| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2020OOP |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2020OOP/homework/10288 |
| 这个作业的目标 |
1.继续完成编程题并制作测试 |
| 作业正文 | 1编程题 |
| 仓库地址 | |
| 参考文献 |
一、编程题
1.扩大数字范围
(1)增加负数范围
在“ 整数 ”运算过程中出现负数时不再报错,而是继续运算,同时输入与输出都可以是负数。同时新增加了“ 自然数 ”,若初始输入“ 自然数 ”,如果运算出现负数则报错。
初始值输入的判断进行了修改。
scanf("%s%s%s%s",a,b,c,d); if(strcmp(a,"整数")!=0&&strcmp(a,"自然数")!=0) { printf("输入有误,请重新输入 "); continue; }
在运算过程中的判断也进行了修改。
if (sum<k && strcmp(a,"自然数")==0) printf("%s不能为负值,请重新输入 ",b); else sum -= k;;
并且在输出的函数中增加了这一部分。
if(w<0) { printf("负"); w=-w; }
(2)实现两位数的输入(输出按照上次作业的可输出三位数)
由于中文占2个字符,所以无法直接判断,因此通过strlen函数得到字符串长度,再用strncpy函数,将字符串拆开,得到每个中文字,再进行对比及运算,其中对于负数的初始值也做了判断。同时新增加了一个函数,借助原来的一位数的转换函数,可以运算两位数。
int tran0(char s[20]) { int len,n1,n2,n; char a1[20]={"0"},b1[20]={"0"},c1[20]={"0"},d1[20]={"0"},t1[20]={"0"}; flag=0; len=strlen(s); strncpy(d1,s,2); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0)//判断是否为负数 { if(strcmp(a,"整数")) flag+=1; strcpy(t1,s+2); len=strlen(t1); if(len<=0) flag+=1; } else strcpy(t1,s); if(len==2) { n=tran(t1); } if(len==4)//判断是否为两个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); if(strcmp(a1,"十")==0) n=10+tran(b1); else if(strcmp(b1,"十")==0) n=tran(a1)*10; else flag+=1; } if(len==6)//判断是否为三个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); strncpy(c1,t1+4,2); if(strcmp(b1,"十")) flag+=1; else { n=tran(a1)*10+tran(c1); } } if(flag) printf("数字输入有误,请重新输入 "); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0) n=-n; return n; } int tran(char s[20]) { int num=0; if(strcmp(s,"零")==0) num=0; else if(strcmp(s,"一")==0) num=1; else if(strcmp(s,"二")==0) num=2; else if(strcmp(s,"三")==0) num=3; else if(strcmp(s,"四")==0) num=4; else if(strcmp(s,"五")==0) num=5; else if(strcmp(s,"六")==0) num=6; else if(strcmp(s,"七")==0) num=7; else if(strcmp(s,"八")==0) num=8; else if(strcmp(s,"九")==0) num=9; else if(strcmp(s,"十")==0) num=10; else flag+=1; return num; }
完整代码
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> char a[20],b[20],c[20],d[20],e[20],f[20],g[20],h[20]; int sum=0,flag=0, flag2=1, i, j, k; int tran0(char s[20]);//中文数字转为阿拉伯数字 int tran(char s[20]);//中文一位数转换为阿拉伯数字 void put(int w);//输出 void tran2(int m);//阿拉伯数字转换为中文 int main() { for (i=0; ; i++)//输入变量及其初始值 { flag=0; scanf("%s%s%s%s",a,b,c,d); if(strcmp(a,"整数")!=0&&strcmp(a,"自然数")!=0) { printf("输入有误,请重新输入 "); continue; } else { if(strcmp(c,"等于")) { printf("输入有误,请重新输入 "); continue; } else { sum=tran0(d); if(flag) continue; else break; } } } for (j=1; flag2; j++) //输入运算过程及结束 { for (i=1; ; i++) { scanf("%s%s",e,f); if (strcmp(e,b) == 0) { scanf("%s",g); k = tran0(g); if (flag) continue; if (strcmp(f,"增加")==0) sum += k; else if (strcmp(f,"减少")==0) { if (sum<k && strcmp(a,"自然数")==0) printf("%s不能为负值,请重新输入 ",b); else sum -= k; } else { printf("输入有误,请重新输入 "); continue; } } else if (strcmp(e,"看看")==0 && strcmp(f,b)==0) { flag2=0; break; } else { printf("输入有误,请重新输入 "); continue; } } } put(sum); return 0; } int tran0(char s[20]) { int len,n1,n2,n; char a1[20]={"0"},b1[20]={"0"},c1[20]={"0"},d1[20]={"0"},t1[20]={"0"}; flag=0; len=strlen(s); strncpy(d1,s,2); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0)//判断是否为负数 { if(strcmp(a,"整数")) flag+=1; strcpy(t1,s+2); len=strlen(t1); if(len<=0) flag+=1; } else strcpy(t1,s); if(len==2) { n=tran(t1); } if(len==4)//判断是否为两个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); if(strcmp(a1,"十")==0) n=10+tran(b1); else if(strcmp(b1,"十")==0) n=tran(a1)*10; else flag+=1; } if(len==6)//判断是否为三个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); strncpy(c1,t1+4,2); if(strcmp(b1,"十")) flag+=1; else { n=tran(a1)*10+tran(c1); } } if(flag) printf("数字输入有误,请重新输入 "); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0) n=-n; return n; } int tran(char s[20]) { int num=0; if(strcmp(s,"零")==0) num=0; else if(strcmp(s,"一")==0) num=1; else if(strcmp(s,"二")==0) num=2; else if(strcmp(s,"三")==0) num=3; else if(strcmp(s,"四")==0) num=4; else if(strcmp(s,"五")==0) num=5; else if(strcmp(s,"六")==0) num=6; else if(strcmp(s,"七")==0) num=7; else if(strcmp(s,"八")==0) num=8; else if(strcmp(s,"九")==0) num=9; else if(strcmp(s,"十")==0) num=10; else flag+=1; return num; } void put(int w) { int p,q; p=w/100; q=w%10; if(w<0) { printf("负"); w=-w; } if(w<=10) //个位数 tran2(w); else if(w>10 && w<20) //小于20的十位数 { printf("十"); tran2(w%10); } else if(w>=20 && w<100)//大于20的十位数 { tran2(w/10); printf("十"); if(w%10!=0) tran2(w%10); } else if(w>=100)//百位数 { tran2(w/100); printf("百"); if(w%100>0) { if(w%100>=10 && w%100<=20) printf("一"); else if(w%100<10 && w%100>0) printf("零"); put(w%100); } } } void tran2(int m) { switch (m) { case 0: printf("零");break; case 1: printf("一");break; case 2: printf("二");break; case 3: printf("三");break; case 4: printf("四");break; case 5: printf("五");break; case 6: printf("六");break; case 7: printf("七");break; case 8: printf("八");break; case 9: printf("九");break; case 10: printf("十"); } }
2.单元测试
由于这次作业修改了一些地方,所以单元测试也需要重新制作,但测试脚本用的是上次的。

(*)对于主要负责输入输出的主函数,我认为只需要通过整个函数的运行就可测试了。
(1)对于新加入的输入两位数的函数和原先的一位数的函数放在一起测试,
测试代码如下:(测试了正负的一位数和两位数及错误输入)
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int flag=0; int tran(char s[20]); int tran0(char s[20]); int main() { int i; char a[20],b[20],c[20],d[20],e[20],f[20],g[20],h[20]; strcpy(a,"三"); strcpy(b,"十七"); strcpy(c,"三十九"); strcpy(d,"七十"); strcpy(e,"负七"); strcpy(f,"负十六"); strcpy(g,"负九十"); strcpy(h,"负"); printf("%s %d ",a,tran0(a)); printf("%s %d ",b,tran0(b)); printf("%s %d ",c,tran0(c)); printf("%s %d ",d,tran0(d)); printf("%s %d ",e,tran0(e)); printf("%s %d ",f,tran0(f)); printf("%s %d ",g,tran0(g)); printf("%s %d ",h,tran0(h)); } int tran0(char s[20]) { int len,n1,n2,n=0; char a1[20]={"0"},b1[20]={"0"},c1[20]={"0"},d1[20]={"0"},t1[20]={"0"}; flag=0; len=strlen(s); strncpy(d1,s,2); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0)//判断是否为负数 { // if(strcmp(a,"整数")) flag+=1; strcpy(t1,s+2); len=strlen(t1); if(len<=0) flag+=1; } else strcpy(t1,s); if(len==2) { n=tran(t1); } if(len==4)//判断是否为两个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); if(strcmp(a1,"十")==0) n=10+tran(b1); else if(strcmp(b1,"十")==0) n=tran(a1)*10; else flag+=1; } if(len==6)//判断是否为三个字 { strncpy(a1,t1,2); strncpy(b1,t1+2,2); strncpy(c1,t1+4,2); if(strcmp(b1,"十")) flag+=1; else { n=tran(a1)*10+tran(c1); } } if(flag) printf("数字输入有误,请重新输入 "); if(strcmp(d1,"负")==0) n=-n; return n; } int tran(char s[20]) { int num=0; if(strcmp(s,"零")==0) num=0; else if(strcmp(s,"一")==0) num=1; else if(strcmp(s,"二")==0) num=2; else if(strcmp(s,"三")==0) num=3; else if(strcmp(s,"四")==0) num=4; else if(strcmp(s,"五")==0) num=5; else if(strcmp(s,"六")==0) num=6; else if(strcmp(s,"七")==0) num=7; else if(strcmp(s,"八")==0) num=8; else if(strcmp(s,"九")==0) num=9; else if(strcmp(s,"十")==0) num=10; else flag+=1; return num; }
用脚本测试结果如下:
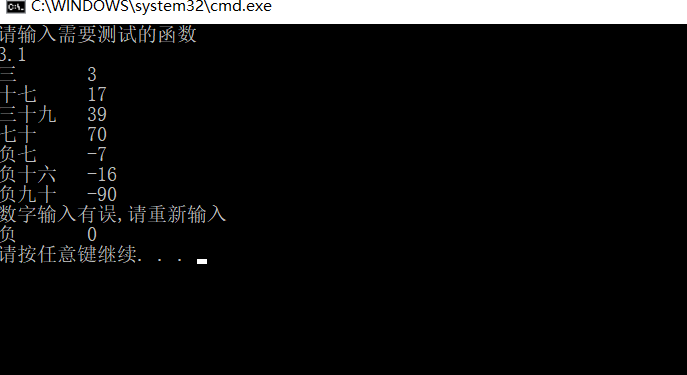
(2)对于将中文转为阿拉伯数字的函数测试。
测试代码如下:(包括正负数、整十、几百零几、几百一十几的特殊情况)
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> void put(int w); void tran2(int m); int main() { printf("3 ");put(3);printf(" "); printf("19 ");put(19);printf(" "); printf("60 ");put(60);printf(" "); printf("905 ");put(905);printf(" "); printf("-8 ");put(-8);printf(" "); printf("-117 ");put(-117);printf(" "); printf("-650 ");put(-650);printf(" "); } void put(int w) { int p,q; p=w/100; q=w%10; if(w<0) { printf("负"); w=-w; } if(w<=10) //个位数 tran2(w); else if(w>10 && w<20) //小于20的十位数 { printf("十"); tran2(w%10); } else if(w>=20 && w<100)//大于20的十位数 { tran2(w/10); printf("十"); if(w%10!=0) tran2(w%10); } else if(w>=100)//百位数 { tran2(w/100); printf("百"); if(w%100>0) { if(w%100>=10 && w%100<=20) printf("一"); else if(w%100<10 && w%100>0) printf("零"); put(w%100); } } } void tran2(int m) { switch (m) { case 0: printf("零");break; case 1: printf("一");break; case 2: printf("二");break; case 3: printf("三");break; case 4: printf("四");break; case 5: printf("五");break; case 6: printf("六");break; case 7: printf("七");break; case 8: printf("八");break; case 9: printf("九");break; case 10: printf("十"); } }
用脚本测试结果如下:
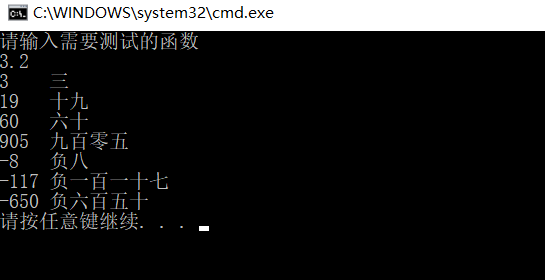
(3)整体运行
运行多个文本如下:
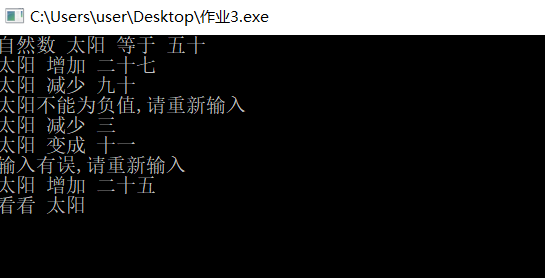

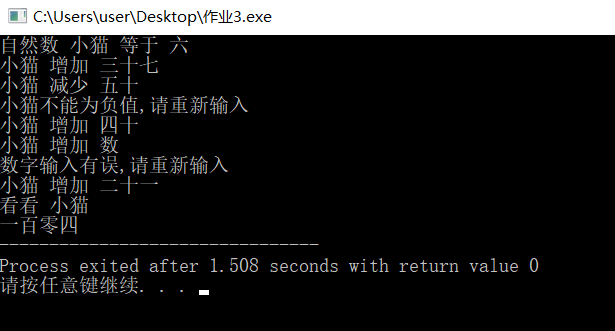
总结
在这次作业中,将代码进行了拓展,首先将数字分为“ 整数 ”和“ 自然数 ”,并在“ 整数 ”中实现了负数输入输出和两位数的输入和运算,其中在两位数的输入输出上花了较多时间,通过多次尝试和查找资料,最后通过strncpy函数实现了两位数的输入和运算,输出则是原来的三位数的范围。但是还是有一些缺陷,有时候输入错误时会多次报错。