An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
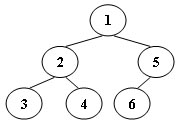
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
我的答案1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 6 typedef struct TreeNode *BinTree; 7 struct TreeNode { 8 int Data; 9 BinTree Left; 10 BinTree Right; 11 }; 12 13 typedef struct SNode *Stack; 14 struct SNode { 15 BinTree Data; 16 Stack Next; 17 }; 18 19 BinTree CreateBinTree(int data); 20 int IsEmptyBinTree(BinTree BST); 21 void InsertLeftLeafe(BinTree BST, int leftData); 22 void InsertRightLeafe(BinTree BST, int rightData); 23 24 Stack CreateStack(); 25 int IsEmptyStack(Stack S); 26 void StackPush(Stack S, BinTree pos); 27 BinTree StackPop(Stack S); 28 void PrintStack(Stack S); 29 30 BinTree Read(); 31 32 BinTree CreateBinTree(int data) 33 { 34 BinTree head; 35 head = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); 36 head->Data = data; 37 head->Left = NULL; 38 head->Right = NULL; 39 return head; 40 } 41 42 int IsEmptyBinTree(BinTree BST) 43 { 44 return (BST == NULL); 45 } 46 47 void InsertLeftLeafe(BinTree BST, int leftData) 48 { 49 BinTree left; 50 left = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); 51 left->Data = leftData; 52 left->Left = NULL; 53 left->Right = NULL; 54 BST->Left = left; 55 } 56 57 void InsertRightLeafe(BinTree BST, int rightData) 58 { 59 BinTree right; 60 right = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); 61 right->Data = rightData; 62 right->Left = NULL; 63 right->Right = NULL; 64 BST->Right = right; 65 } 66 67 Stack CreateStack() 68 { 69 Stack S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode)); 70 S->Data = NULL; 71 S->Next = NULL; 72 return S; 73 } 74 75 int IsEmptyStack(Stack S) 76 { 77 return (S->Next == NULL); 78 } 79 80 void StackPush(Stack S, BinTree pos) 81 { 82 Stack TmpCell = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode)); 83 TmpCell->Data = pos; 84 TmpCell->Next = S->Next; 85 S->Next = TmpCell; 86 } 87 88 BinTree StackPop(Stack S) 89 { 90 Stack FirstCell; 91 BinTree pos; 92 if(S->Next == NULL) { 93 printf("Stack Empty"); 94 return NULL; 95 } else { 96 FirstCell = S->Next; 97 S->Next = FirstCell->Next; 98 pos = FirstCell->Data; 99 free(FirstCell); 100 return pos; 101 } 102 } 103 104 void PrintStack(Stack S) 105 { 106 Stack head = S; 107 while(head) { 108 printf("%p ", head->Next); 109 head = head->Next; 110 } 111 printf(" "); 112 } 113 114 115 116 BinTree Read() 117 { 118 int N, data, count=0; 119 char str[10]; 120 Stack S = CreateStack(); 121 BinTree head; 122 BinTree BT = CreateBinTree(0); 123 head = BT; 124 scanf("%d ", &N); 125 scanf("Push %d ", &BT->Data); 126 StackPush(S, BT); 127 count++; 128 if(N) { 129 while(!IsEmptyStack(S)||count<N) { //是否堆栈为空,输入足够的结点 130 scanf("%s", str); 131 if(strcmp("Push", str) == 0) { //区分Push和Pop 132 scanf("%d", &data); 133 if(BT->Left == NULL) { 134 InsertLeftLeafe(BT, data); 135 BT = BT->Left; 136 StackPush(S, BT); 137 count++; 138 } else if(BT->Right==NULL) { 139 InsertRightLeafe(BT, data); 140 BT = BT->Right; 141 StackPush(S, BT); 142 count++; 143 } else { 144 printf("can't go here "); 145 } 146 } else { 147 BT = StackPop(S); 148 } 149 // printf("head:"); 150 // PreOrderTraversal(head); 151 // printf(" stack:"); 152 // PrintStack(S); 153 } 154 return head; 155 } 156 return NULL; 157 } 158 159 void PostOrderTraversal(BinTree BST) 160 { 161 int count = 0; 162 if(BST == NULL) 163 return; 164 Stack S = CreateStack(); 165 BinTree Prev = NULL, Curr = NULL; 166 StackPush(S, BST); 167 while(!IsEmptyStack(S)) { 168 Curr = S->Next->Data; 169 if(Prev == NULL||Prev->Left == Curr || Prev->Right == Curr) { 170 if(Curr->Left != NULL) 171 StackPush(S, Curr->Left); 172 else if(Curr->Right != NULL) 173 StackPush(S, Curr->Right); 174 } else if(Curr->Left == Prev) { 175 if(Curr->Right != NULL) 176 StackPush(S, Curr->Right); 177 } else { 178 if(!count) { 179 printf("%d", Curr->Data); 180 count++; 181 } else { 182 printf(" %d", Curr->Data); 183 } 184 StackPop(S); 185 } 186 Prev = Curr; 187 } 188 } 189 190 int main() 191 { 192 int N; 193 BinTree BT; 194 BT = Read(); 195 PostOrderTraversal(BT); 196 197 return 0; 198 }