赛题数据链接 https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/231784/information
字典
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| SaleID | 交易ID,唯一编码 |
| name | 汽车交易名称,已脱敏 |
| regDate | 汽车注册日期,例如20160101,2016年01月01日 |
| model | 车型编码,已脱敏 |
| brand | 汽车品牌,已脱敏 |
| bodyType | 车身类型:豪华轿车:0,微型车:1,厢型车:2,大巴车:3,敞篷车:4,双门汽车:5,商务车:6,搅拌车:7 |
| fuelType | 燃油类型:汽油:0,柴油:1,液化石油气:2,天然气:3,混合动力:4,其他:5,电动:6 |
| gearbox | 变速箱:手动:0,自动:1 |
| power | 发动机功率:范围 [ 0, 600 ] |
| kilometer | 汽车已行驶公里,单位万km |
| notRepairedDamage | 汽车有尚未修复的损坏:是:0,否:1 |
| regionCode | 地区编码,已脱敏 |
| seller | 销售方:个体:0,非个体:1 |
| offerType | 报价类型:提供:0,请求:1 |
| creatDate | 汽车上线时间,即开始售卖时间 |
| price | 二手车交易价格(预测目标) |
| v系列特征 | 匿名特征,包含v0-14在内15个匿名特征 |
step1:导入模块
## 基础工具 import numpy as np import pandas as pd import warnings import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from scipy.special import jn from IPython.display import display, clear_output import time warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') %matplotlib inline ## 模型预测的 from sklearn import linear_model from sklearn import preprocessing from sklearn.svm import SVR from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor,GradientBoostingRegressor ## 数据降维处理的 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA,FastICA,FactorAnalysis,SparsePCA import lightgbm as lgb import xgboost as xgb ## 参数搜索和评价的 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV,cross_val_score,StratifiedKFold,train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
step2:数据读取
#导入训练集和测试集 train_data =pd.read_csv('F:\python\天池_二手车交易价格预测\used_car_train_20200313.csv',sep=' ') test_data=pd.read_csv('F:\python\天池_二手车交易价格预测\used_car_testB_20200421.csv',sep=' ')
1.数据量大小
## 输出数据的大小信息 print('Train data shape:',train_data.shape) print('TestA data shape:',test_data.shape)
Train data shape: (150000, 31)
TestA data shape: (50000, 30)
2.数据浏览
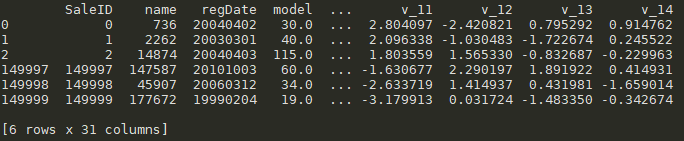
#前面三条数据+后面三条数据 train_data.head(3).append(train_data.tail(3))
3.数据信息查看info()
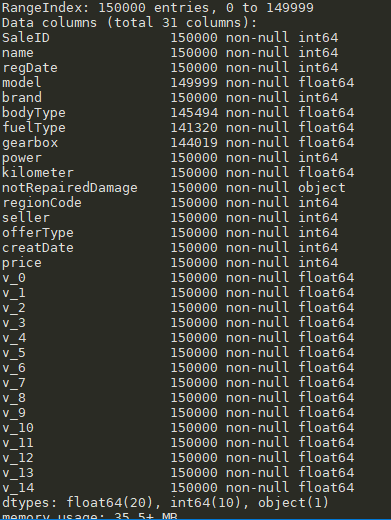
#info()可以查看特征类型,缺失情况 train_data.info()
4.查看列名
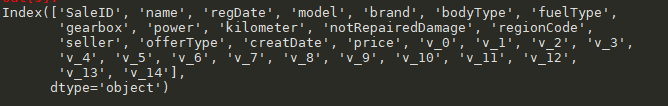
#通过.columns查看列名 train_data.columns
5.数据统计浏览
#.describe() train_data.describe()


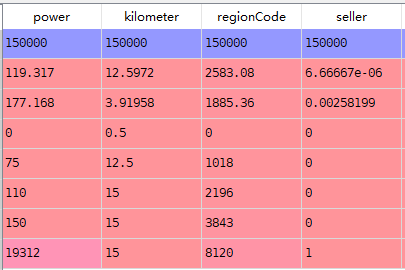
剩下的不复制过来了
step3:缺失值
#查看每列缺失情况 train_data.isnull().sum() #查看缺失占比情况 train_data.isnull().sum()/len(train_data) #缺失值可视化 missing=train_data.isnull().sum() missing[missing>0].sort_values().plot.bar() #将大于0的拿出来并排序
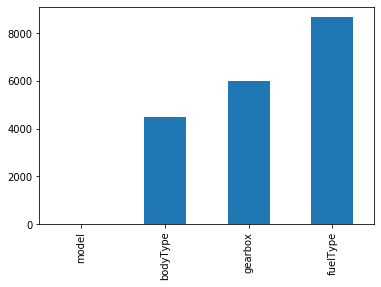
查看其他类型的空值,如‘-'’
#查看每个特征每个值的分布 for i in train_data.columns: print(train_data[i].value_counts())
发现notRepairedDamage:

#使用nan替代 train_data['notRepairedDamage'].replace('-',np.nan,inplace=True)
严重倾斜的数据,对因变量没有意义,可以删除
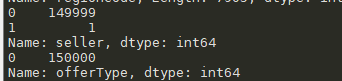
#删除特征 del train_data["seller"] del train_data["offerType"]
step4:y值的分布
#y值的画图 plt.figure(1) train_data['price'].plot.hist() plt.figure(2) sns.distplot(train_data['price'])


价格不符合正态分布
step5:特征分析
1.区分类别特征和数字特征
#1.直接根据特征字段类型进行划分 #数据特征 numeric_features = train_data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]) numeric_features.columns #类别特征 categorical_features = train_data.select_dtypes(include=[np.object]) categorical_features.columns #2.根据字典去分类,我们这次采用的是第二种 numeric_features = ['power', 'kilometer', 'v_0', 'v_1', 'v_2', 'v_3', 'v_4', 'v_5', 'v_6', 'v_7', 'v_8', 'v_9', 'v_10', 'v_11', 'v_12', 'v_13','v_14' ] categorical_features = ['name', 'model', 'brand', 'bodyType', 'fuelType', 'gearbox', 'notRepairedDamage', 'regionCode', 'seller', 'offerType']
查看每个类别特征有多少个nunique分布
#nunique for i in categorical_features: print(i+'特征分布如下:') print('{}特征有{}个不同的值'.format(i,train_data[i].nunique())) print(train_data[i].value_counts())
数据特征
#相关性分析 numeric_features.append('price') corr=train_data[numeric_features].corr() print(corr['price'].sort_values(ascending=False),' ') #换行输出
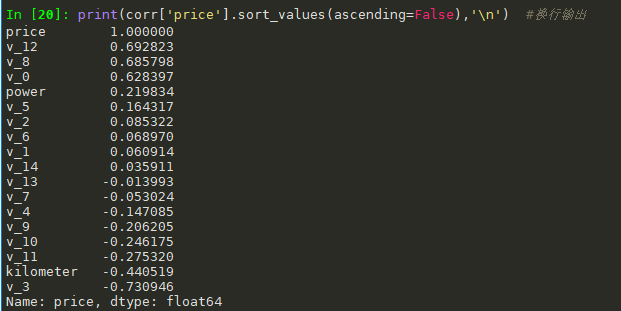
画地热图
sns.heatmap(corr)

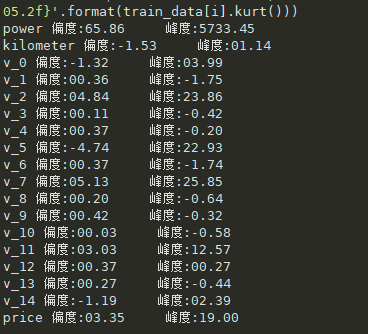
查看数字特征的偏度和峰度
#查看偏度峰度
for i in numeric_features:
print('{}'.format(i),'偏度:{:05.2f}'.format(train_data[i].skew()),' ','峰度:{:05.2f}'.format(train_data[i].kurt()))
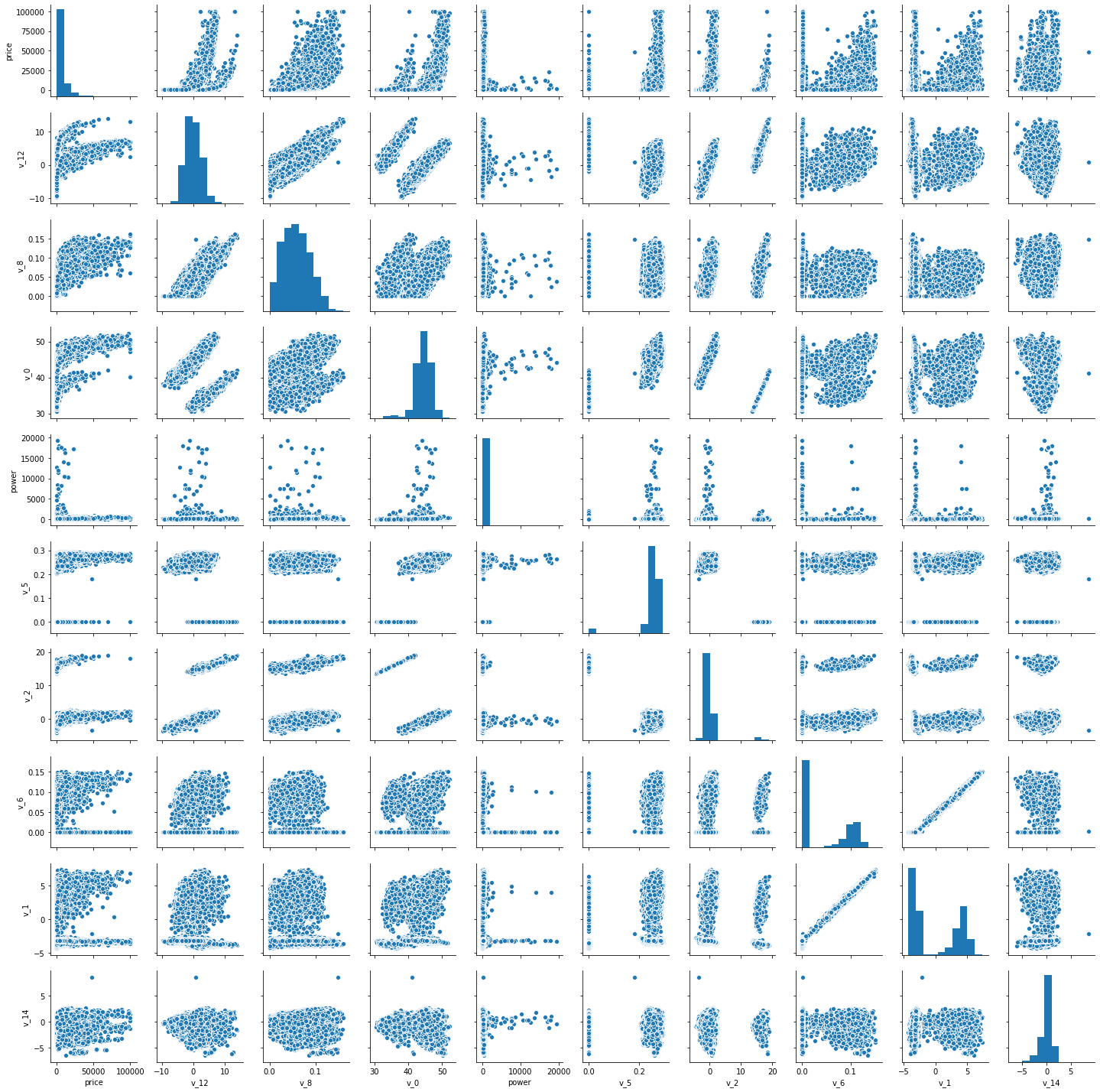
数字特征可视化
#方法一 f=pd.melt(train_data,value_vars=numeric_features) g=sns.FacetGrid(f,col='variable',col_wrap=2,sharex=False,sharey=False) g=g.map(sns.distplot,'value') #方法二,不过这个画的图片 比较拥挤 for i,col in enumerate(numeric_features): plt.subplot(9,2,i+1) sns.distplot(train_data[col])

#查看数据特征相互关系 columns = ['price', 'v_12', 'v_8' , 'v_0', 'power', 'v_5', 'v_2', 'v_6', 'v_1', 'v_14'] sns.pairplot(train_data[columns],size=2)
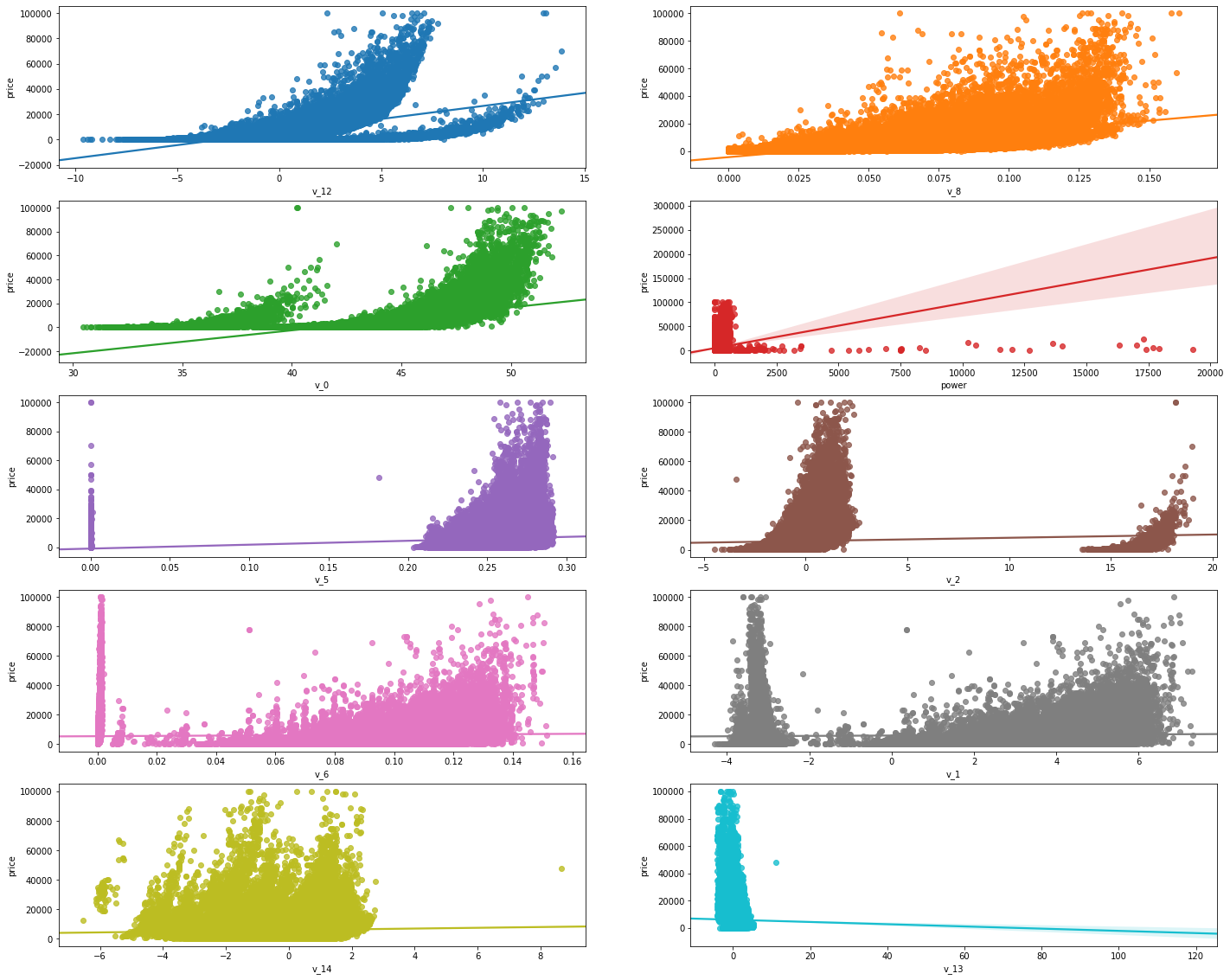
变量和y的回归关系可视化
fig,((ax1,ax2),(ax3,ax4),(ax5,ax6),(ax7,ax8),(ax9,ax10))=plt.subplots( nrows=5,ncols=2,figsize=(24,20)) v_12_plot=train_data[['v_12','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_12',y='price',data=v_12_plot,ax=ax1) v_8_plot=train_data[['v_8','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_8',y='price',data=v_8_plot,ax=ax2) v_0_plot=train_data[['v_0','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_0',y='price',data=v_0_plot,ax=ax3) power_plot=train_data[['power','price']] sns.regplot(x='power',y='price',data=power_plot,ax=ax4) v_5_plot=train_data[['v_5','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_5',y='price',data=v_5_plot,ax=ax5) v_2_plot=train_data[['v_2','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_2',y='price',data=v_2_plot,ax=ax6) v_6_plot=train_data[['v_6','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_6',y='price',data=v_6_plot,ax=ax7) v_1_plot=train_data[['v_1','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_1',y='price',data=v_1_plot,ax=ax8) v_14_plot=train_data[['v_14','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_14',y='price',data=v_14_plot,ax=ax9) v_13_plot=train_data[['v_13','price']] sns.regplot(x='v_13',y='price',data=v_13_plot,ax=ax10)
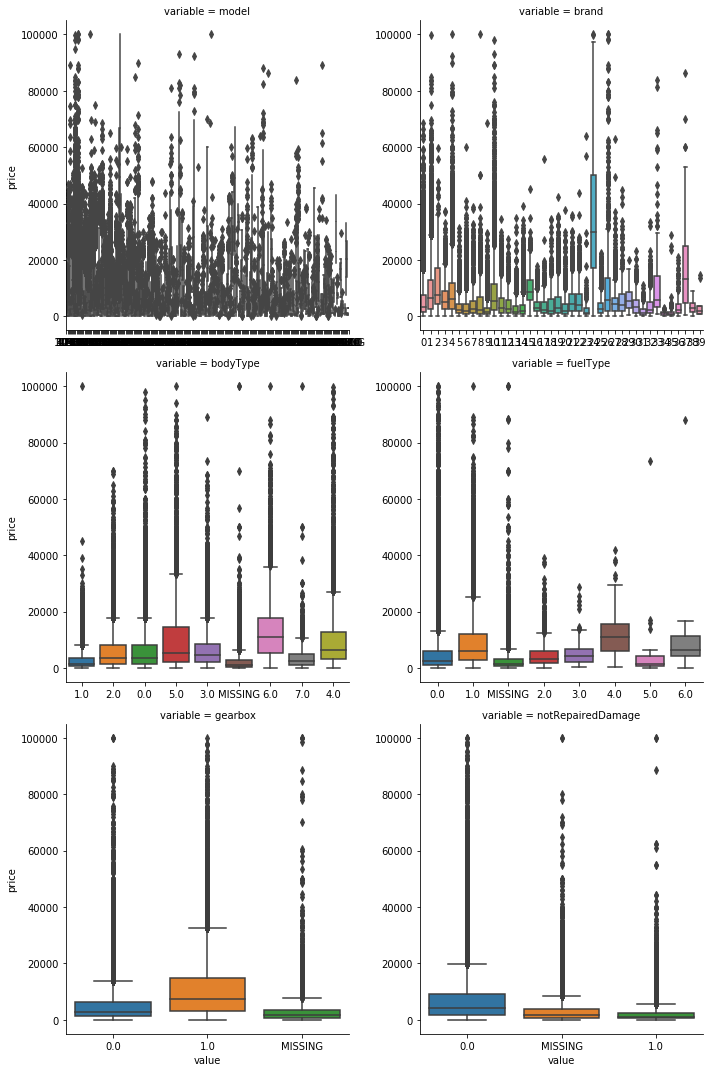
#类别特征的nunique分布 for i in categorical_features: print('{}: 有 {} 个不重复的值'.format(i,train_data[i].nunique()))

类别特征可视化
#类别特征画箱型图 #由上面的nunique()可见name和regionCode的值太多,不宜做图,以此将这2个去掉 cols=['model', 'brand', 'bodyType', 'fuelType', 'gearbox', 'notRepairedDamage'] for i in cols: train_data[i]=train_data[i].astype('category') #将数据类型变成类别型 if train_data[i].isnull().any(): train_data[i]=train_data[i].cat.add_categories(['MISSING']) train_data[i]=train_data[i].fillna('MISSING') def boxplot(x,y,**kwargs): sns.boxplot(x=x,y=y) f=pd.melt(train_data,id_vars=['price'],value_vars=cols) g=sns.FacetGrid(f,col='variable',col_wrap=2, sharex=False, sharey=False, size=5) g.map(boxplot,'value','price')
#画小提琴图 for i in cols: sns.violinplot(x=i,y='price',data=train_data) plt.show() #很奇怪,如果没有这个语句就只有一张图片,有了就会继续for循环


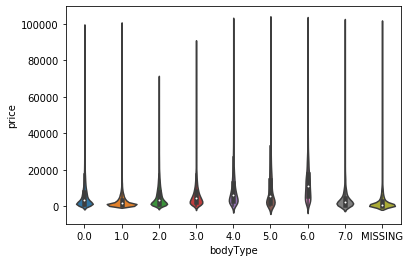
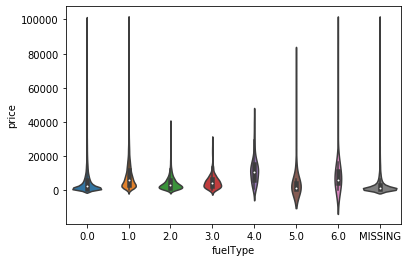


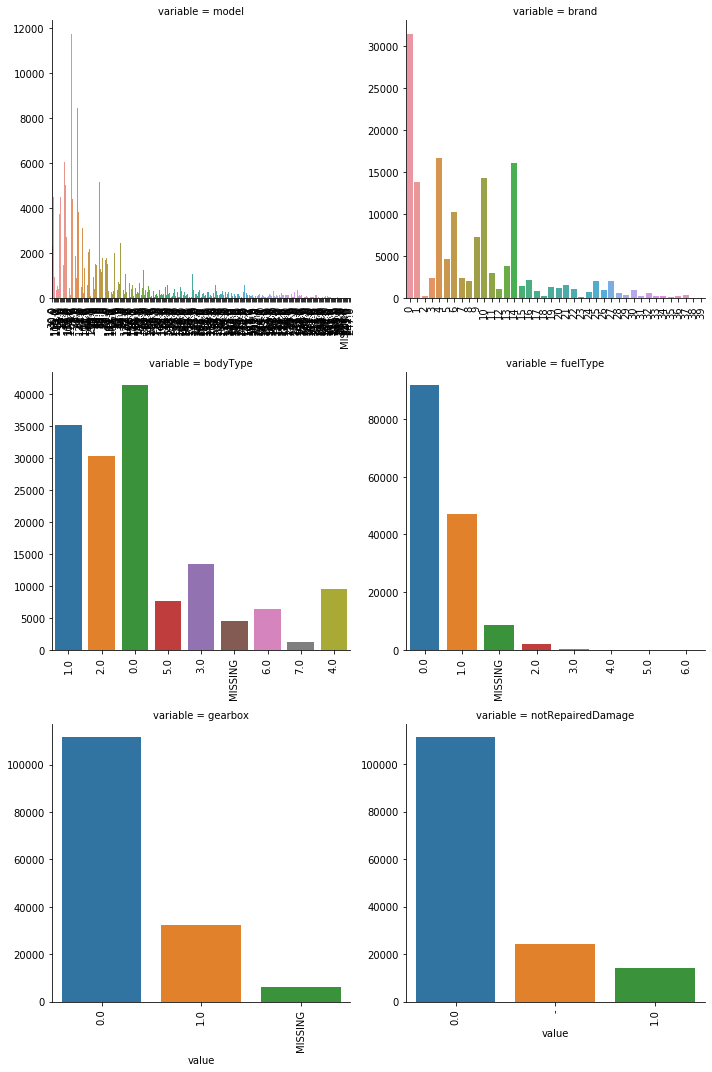
categorical_features = ['model', 'brand', 'bodyType', 'fuelType', 'gearbox', 'notRepairedDamage'] #类别特征的类别个数和y值的柱状图 def bar_plot(x,y,**kwargs): sns.barplot(x=x,y=y) x=plt.xticks(rotation=90) f = pd.melt(train_data, id_vars=['price'], value_vars=categorical_features) g = sns.FacetGrid(f, col="variable", col_wrap=2, sharex=False, sharey=False, size=5) g = g.map(bar_plot, "value", "price")

#类别特征的每个类别频数可视化(count_plot) def count_plot(x, **kwargs): sns.countplot(x=x) x=plt.xticks(rotation=90) f = pd.melt(train_data, value_vars=categorical_features) g = sns.FacetGrid(f, col="variable", col_wrap=2, sharex=False, sharey=False, size=5) g = g.map(count_plot, "value")