带着问题去思考!大家好
并发集合(线程安全),既然是并发集合。那就要知道什么是并发。
并发:同一时间间隔对资源的共享。
| ConcurrentDictionary | 线程安全字典集合,对于读操作无需使用锁,写操作则需要锁。该并发使用多个锁。 |
| ConcurrentQueue | 使用了原子的比较和交换,使用SpanWait来保证线程安全,实现了FIFO.可以调用Enqueue方法向队列中加入元素。TryDequequ方法试图取出队列中的第一个元素,TryPeek方法则试图得到第一个元素但并不从队列中删除元素 |
| ConcurrentStack |
实际中没有任何锁,采用CAS操作,LIFO集合,可以用push,pushRange方法添加元素,使用tryPop和TryPopRange方法获取元素,使用TryPeek方法检查 |
| ConcurrentBag | 支持重复元素无序集合,针对这样以下情况进行了优化,及多个线程以这样的方式工作,每个线程产生和消费自己的任务,极少与其他线程的任务交互,Add添加,TryPeek方法,获取元素用TryTask方法 |
| BlockingCollection | 是对IprodicerConsumerCollection泛型接口的实现的一个高级封装。支持如下功能,分块,调整内部集合容量,取消集合操作。从多块中获取元素 |
其中ConcurrentQueue,ConcurrentStack,ConcurrentBag避免使用上面提及的集合的Count属性,实现这些集合使用的是链表。Count时间复杂度为O(N).检查集合是否为空,使用IsEmpty属性,时间复杂度为O(1).
这里我们基本介绍下功能:
ConcurrentDictionary
单线程环境中的字典集合与使用并发字典的性能。

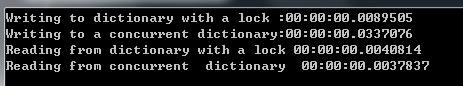
const string Item = "Dictionary item"; public static string CurrentItem; /// <summary> /// ConcurrentDictionary写操作比使用锁的通常的字典要慢得多。而读操作则要快些。 /// 因此如果对字典需要大量的线程安全读操作,concurrentDictionary是最好的选择。 /// </summary> /// <param name="args"></param> static void Main(string[] args) { var concurrentDictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<int, string>(); //并发集合 var dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>(); //正常集合 var sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { //锁机制向标准的字典中添加元素,并测量完成100万次迭代的时间。 lock(dictionary) { dictionary[i] = Item; } } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Writing to dictionary with a lock :{0}", sw.Elapsed); sw.Restart(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { //比较两个集合中获取值的性能 concurrentDictionary[i] = Item; } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Writing to a concurrent dictionary:{0}",sw.Elapsed); sw.Restart(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { lock(dictionary) { CurrentItem = dictionary[i]; } } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Reading from dictionary with a lock {0}",sw.Elapsed); sw.Restart(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { CurrentItem = concurrentDictionary[i]; } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Reading from concurrent dictionary {0}", sw.Elapsed); }
创建两个集合,其中一个是标准的字典集合,另一个是新的并发字典集合。采用锁的机制想标准的字典中添加元素。比较两者之间。我们发现ConcurrentDictionary写操作比使用锁的通常的字典要慢的多,而读操作则要快些。因此如果对字典需要大量的线程安全的操作。ConcurrentDictionary是最好的选择。
ConcurrentDictionary的实现使用了细粒度锁技术,在多线程写入方面比使用锁的通常的字典的可伸缩性更好。在本例中,当只用一个线程时,并发字典非常慢。但是扩展到5-6个线程,并发字典的性能会更好
如果你对字典只需要多线程访问只读元素,则没必要执行线程安全的读操作。在此场景中最好只使用通常的字典或者ReadOnlyDictionary集合。
ConcurrentQueue
创建能被多个工作者异步处理的一组任务的例子

static async Task RunProgram() { var taskQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<CustomerTask>();//任务队列 var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); //取消标志 var taskSource = Task.Run(() => TaskProducer(taskQueue)); Task[] processors = new Task[4]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { string processorId = i.ToString(); processors[i - 1] = Task.Run(() => TaskProcessor(taskQueue, "Processor" + processorId, cts.Token)); await taskSource; cts.CancelAfter(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); await Task.WhenAll(processors); } } private static async Task TaskProducer(ConcurrentQueue<CustomerTask> taskQueue) { for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { await Task.Delay(50); var workItem = new CustomerTask { Id = i }; taskQueue.Enqueue(workItem); Console.WriteLine("Task {0} has been posted", workItem.Id); } } private static async Task TaskProcessor(ConcurrentQueue<CustomerTask> queue, string name, CancellationToken token) { CustomerTask customerTask; bool dequeueSuccesful = false; await GetRandomDelay(); do { dequeueSuccesful = queue.TryDequeue(out customerTask); if (dequeueSuccesful) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} has been processed by {1}", customerTask.Id, name); } await GetRandomDelay(); } while (!token.IsCancellationRequested); } static Task GetRandomDelay() { int delay = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond).Next(1, 500); return Task.Delay(delay); } public class CustomerTask { public int Id { get; set; } } static void Main(string[] args) { Task t = RunProgram(); t.Wait(); }
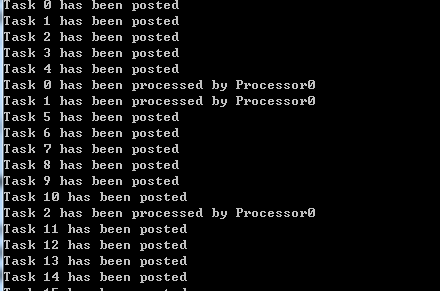
我们使用ConcurrentQueue集合实例创建了一个任务队列,然后一个取消标志,用来在我们将任务放入队列后停止工作的。接下来启动了一个单独的工作线程来将任务放入任务队列中。现在定义该程序中消费任务的部分。我们创建了四个工作者,它们会随时等待一段时间,然后从任务中获取一个任务,处理该任务,一直重复整个过程直到我们发出取消标志信号。
ConcurrentStack异步处理
创建了被多个工作者异步处理的一组任务。

static async Task RunProgram() { var tasks = new ConcurrentStack<CustomerTask>();//任务 var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); //取消标志 var taskSource = Task.Run(() => TaskProducer(tasks)); Task[] processors = new Task[4]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { string processorId = i.ToString(); processors[i - 1] = Task.Run(() => TaskProcessor(tasks, "Processor" + processorId, cts.Token)); await taskSource; cts.CancelAfter(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); await Task.WhenAll(processors); } } private static async Task TaskProducer(ConcurrentStack<CustomerTask> tasks) { for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { await Task.Delay(50); var workItem = new CustomerTask { Id = i }; tasks.Push(workItem); Console.WriteLine("Task {0} has been posted", workItem.Id); } } private static async Task TaskProcessor(ConcurrentStack<CustomerTask> queue, string name, CancellationToken token) { CustomerTask customerTask; bool dequeueSuccesful = false; await GetRandomDelay(); do { dequeueSuccesful = queue.TryPop(out customerTask); if (dequeueSuccesful) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} has been processed by {1}", customerTask.Id, name); } await GetRandomDelay(); } while (!token.IsCancellationRequested); } static Task GetRandomDelay() { int delay = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond).Next(1, 500); return Task.Delay(delay); } public class CustomerTask { public int Id { get; set; } } static void Main(string[] args) { Task t = RunProgram(); t.Wait(); }
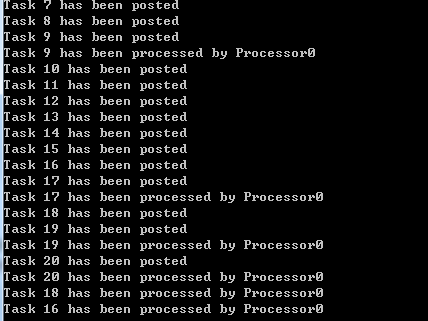
与之前的代码几乎一样。唯一不同之处是我们对并发堆栈使用Push和TryPop方法。而对并发队列使用Enqueue和TryDequeue方法。
处理的顺序被改变了了、堆栈是一个LIFO集合,工作者先处理最近的任务。在并发队列中,任务被处理的顺序与被添加的顺序几乎一致。在堆栈中,早先创建的任务具有较低的优先级。而且直到生产者停止向堆栈中放入更多的任务后,该任务才有可能停止。
ConcurrentBag
多个独立的既可以生产工作又可消费工作的工作者如果扩展工作量。
具体可以借鉴https://www.cnblogs.com/InCerry/p/9497729.html
