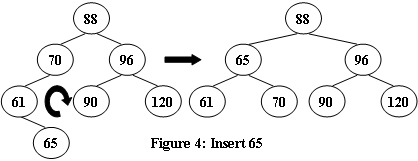
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
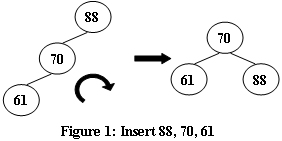
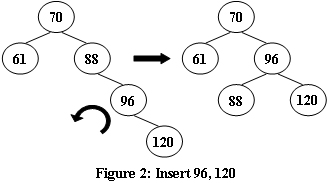
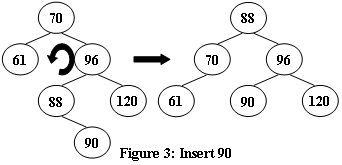
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
我的答案:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 5 typedef int ElementType; 6 typedef struct AVLNode *Position; 7 typedef Position AVLTree; 8 9 struct AVLNode { 10 ElementType Data; 11 AVLTree Left; 12 AVLTree Right; 13 int Height; 14 }; 15 16 int Max(int a, int b) 17 { 18 return a>b?a:b; 19 } 20 21 int GetHeight(AVLTree A) 22 { 23 int MaxH, HR, HL; 24 if(A) { 25 HL = GetHeight(A->Left); 26 HR = GetHeight(A->Right); 27 MaxH = (HL>HR)?HL:HR; 28 return MaxH+1; 29 } 30 return -1; 31 } 32 33 AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A) 34 { 35 AVLTree B = A->Left; 36 A->Left = B->Right; 37 B->Right = A; 38 A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1; 39 B->Height = Max(GetHeight(B->Left), A->Height) + 1; 40 41 return B; 42 } 43 44 AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A) 45 { 46 AVLTree B = A->Right; 47 A->Right = B->Left; 48 B->Left = A; 49 A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1; 50 A->Height = Max(GetHeight(B->Right), A->Height) + 1; 51 52 return B; 53 } 54 55 AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A) 56 { 57 A->Left = SingleRightRotation(A->Left); 58 59 return SingleLeftRotation(A); 60 } 61 62 AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A) 63 { 64 A->Right = SingleLeftRotation(A->Right); 65 66 return SingleRightRotation(A); 67 } 68 69 AVLTree Insert(AVLTree T, ElementType X) 70 { 71 if(!T) { 72 T = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode)); 73 T->Data = X; 74 T->Height = 0; 75 T->Left = T->Right = NULL; 76 } else if(X < T->Data) { 77 T->Left = Insert(T->Left, X); 78 if(GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == 2) { 79 if(X < T->Left->Data) 80 T = SingleLeftRotation(T); 81 else 82 T = DoubleLeftRightRotation(T); 83 } 84 } else if(X > T->Data) { 85 T->Right = Insert(T->Right, X); 86 if(GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == -2) { 87 if(X > T->Right->Data) 88 T = SingleRightRotation(T); 89 else 90 T = DoubleRightLeftRotation(T); 91 } 92 } 93 94 T->Height = Max(GetHeight(T->Left), GetHeight(T->Right)) + 1; 95 return T; 96 } 97 98 int main() 99 { 100 int N, i; 101 ElementType data; 102 AVLTree T; 103 104 scanf("%d ", &N); 105 for(i=0;i<N;i++) { 106 scanf("%d", &data); 107 T = Insert(T, data); 108 } 109 if(T) 110 printf("%d", T->Data); 111 return 0; 112 }