一、原型模式
原型模式就是从一个对象再创建另一个可定制的对象,而且不需要知道任何创建的细节。
二、基本的原型模式
这里模拟简历的创建与复制来说明原型模式的应用。
class Resume implements Cloneable{ private String name; private String sex; private String age; private String timeArea; private String company; public Resume(String name){ this.name=name; } //设置个人信息 public void setPersonalInfo(String sex,String age){ this.sex=sex; this.age=age; } //设置工作经历 public void setWorkExperience(String timeArea,String company){ this.timeArea=timeArea; this.company=company; } //打印 public void display(){ System.out.println("name sex age:"+name+" "+sex+" "+age); System.out.println("work experience"+timeArea+" "+company); } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class PrototypePattern { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{ Resume a = new Resume("a的简历"); a.setPersonalInfo("male", "18"); a.setWorkExperience("2017", "companya"); Resume b=(Resume) a.clone(); b.setWorkExperience("2016","companyb"); Resume c=(Resume) a.clone(); c.setWorkExperience("2019","companyc"); a.display(); b.display(); c.display(); } }
输出结果:

三、原型模式中的浅复制与深复制
上面的Resume类通过实现Cloneable接口才能使用clone方法,进行对象的克隆。
Java中对象的创建通常是通过new来实现的,通过从堆中申请一块与需要的对象类型对应的内存空间的大小,在调用构造方法返回对象给引用,
假如需要创建一批属性值都相同的对象,或许可以通过new一批对象来实现,但是这样的话,效率未免太低,并不划算。
那么如果是这样呢?
class PersonTest{ } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { PersonTest personTest=new PersonTest(); PersonTest personTest1=personTest; System.out.println(personTest); System.out.println(personTest1); } }
输出结果:
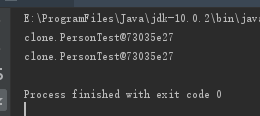
可见personTest和personTest1的地址是一样的,说明他们两个其实是指向同一个对象的引用,在这个过程中并没有进行对象的复制。
那如果是进行一次克隆呢?像这样:
class Person implements Cloneable{ int id; String name; Education education; public Person(int id, String name,Education education) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.education=education; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Education getEducation() { return education; } public void setEducation(Education education) { this.education = education; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } class Education{ String theUniversity; String degree; public Education(String theUniversity, String degree) { this.theUniversity = theUniversity; this.degree = degree; } public String getTheUniversity() { return theUniversity; } public void setTheUniversity(String theUniversity) { this.theUniversity = theUniversity; } public String getDegree() { return degree; } public void setDegree(String degree) { this.degree = degree; } } public class ObjectClone { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{ Education educationA=new Education("清华大学","学士"); Person personA=new Person(1,"小明",educationA); Person personB=(Person) personA.clone(); System.out.println(personA==personB); System.out.println(personA.id==personB.id); System.out.println(personA.name==personB.name); System.out.println(personA.education==personB.education); System.out.println(); System.out.println(personA); System.out.println(personB); System.out.println(personA.id); System.out.println(personB.id); System.out.println(personA.name); System.out.println(personB.name); System.out.println(personA.education); System.out.println(personB.education); } }
输出结果:
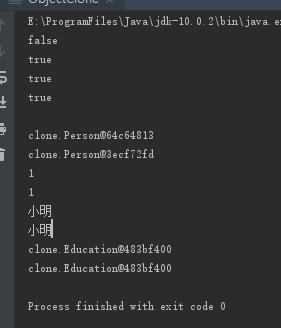
可见克隆以后进行了对象的复制,personA与personB的地址是不同的,复制以后两个对象的id值与name,education都相同,比较结果都为true,乍看上去这好像是预期中的现象。
但是,
name作为String对象,在进行“==”的比较时比较的是对象是否相同,可见这次复制过程中,name的值并没有复制,
Education的值是一个对象,education的地址也相同,
所以这次对象复制后的情况,为什么跟上面的例子只传引用没有什么区别啊?
克隆的过程中有几个问题需要进行思考,
id作为int型数据,int是基本数据类型,复制的过程当中是逐位复制的,
但是对于String类型与其他引用类型,这里都只是将原对象的引用值拷贝给了新对象的相应字段。
这种就是浅复制,clone()方法进行的就是浅拷贝,这是需要注意的问题。
那么如果需要进行深拷贝,则需要将clone()方法进行覆盖,并且在clone()方法内把原对象引用的其他对象也拷贝一份。
那么被引用的对象也需要实现Cloneable接口,并且实现clone()方法。
class Person implements Cloneable{ int id; String name; Education education; public Person(int id, String name,Education education) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.education=education; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Person person=(Person) super.clone(); person.education=(Education) education.clone(); return person; } } class Education implements Cloneable{ String theUniversity; String degree; public Education(String theUniversity, String degree) { this.theUniversity = theUniversity; this.degree = degree; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class ObjectClone { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{ Education educationA=new Education("清华大学","学士"); System.out.println(educationA); Person personA=new Person(1,"小明",educationA); Person personB=(Person) personA.clone(); System.out.println(personA==personB); System.out.println(personA.id==personB.id); System.out.println(personA.name==personB.name); System.out.println(personA.education==personB.education); System.out.println(); System.out.println(personA); System.out.println(personB); System.out.println(personA.id); System.out.println(personB.id); System.out.println(personA.name); System.out.println(personB.name); System.out.println(personA.education); System.out.println(personB.education); } }
输出结果如下:
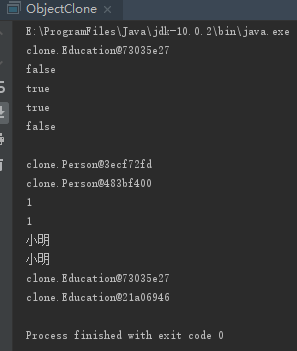
代码跟上方相比,有一点点改动,但是根据输出结果来看,这次原对象中的某些字段的所引用的对象也进行了拷贝了。
四、关于clone的总结
由此可见clone()只是浅拷贝,也就是说除非基本类型外,引用类型只是拷贝引用,不会复制对象。
如果需要进行深拷贝,则需要使原对象所引用的对象类型也要继承Cloneable接口,并且实现clone()方法,同时要注意对象与对象之间存在的嵌套问题,避免拷贝后的两个对象仍然因为引用的某个对象存在关系。
五、关于Cloneable接口
上面提到了Cloneable接口,再对这个东西多了解一点,下面这个就是Cloneable接口,可见当中没有任何方法和属性。
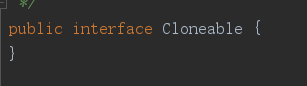
Cloneable接口与Serializable接口一样,都是标记型的接口,
实现 Cloneable来表示该对象能被克隆,能使用Object.clone()方法。如果没有实现 Cloneable的类对象调用clone()就会抛出CloneNotSupportedException。
如果将上面最后一个实例代码中Education类实现的Cloneable接口去除,那么程序运行时会出现异常,

这里想思考的是标记型接口是如何起作用的呢?
标记接口是没有任何方法和属性的接口,仅仅表明实现它的类是属于一个特定的类型,我们知道实现一个接口的类是可以来代表这个接口类型的。
通常创建标记接口的目的就是主要是:
建立一个公共的父接口,之后可以通过多态对其进行扩展,但是Java虚拟机却可以根据这个接口的类型选择相应的事件处理方案,也就是对实现这个标记接口的对象进行这个处理方案。
关于标记接口的作用描述还是不够清晰,待之后学习的再深入一点再继续探究吧。