C#里结构体是值类型,其局部变量的空间分配在栈上。很多同学喜欢用它,是因为它的存储密度高、分配和回收成本非常低。
但是前几天在查热点的时候,却碰到结构体的性能非常慢,甚至远低于把同样数据结构做成的引用类型。下文对这个问题做了些简化,方便大家理解。
代码分析
优化前的源代码示例:
//结构体声明 public struct Point2D { public int X { get; set; } public int Y { get; set; } } var target = new Point2D() { X = 99, Y = 100 }; //热点语句,points 是一个有几百万元素的链表: foreach(var item in point2Ds) { if (item.Equals(target)) return target; }
优化方法很简单,就是在Point2D的结构体声明中,加一个手写的Equals方法:
//优化后: public struct Point2D { public int X { get; set; } public int Y { get; set; } public bool Equals(Point2D obj) { return obj.X == this.X && obj.Y == this.Y; } }
性能测试
构造一个有1千万元素的points。
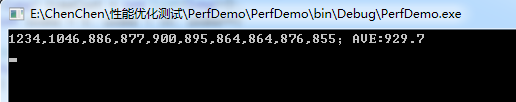
优化前的执行时间(单位:ms)
优化后的执行时间(单位:ms)
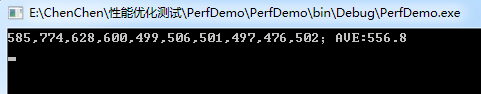
前后提升差不多50%。
原理分析
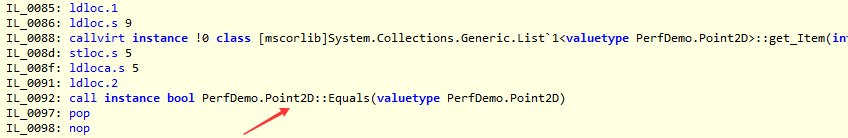
查看IL可以发现,优化后是调用的Point2D.Equals方法,也就是我们写的方法:
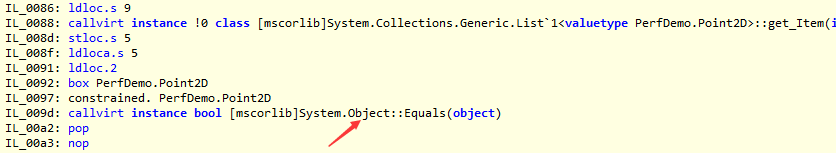
而优化前的IL如下,是调用Object.Equals方法:
那么,这两者有什么区别呢?
可以查看一下struct的Equals方法。由于struct是值类型,它从ValueType继承来,因此Equals方法实际是执行的ValueType.Equals。
源码地址:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/mscorlib/system/valuetype.cs.html
public abstract class ValueType { [System.Security.SecuritySafeCritical] public override bool Equals (Object obj) { BCLDebug.Perf(false, "ValueType::Equals is not fast. "+this.GetType().FullName+" should override Equals(Object)"); if (null==obj) { return false; } RuntimeType thisType = (RuntimeType)this.GetType(); RuntimeType thatType = (RuntimeType)obj.GetType(); if (thatType!=thisType) { return false; } Object thisObj = (Object)this; Object thisResult, thatResult; // if there are no GC references in this object we can avoid reflection // and do a fast memcmp if (CanCompareBits(this)) return FastEqualsCheck(thisObj, obj); FieldInfo[] thisFields = thisType.GetFields(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic); for (int i=0; i<thisFields.Length; i++) { thisResult = ((RtFieldInfo)thisFields[i]).UnsafeGetValue(thisObj); thatResult = ((RtFieldInfo)thisFields[i]).UnsafeGetValue(obj); if (thisResult == null) { if (thatResult != null) return false; } else if (!thisResult.Equals(thatResult)) { return false; } } return true; } }
可以发现,ValueType.Equals方法并不是直接比较的两者引用地址是否相等,而是递归遍历struct的每个字段,判断它们是否相等。而在遍历struct字段时,使用了反射取值,这是很耗性能的。
另外,由于其参数是Object类型,会把传入的struct做一次装箱,这也是热点。
而我们写的方法,是直接对比属性,而且传入参数是Point2D类型,也不用装箱,可以直接使用。
总结一下,在使用结构体的时候,避免装箱,重写Equals方法避免原Equals的反射。
性能优化相关文章: