极大值抑制取出局部较密集特征点的思想:使用非极大值抑制算法去除临近位置多个特征点的问题。为每一个特征点计算出其响应大小。计算方式是一个特征点和其周围n个特征点偏差的绝对值和。在比较临近的特征点中,保留响应值较大的特征点,删除其余的特征点。
10.在Ceres中实现PnP和ICP的优化
PnP:
求解一个优化问题,关键是是要写出它的cost Fuction的最小二乘形式。
根据教材的分析,本题的最小二乘问题可写作:(见P162)
这个误差项表示的是将像素坐标(观测到的投影位置)与3D点按照当前估计的位姿进行投影得到的位置相比较得到的误差。所以,我们可以得到以下信息:
已知的有:3D点——我们用p_3D表示(等下程序中用),其对应得投影坐标记为(u, v)
观测得到的投影位置的像素坐标——p_p
待估计的变量:R,t
并且在利用ceres优化时,我们还要给出残差的形式:
residual[0]=u-p_p(0,0)
residual[1]=v-p_p(0,1)
Ceres的用法步骤:1)定义Cost Function模型;2)调用AddResidualBlock将误差项添加到目标函数中;3)自动求导需要指定误差项和优化变量得维度;4)定好问题后,调用solve函数求解。
理清楚整个问题的流程,我们就可以利用Ceres优化库来实现PnP优化了。同时优化相机的位姿(即内参,R,t)和外参,代码如下:参考https://www.jianshu.com/p/34cb21e00264
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 4 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 5 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 6 #include <Eigen/Core> 7 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 8 #include <ceres/ceres.h> 9 #include <Eigen/SVD> 10 #include <chrono> 11 12 #include "common/tools/rotation.h" 13 14 15 using namespace std; 16 using namespace cv; 17 18 19 //第一步:定义Cost Function函数 20 struct cost_function 21 { 22 cost_function(Point3f p_3D,Point2f p_p):_p_3D(p_3D),_p_p(p_p) {}//3D-2D:知道n个3D空间点以及其投影位置,然后估计相机位姿 23 //计算残差 24 template <typename T>//模板:使得在定义时可以模糊类型 25 bool operator() ( 26 const T* const r, const T* const t,//r,t为待优化的参数 27 const T* K,//k为待优化的参数 28 T* residual ) const //殘差 29 { 30 T p_3d[3]; 31 T p_Cam[3];//相机坐标系下空间点的坐标 32 p_3d[0]=T(_p_3D.x); 33 p_3d[1]=T(_p_3D.y); 34 p_3d[2]=T(_p_3D.z); 35 // 通过tool文件夹中的rotation.h中的AngleAxisRotatePoint()函数 36 // 计算在相机仅旋转的情况下,新坐标系下的坐标 37 // 也就是p_Cam=R*p_3d 38 cout<<"point_3d: "<<p_3d[0]<<" "<<p_3d[1]<<" "<<p_3d[2]<<endl; 39 AngleAxisRotatePoint(r,p_3d,p_Cam); 40 41 p_Cam[0]=p_Cam[0]+t[0]; 42 p_Cam[1]=p_Cam[1]+t[1]; 43 p_Cam[2]=p_Cam[2]+t[2]; 44 //R,t计算T 45 //Eigen::Isometry3d T_w_c; 46 // T_w_c.rotate(r); 47 48 const T x=p_Cam[0]/p_Cam[2]; 49 const T y=p_Cam[1]/p_Cam[2]; 50 //3D点投影后的像素坐标 51 // const T u=x*520.9+325.1; 52 // const T v=y*521.0+249.7; 53 const T u=x*K[0]+K[1]; 54 const T v=y*K[2]+K[3]; 55 56 //观测到的投影位置的像素坐标 57 T u1=T(_p_p.x); 58 T v1=T(_p_p.y); 59 60 //残差 61 residual[0]=u-u1; 62 residual[1]=v-v1; 63 } 64 Point3f _p_3D; 65 Point2f _p_p; 66 }; 67 68 void find_feature_matches ( 69 const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 70 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 71 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 72 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ); 73 74 // 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 75 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ); 76 77 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> points_3d, 78 const vector<Point2f> points_2d, Mat K, Mat &r, Mat &t); 79 80 int main ( int argc, char** argv ) 81 { 82 if ( argc != 4 ) 83 { 84 cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1"<<endl; 85 return 1; 86 } 87 //-- 读取图像 88 Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 89 Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); 90 91 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2; 92 vector<DMatch> matches; 93 find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches ); 94 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; 95 96 // 建立3D点 97 Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 98 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); 99 vector<Point3f> pts_3d; 100 vector<Point2f> pts_2d; 101 for ( DMatch m:matches ) 102 { 103 ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ]; 104 if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth 105 continue; 106 float dd = d/5000.0; 107 Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K ); 108 pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) ); 109 pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt ); 110 } 111 112 cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl; 113 114 Mat r, t; 115 // solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false,cv::SOLVEPNP_EPNP ); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法 116 // solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false,CV_ITERATIVE ); 117 solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); 118 Mat R; 119 cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 120 121 cout<<"optional before: "<<endl; 122 cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl; 123 cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl<<endl; 124 125 cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl; 126 127 bundleAdjustment(pts_3d,pts_2d,K,r,t); 128 } 129 130 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 131 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 132 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 133 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 134 { 135 //-- 初始化 136 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 137 // used in OpenCV3 138 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 139 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 140 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 141 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 142 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 143 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 144 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 145 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 146 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 147 148 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 149 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 150 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 151 152 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 153 vector<DMatch> match; 154 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 155 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 156 157 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 158 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 159 160 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 161 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 162 { 163 double dist = match[i].distance; 164 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 165 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 166 } 167 168 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 169 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 170 171 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 172 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 173 { 174 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 175 { 176 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 177 } 178 } 179 } 180 181 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ) 182 { 183 return Point2d 184 ( 185 ( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), 186 ( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 ) 187 ); 188 } 189 190 //构建最小二乘问题 191 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> points_3d, 192 const vector<Point2f> points_2d,Mat K, Mat &r, Mat &t) 193 { 194 // cout<<"R = "<<endl<<R<<endl; 195 cout<<"start:"<<endl; 196 double rotation_vector[3],tranf[3];//旋转向量r,平移t 197 double k[4]; 198 rotation_vector[0]=r.at<double>(0,0); 199 rotation_vector[1]=r.at<double>(0,1); 200 rotation_vector[2]=r.at<double>(0,2); 201 202 tranf[0]=t.at<double>(0,0); 203 tranf[1]=t.at<double>(1,0); 204 tranf[2]=t.at<double>(2,0); 205 206 k[0]=520.9; 207 k[1]=325.1; 208 k[2]=521.0; 209 k[3]=249.7; 210 211 ceres::Problem problem; 212 for(int i=0;i<points_3d.size();++i) 213 { 214 ceres::CostFunction* costfunction=new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<cost_function,2,3,3,4>(new cost_function(points_3d[i],points_2d[i])); 215 problem.AddResidualBlock(costfunction,NULL,rotation_vector,tranf,k); 216 } 217 // cout<<rotation_vector[0]<<" "<<rotation_vector[1]<<" "<<rotation_vector[2]<<endl; 218 //配置求解器 219 ceres::Solver::Options option; 220 option.linear_solver_type=ceres::DENSE_QR;//DENSE_SCHUR 221 //true:迭代信息输出到屏幕.false:不输出 222 option.minimizer_progress_to_stdout=true; 223 224 ceres::Solver::Summary summary;//优化信息 225 //可以和g2o优化做对比 226 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 227 //开始优化 228 ceres::Solve(option,&problem,&summary); 229 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2=chrono::steady_clock::now(); 230 chrono::duration<double> time_used=chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2-t1); 231 cout<<"solve time cost = "<<time_used.count()<<" second."<<endl; 232 233 //输出结果 234 cout<<summary.BriefReport()<<endl; 235 Mat Rotaion_vector=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<rotation_vector[0],rotation_vector[1],rotation_vector[2]); 236 // cout<<rotation_vector[0]<<" "<<rotation_vector[1]<<""<<rotation_vector[2]<<endl;//0,1,2 237 Mat Rotation_matrix; 238 Rodrigues(Rotaion_vector,Rotation_matrix);//r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 239 cout<<"after optional:"<<endl; 240 cout<<"R = "<<endl<<Rotation_matrix<<endl; 241 // cout<<"R = "<<endl<<<<endl; 242 cout<<"t = "<<tranf[0]<<" "<<tranf[1]<<" "<<tranf[2]<<endl; 243 }
结果:
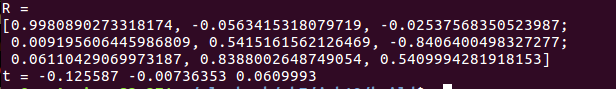
和g2o优化所得结果做对比:结果大致相同,优化用时也差不多。
ICP:
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1b02e9a36cc4
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <ceres/ceres.h> 4 5 #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 6 #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> 7 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> 8 #include <Eigen/Core> 9 #include <Eigen/Geometry> 10 #include <Eigen/SVD> 11 12 #include <chrono> 13 14 #include "common/tools/rotation.h" 15 16 using namespace std; 17 using namespace cv; 18 19 void find_feature_matches(const Mat& img_1,const Mat& img_2, 20 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 21 vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 22 vector<DMatch>& matches); 23 24 //像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 25 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d& p,const Mat& K); 26 27 void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f>& pts1, 28 const vector<Point3f>& pts2, 29 Mat& r,Mat& t_inv); 30 31 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f>& points_3f, 32 const vector<Point3f>& points_2f, 33 Mat& R, Mat& t_inv);//test 声明的行参和定义的不同是否可行:可以的! 34 35 struct cost_function_define 36 { 37 cost_function_define(Point3f p1,Point3f p2):_p1(p1),_p2(p2){} 38 template<typename T> 39 bool operator()(const T* const cere_r,const T* const cere_t,T* residual) const 40 { 41 T p_1[3]; 42 T p_2[3]; 43 p_1[0]=T(_p1.x); 44 p_1[1]=T(_p1.y); 45 p_1[2]=T(_p1.z); 46 AngleAxisRotatePoint(cere_r,p_1,p_2); 47 p_2[0]=p_2[0]+cere_t[0]; 48 p_2[1]=p_2[1]+cere_t[1]; 49 p_2[2]=p_2[2]+cere_t[2]; 50 const T x=p_2[0]/p_2[2]; 51 const T y=p_2[1]/p_2[2]; 52 const T u=x*520.9+325.1; 53 const T v=y*521.0+249.7; 54 T p_3[3]; 55 p_3[0]=T(_p2.x); 56 p_3[1]=T(_p2.y); 57 p_3[2]=T(_p2.z); 58 59 const T x1=p_3[0]/p_3[2]; 60 const T y1=p_3[1]/p_3[2]; 61 62 const T u1=x1*520.9+325.1; 63 const T v1=y1*521.0+249.7; 64 65 residual[0]=u-u1; 66 residual[1]=v-v1; 67 } 68 Point3f _p1,_p2; 69 }; 70 71 int main(int argc,char** argv) 72 { 73 if(argc!=5) 74 { 75 cout<<"usage:pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"<<endl; 76 return 1; 77 } 78 79 //读取图像 80 Mat img_1=imread(argv[1],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);//test 81 Mat img_2=imread(argv[2],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); 82 83 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2; 84 vector<DMatch> matches; 85 find_feature_matches(img_1,img_2,keypoints_1,keypoints_2,matches); 86 cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size()<<"组匹配点"<<endl; 87 88 //建立3D点 89 Mat depth_1=imread(argv[3],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 90 Mat depth_2=imread(argv[4],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 91 Mat K=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<520.9,0,325.1, 92 0,521.0,249.7, 93 0,0,1); 94 vector<Point3f> pts1,pts2; 95 for(DMatch m:matches) 96 { 97 ushort d1=depth_1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)]; 98 ushort d2=depth_2.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x)]; 99 if(d1==0 || d2==0)//bad depth 100 continue; 101 Point2d p1=pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt,K); 102 Point2d p2=pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt,K); 103 float dd1=float(d1)/5000.0; 104 float dd2=float(d2)/5000.0; 105 pts1.push_back(Point3f(p1.x*dd1,p1.y*dd1,dd1)); 106 pts2.push_back(Point3f(p2.x*dd2,p2.y*dd2,dd2)); 107 } 108 109 cout<<"3d-3d pairs: "<<pts1.size()<<endl; 110 Mat R,t; 111 pose_estimation_3d3d(pts1,pts2,R,t); 112 cout<<"ICP via SVD results: "<<endl; 113 cout<<"R ="<<endl<<R<<endl; 114 cout<<"t ="<<endl<<t<<endl; 115 Mat R_inv=R.t(); 116 Mat t_inv=-R.t()*t; 117 cout<<"R_inv ="<<endl<<R_inv<<endl;//R^(-1) 118 cout<<"t_inv ="<<endl<<t_inv<<endl; 119 120 Mat r; 121 Rodrigues(R_inv,r);//R_inv->r 122 cout<<"r= "<<endl<<r<<endl; 123 124 for(int i=0;i<5;++i) 125 { 126 cout<<"p1= "<<pts1[i]<<endl;//?? 127 cout<<"p2= "<<pts2[i]<<endl;//?? 128 cout<<"(R*p2+t) = "<< 129 R*(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<pts2[i].x,pts2[i].y,pts2[i].z)+t 130 <<endl; 131 cout<<endl; 132 } 133 134 cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl; 135 bundleAdjustment(pts1,pts2,r,t_inv); 136 137 return 0; 138 } 139 140 //匹配特征点对 141 void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, 142 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, 143 std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, 144 std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) 145 { 146 //-- 初始化 147 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; 148 // used in OpenCV3 149 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); 150 Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); 151 // use this if you are in OpenCV2 152 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); 153 // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); 154 Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); 155 //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 156 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); 157 detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); 158 159 //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 160 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); 161 descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); 162 163 //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 164 vector<DMatch> match; 165 // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); 166 matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); 167 168 //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 169 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; 170 171 //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 172 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 173 { 174 double dist = match[i].distance; 175 if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; 176 if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; 177 } 178 179 printf ( "-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist ); 180 printf ( "-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist ); 181 182 //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. 183 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) 184 { 185 if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) 186 { 187 matches.push_back ( match[i] ); 188 } 189 } 190 } 191 192 Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) 193 { 194 return Point2d( 195 (p.x-K.at<double>(0,2))/K.at<double>(0,0), 196 (p.y-K.at<double>(1,2))/K.at<double>(1,1) 197 ); 198 } 199 200 void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1, const vector<Point3f> &pts2, Mat &r, Mat &t_inv) 201 { 202 Point3f p1,p2;//center of mass 203 int N=pts1.size(); 204 //计算两组点的质心位置p1,p2 205 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 206 { 207 p1+=pts1[i]; 208 p2+=pts2[i]; 209 } 210 p1=Point3f(Vec3f(p1)/N);//test 211 cout<<"p1 ="<<endl<<p1<<endl; 212 p2=Point3f(Vec3f(p2)/N);//test 213 214 //计算每个点的去质心坐标q1,q2 215 vector<Point3f> q1(N),q2(N); 216 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 217 { 218 q1[i]=pts1[i]-p1; 219 q2[i]=pts2[i]-p2; 220 } 221 222 //compute q1*q2^T,即书中P174的矩阵W(7.56) 223 Eigen::Matrix3d W=Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero(); 224 for(int i=0;i<N;++i) 225 { 226 W+=Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x,q1[i].y,q1[i].z)*Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x,q2[i].y,q2[i].z).transpose(); 227 } 228 cout<<"W ="<<endl<<W<<endl<<endl; 229 230 //SVD on W 231 Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W,Eigen::ComputeFullU|Eigen::ComputeFullV); 232 Eigen::Matrix3d U=svd.matrixU(); 233 Eigen::Matrix3d V=svd.matrixV(); 234 235 if(U.determinant()*V.determinant()<0) 236 { 237 for(int x=0;x<3;++x) 238 { 239 U(x,2)*=-1; 240 } 241 } 242 243 cout<<"U="<<U<<endl; 244 cout<<"V="<<V<<endl; 245 246 Eigen::Matrix3d R_=U*(V.transpose()); 247 Eigen::Vector3d t_=Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x,p1.y,p1.z)-R_*Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x,p2.y,p2.z); 248 249 //convert to cv::Mat 250 r=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<< 251 R_(0,0),R_(0,1),R_(0,2), 252 R_(1,0),R_(1,1),R_(1,2), 253 R_(2,0),R_(2,1),R_(2,2)); 254 t_inv=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<t_(0,0),t_(1,0),t_(2,0)); 255 } 256 257 void bundleAdjustment(const vector<Point3f> &pts1, const vector<Point3f> &pts2, Mat &r, Mat &t_inv) 258 { 259 260 double cere_rot[3], cere_tranf[3]; 261 //关于初值的选取有疑问,随便选择一个初值时,结果不正确,why?? 262 cere_rot[0]=r.at<double>(0,0); 263 cere_rot[1]=r.at<double>(1,0); 264 cere_rot[2]=r.at<double>(2,0); 265 266 cere_tranf[0]=t_inv.at<double>(0,0); 267 cere_tranf[1]=t_inv.at<double>(1,0); 268 cere_tranf[2]=t_inv.at<double>(2,0); 269 270 271 ceres::Problem problem; 272 for(int i=0;i<pts1.size();++i) 273 { 274 ceres::CostFunction* costfunction=new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<cost_function_define,2,3,3>(new cost_function_define(pts1[i],pts2[i])); 275 problem.AddResidualBlock(costfunction,NULL,cere_rot,cere_tranf); 276 } 277 278 ceres::Solver::Options option; 279 option.linear_solver_type=ceres::DENSE_SCHUR; 280 option.minimizer_progress_to_stdout=true; 281 ceres::Solver::Summary summary; 282 ceres::Solve(option,&problem,&summary); 283 cout<<summary.BriefReport()<<endl; 284 285 cout<<"optional after: "<<endl; 286 Mat cam_3d=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<cere_rot[0],cere_rot[1],cere_rot[2]); 287 // cout<<"cam_3d : "<<endl<<cam_3d<<endl; 288 Mat cam_9d; 289 Rodrigues(cam_3d,cam_9d); 290 291 292 cout<<"cam_9d: "<<endl<<cam_9d<<endl; 293 cout<<"cam_t: "<<endl<<cere_tranf[0]<<" "<<cere_tranf[1]<<" "<<cere_tranf[2]<<endl; 294 Mat tranf_3d=(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<cere_tranf[0],cere_tranf[1],cere_tranf[2]); 295 296 for(int i=0;i<5;++i) 297 { 298 cout<<"p1= "<<pts1[i]<<endl; 299 cout<<"p2= "<<pts2[i]<<endl; 300 cout<<"(R*p1+t)= "<< 301 cam_9d*(Mat_<double>(3,1)<<pts1[i].x,pts1[i].y,pts1[i].z)+tranf_3d<<endl; 302 cout<<endl; 303 } 304 }
结果:
仅用ICP得到的位姿为:
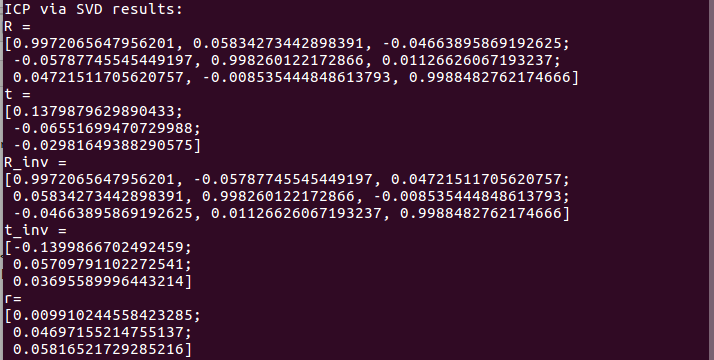
我们在两幅图片上分别找一些特征点验证得到的位姿结果:p1=R*p2+t

利用Ceres优化之后:

进行验证:
