带着问题去思考!大家好!
今天我们说说线程池,线程池为什么来呢?
之前我们讲过线程,它的创建和协作的几种方式。花费极少的时间来完成创建很多异步操作。创建线程是昂贵的操作,所以为每个短暂的异步操作创建线程会产生显著的开销
那么为了解决这一问题,有一个常用的方式叫做池,线程池可以成功的适用于任何需要大量短暂的开销大的资源情形。事先分配一定的资源,将这些资源放到资源池中。每次需要新的资源,只需要从池中获取一个,不需要创建新的。
通过System.Threading.ThreadPool类型可以使用线程池。线程池是受.NET通用语言运行时(CLR)管理的。每个CLR都有一个线程池的实例,ThreadPool类型拥有一个QueueUserWorkItem静态方法,该静态方法接受一个委托。方法被调用后,委托会进入内部队列中,如果池中没有任何线程,将创建一个新的工作线程并将队列中第一个委托放入到该工作线程中。
注意:保持线程中的操作都是短暂的。
停止:停止线程池中放置新操作时,线程池最终会删除一定时间后过期的不再使用的线程。这将释放所有那些不再需要的系统资源。
线程池中的的工作线程都是后台线程。这意味着当所有的前台线程(主线程)完成后,所有的后台线程将停止工作。
在线程池中使用委托
这里我们将说到异步编程模型(Asynchronous Programming Model,简称APM)的方式。
private delegate string RunOnThreadPool(out int threadId); private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar) { Console.WriteLine("Starting a callback..."); Console.WriteLine("State passed to a callback:{0}", ar.AsyncState); Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } private static string Test(out int threadId) { Console.WriteLine("Starting...."); Console.WriteLine("Is thraed pool thread :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; return string.Format("Thread pool worker thread id was:{0}", threadId); } static void Main(string[] args) { int threadId = 0; RunOnThreadPool poolDelegate = Test; var t = new Thread(() => Test(out threadId)); t.Start(); t.Join(); Console.WriteLine("Thread id:{0}", threadId); //使用APM方式,进行异步调用, IAsyncResult r = poolDelegate.BeginInvoke(out threadId, Callback, "a delege asynchronous call"); r.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(); string result = poolDelegate.EndInvoke(out threadId, r); Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id:{0}", threadId); Console.WriteLine(result); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }
运行结果:
.NET CORE不支持BeginInvoke
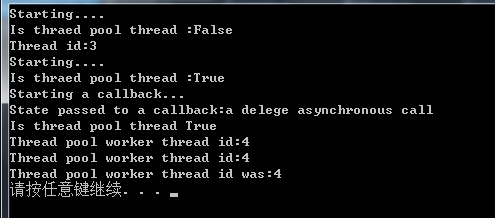
首先开始我们使用以前的方式创建一个线程,然后启动它并等待完成。而TheadPool为开始线程池任务输出的信息,Callback为APM模式运行任务结束后,执行的回调方法。
使用BeginOperationName/EndOperationName方法和.NET中的IAsyncResult对象等方式称为异步编程模型(或APM模式),这样的方法称为异步方法,但在现代编程中,更推荐使用任务并行库(Task Parallel Libary,TPL)来组织异步API
向线程池中放入异步操作
private static void AsyncOperation(object state) { Console.WriteLine("Operation state:{0}",state??"(null)"); Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); } static void Main(string[] args) { const int x = 1; const int y = 2; const string lambdaState = "lambda state 2"; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation, "async state"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(state => { Console.WriteLine("Operation state:{0}", state); Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }, "lambda state"); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => { Console.WriteLine("Operation state:{0},{1}", x+y,lambdaState); Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }, "lambda state"); }
定义一个方法,首先接受单个object类型的参数,通过QueueUserWorkItem方法将该方法放到线程池.接着再次放入该方法,但是这次给方法调用传入一个状态对象,该对象将作为状态参数给AsynchronousOperation方法,
闭包机制,无需传递lambda表达式的状态,闭包更灵活,允许我们向异步操作传递一个以上的对象而且这些对象具有静态类型。
线程池与并行度
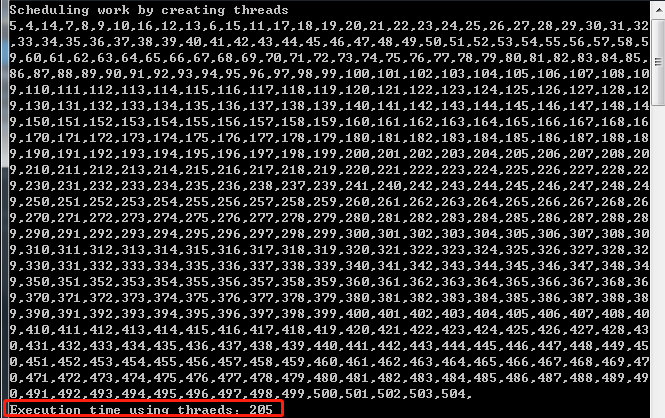
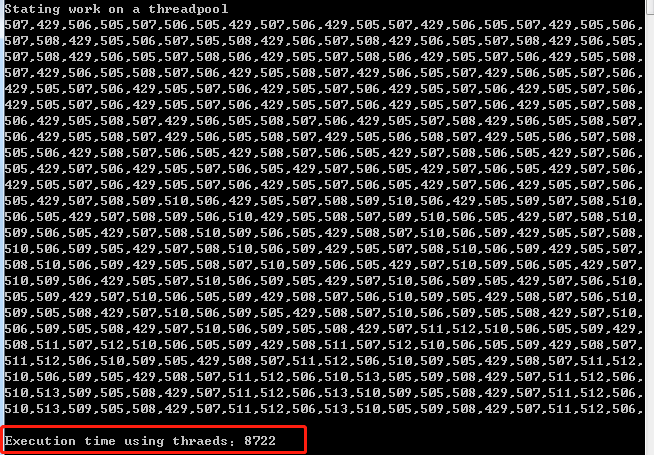
static void UseThreads(int numberOfOperations) { using (var countdown=new CountdownEvent(numberOfOperations)) { Console.WriteLine("Scheduling work by creating threads"); for (int i = 0; i < numberOfOperations; i++) { var thread = new Thread(()=> { Console.Write("{0},", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); countdown.Signal();//向 CountdownEvent 注册信号,同时减小 CurrentCount 的值。 }); thread.Start(); } countdown.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(); } } static void UseThreadPool(int numberOfOperations) { using (var countdown=new CountdownEvent(numberOfOperations)) { Console.WriteLine("Stating work on a threadpool"); for (int i = 0; i < numberOfOperations; i++) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_=> { Console.Write("{0},", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); countdown.Signal();//向 CountdownEvent 注册信号,同时减小 CurrentCount 的值。 }); } countdown.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { const int numberOfOperations = 500; var sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); UseThreads(numberOfOperations); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Execution time using thraeds:{0}",sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); sw.Reset(); sw.Start(); UseThreadPool(numberOfOperations); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Execution time using thraeds:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); }
当程序启动的时候,创建很多不同的线程,每个线程运行一个操作,该操作打印出线程id并阻塞线程100毫秒,我们创建500个线程,虽然使用了205毫秒,但是线程消耗了大量的操作系统资源。
然后我们执行同样的任务,只不过不为每个操作创建一个线程,将它们放入到线程池当中。线程池在快结束的时候创建更多的线程,但是仍然花费了更多的时间,在我的机器上是接近9秒,我们为操作系统节省了内存和线程数,但是执行时间长了


实现一个取消
static void AsyncOperation1(CancellationToken token) { Console.WriteLine("Starting the first task"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if (token.IsCancellationRequested) { Console.WriteLine("The first task has been canceled"); return; } Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } Console.WriteLine("The first task has completed succesfuly"); } static void AsyncOperation2(CancellationToken token) { try { Console.WriteLine("Starting the first task"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } Console.WriteLine("The second task has completed succesfuly"); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { Console.WriteLine("The second task has been canceld"); } } private static void AsyncOperation3(CancellationToken token) { bool cancellationFlag = false; token.Register(() => cancellationFlag = true); Console.WriteLine("Starting the third task"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if (cancellationFlag) { Console.WriteLine("The third task has been canceld"); return; } Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } Console.WriteLine("The third task has been succesfuly"); } static void Main(string[] args) { using (var cts=new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_=>AsyncOperation1(token)); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); cts.Cancel(); } using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => AsyncOperation2(token)); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); cts.Cancel(); } using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => AsyncOperation3(token)); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); cts.Cancel(); } Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }

这里我们用了CancellationTokenSource和CancellationToken两个新类,它们在.NET4.0被引入,这里使用了三种方式来实现取消标记功能。
第一种使用轮询来检查CancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested属性。如果该属性为true,则说明操作需要被取消,
第二种是抛出一个OperationCancelledException异常。这允许在操作之外控制取消过程,需要取消操作时,通过操作之外的代码来处理。
最后一种是注册一个回调函数,当操作被取消时,在线程池调用该回调函数,这允许链式传递一个取消逻辑到另一个异步操作中
在线程池中使用等待事件处理器及超时
static void RunOperations(TimeSpan workOperationTimeOut)
{
using (var evt = new ManualResetEvent(false))
using (var cts=new CancellationTokenSource())
{
Console.WriteLine("Registering timeout operation....");
var worker = ThreadPool.RegisterWaitForSingleObject(evt, (state, isTimedOut) => WorkOperationWait(cts, isTimedOut), null, workOperationTimeOut, true);
Console.WriteLine("Statrting long running operation...");
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => WorkOperation(cts.Token, evt));
Thread.Sleep(workOperationTimeOut.Add(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)));
worker.Unregister(evt);
}
}
private static void WorkOperationWait(CancellationTokenSource cts, bool isTimedOut)
{
if(isTimedOut)
{
cts.Cancel();
Console.WriteLine("Worker operation timed out and was canceled");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Worker operation successed");
}
}
private static void WorkOperation(CancellationToken token,ManualResetEvent evt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
if(token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
return;
}
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)) ;
}
evt.Set();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
RunOperations(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5));
RunOperations(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(7));
}
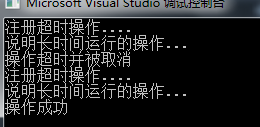
线程池还有一个有用的方法:ThreadPool.RegisterWaitForSingleObject.该方法允许我们将回调函数放入线程池中的队列中。当提供的等待事件处理器收到信号或发生超时时,该回调函数将被调用,这允许我们为线程池中的操作实现超时功能。
首先按顺序向线程池中放入一个耗时长的操作,它运行6秒,一旦完成,会设置一个ManualResetEvent信号类。其他情况。比如取消,则操作会被丢弃、
注册第二个异步操作,当从ManualResetEvent对象接受一个信号后,该异步操作会被调用。如果一个操作顺利完成,会设置该信号量。另一种情况是第一个操作还未完成就已经超时,如果发生该情况,会使用CancellationToken来取消第一个操作。
最后,为操作提供5秒的超时时间是不够的,这是因为操作会花费6秒来完成,只能取消该操作。所以如果提供7秒的超时时间是可行的。该操作会顺利完成。