Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
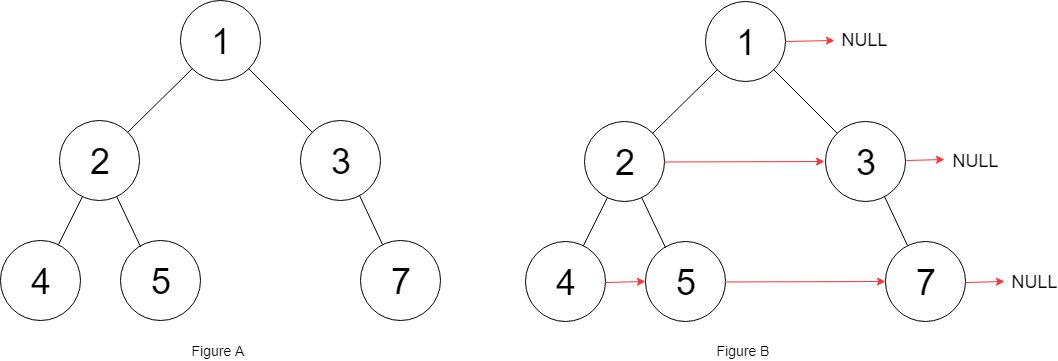
Input: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":4},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":5},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"val":3},"val":1}
Output: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"right":null,"val":5},"right":null,"val":4},"next":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"5"},"val":3},"right":{"$ref":"4"},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"6"},"val":1}
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
题目大意:
方法:
方法一:迭代法
看到图片的第一想法是使用队列进行层序遍历。
本题和116题很类似,只不过本题中的二叉树不再是完全二叉树。方法和116一模一样。
116题参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/cff2121/p/11008784.html
代码如下:
class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(!root)return NULL; queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()){ int size=q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;++i){ Node* cur=q.front(); q.pop(); if(i<size-1)cur->next=q.front(); if(cur->left)q.push(cur->left); if(cur->right)q.push(cur->right); } } return root; } };
方法二:递归
递归层序遍历,然后给每个元素的next指定节点。
代码如下:
class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(!root)return NULL; Node* p=root->next; while(p){ if(p->left){ p=p->left; break; } if(p->right){ p=p->right; break; } p=p->next; } if(root->right)root->right->next=p; if(root->left)root->left->next=root->right?root->right:p; connect(root->right); connect(root->left); return root; } };
方法三:使用迭代器
依旧是使用两个迭代器,一个用于从上向下移动,一个用于每层的从左向右移动。
代码如下:
class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(!root)return NULL; Node *dummy=new Node(0,NULL,NULL,NULL),*cur=dummy,*temp=root; while(temp){ if(temp->left){ cur->next=temp->left; cur=cur->next; } if(temp->right){ cur->next=temp->right; cur=cur->next; } temp=temp->next; if(!temp){ cur=dummy; temp=dummy->next; dummy->next=NULL; } } return root; } };